Why is the PCI Express port on the motherboard different in size? What does x16, x8, x4 and x1 mean?
If you have a look at the computer hardware devices in general and the motherboard in particular, you probably already know that PCI Express connection standards are one of the important components of the systems. modern computer.But the nature of this connection standard is somewhat somewhat vague.For example, on newer PCs, you might find PCI Express ports come in three or four different sizes, all labeled with PCIE or PCI-E.
So what is the difference between them, naming things that are confusing?And which size should I use?Read the article below for more details.

What is PCI Express?
Launched in 2000 as an upgrade to the Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) standard, PCI Express has a huge advantage, which is to use bus access from point to point (point-to-point). access bus) instead of serial bus (serial bus) as traditional.That means that each individual PCI port and the cards attached to it can take full advantage of the speed at which they are designed, and it is important not to worry about phenomena such as congestion at the same time. save through a single bus.

Still a bit difficult to understand?Okay, now try to imagine your PC system is a luxury restaurant.The old PCI standard was like a small restaurant counter in the restaurant, everyone lined up waiting in front of the counter to wait for their turn to be served.With the PCI standard there is only one single bus, which means that the delivery desk only has one employee, so the service speed will certainly not be fast.As PCI-E is like a bar, every customer sitting at a designated or reserved table, in the bar, has a bartender 'bartender' who quickly and swiftly divides each other to close customers' orders.In short, on PCI-E, there are dedicated data transmission routes dedicated to each expansion card or peripheral device, thereby enabling your computer to access external accessories as well as Peripherals at the same time a lot faster.
Now to add to our above example of a bar and a food stall, imagine that each wine table has several employees serving at the same time, a main employee and a few guys. ve 'behind ready to fulfill all customer requests if needed.This is also the idea of multiple lanes that we mentioned above.
Learn about multi-lane in PCI-E
PCI-E has undergone a lot of upgrades since this standard was released.Currently new motherboards often have to use at least version 3 of PCI-E, or version 4 with faster and more popular speeds.In addition, version 5 is expected to be introduced in 2019. However, whatever version you are using, you must understand that they all share a physical connection mechanism, and connections. it can be further divided into four different sizes, namely x1, x4, x8, and x16.In addition, the actual x32 ports also exist, but are extremely rare and are often not used in conventional mass-scale systems.

So why use so many port sizes for headaches?It turns out that the different port sizes give the same amount of data connection pins to the motherboard.For example, if the ports are larger, it means that the number of pins connected on the card and the port is also higher.These connections are often referred to as lanes, with each PCI-E lane consisting of two pairs of signals, one for sending data and one for receiving data.Different versions of the PCI-E standard allow each lane to have a different speed.But in general, you just need to understand that the more lanes the PCI-E port and the device connected to that port, the faster the data transfer rate between the device and the system will be.
Back to our bar metaphor.If you imagine every customer sitting in a bar like a PCI-E device, then the x1 lane is a service pack where only a single bartender serves a wine table.But the x4 lane is equivalent to the service pack, which will have four bartenders serving one wine table.Similarly, with the x8 lane you will have 8 bartenders in service and with x16, you will have a 'platoon' that will only serve you.Good guys will probably like this service model very much.Just kidding!Through the above example, you probably have somewhat understood the mechanism of PCI-E as well as the parameters like x16, x8, x4 and x1 mean.
How will these ports use these ports?
For the upgraded version 3.0 of PCI Express that is in common use today, the maximum data transfer rate per lane is eight gigatransfer.In fact, the speed for the 3rd PCI-E standard is equivalent to about 1GB of data per second in each lane.
So, if a device uses PCI-E x1, for example, a low-power sound card or Wi-Fi antenna, for example, it can transfer data to the system at about 1GB on. seconds.Another device uses larger x4 or x8 ports, like USB 3.0, with more than 2 USB ports being used at maximum speed will be able to transfer data at a rate 4 or 8 times faster.PCI-E x16 ports, with a theoretical maximum data transfer rate of about 15GBps (on PCI-E version 3.0), are often used for most high-performance modern graphics cards from NVIDIA and AMD design.

There are no instructions on which lanes the card will use.Graphics cards tend to use x16 only for maximum data transfer, but obviously you don't need to plug the network card into the x16 port and use sixteen full lanes to do when the Ethernet port is only capable of data transmission. at 1 gigabit per second (about one-eighth of the throughput of a PCI-E lane).There are a small number of solid-state drives mounted on PCI-E that are compatible with x4 ports, but these ports seem to be quickly surpassed by the new M.2 standard, which can also use the PCI-E bus. .High-end network cards and user-friendly devices such as adapters and RAID controllers use a combination of x4 and x8 formats.
Remember: PCI-E port size and lanes may not be the same
One of the other problems that many people find confusing when it comes to the settings of PCI-E, is that sometimes a port may be the size of an x16 card, but there are only enough data lanes equivalent to an x4 card.It may sound 'paradoxical' but in fact, this is because the PCI-E standard can meet an unlimited number of individual connections, but there will still be practical limitations on the throughput of chipset.Because cheaper motherboards with many chipsets can only support one PCI-E x8 slot, this slot can physically fit an x16 card.Meanwhile, the gaming motherboard will include up to four PCI-E x16-x16 slots and full x16 lanes, for maximum GPU compatibility.

Obviously this fact can lead to several problems.If your motherboard has two x16 slots, but one of them only has x4 lanes, plugging in the new graphics card into the wrong size slot may clog the data, resulting in 75% performance. That graphics card can't be used.That's in theory, but in fact, the motherboard architecture doesn't allow this to happen.The problem here is that the cards need to be plugged into the correct slot.
Fortunately, manufacturers often have a clear explanation of which slot has the speed lane right on the motherboard, or in the manual to minimize confusion.If you do not have a user manual, the lane numbers are usually written on the motherboard PCB next to the port, as follows:
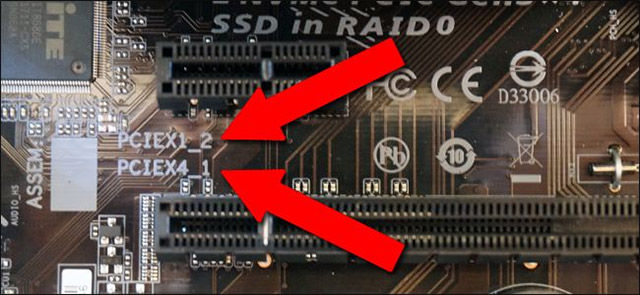
The sign on the motherboard in the illustration shows that the PCI-E x1 port on the top has 1 lane, while the PCI-E x16 port below has only 4 lanes.PCIEX1_2 means that this is the second x1 port on the motherboard.
In addition, shorter x1 or x4 cards can fit into longer x8 or x16 slots, configuring the initial connector pins of electrical contacts to make them compatible.However, it will be slightly loose and you will need to fix it to the back of the case with a small snail.Of course, large size cards like x8 or x16 will not be able to fit into smaller slots like x1 or x4 is sure!
So remember, when buying expansion cards or upgrading PCI Express slots, you need to keep in mind both the size and the data lanes of the existing ports.Wish you can choose the best PCI-E cards!
See more:
- 16 connection ports are commonly found on computers and their functions
- Basic functions of some HDMI connectors
- Want to know if your computer supports USB 3.0, read this article
- Self-assembling computers, build desktop computers (P1): Choose hardware