To read financial statements, you must understand these basic indicators
For those who do not major in finance - accounting or spend enough time researching them, reading financial statements is a very challenging challenge.
For example, can you distinguish the difference between gross profit, gross margin, sales profit and gross income ? Don't try to find the difference anymore, because these 4 terms all mean the same thing: gross profit!
So, if you are passionate about accounting - finance but are not eager to be ready to take intensive training courses, this article can help you master some basic indicators to no longer feel. feel dizzy whenever looking at a financial report anymore.
Suppose, you own an apple farm. So how do you keep track of all the financial activities involved in your production, harvesting and sales processes?

First, a financial report will include balance sheet (Balance Sheet) - reflecting the situation of assets, debt and shareholder capital within a defined period of time, reporting business results (Income Statement) ) - reflecting revenue and expenses, Cash Flow Statement - reflecting cash flows and / or equivalent cash flows in and out arising in a specific period. When looking at financial statements, one thing to note is that for negative data, instead of writing - $ 100,000, they can be written in the form of ($ 100,000).
Balance sheet (Balance Sheet)
Balance sheet is a summary of assets and liabilities of a business at a specific time, also considered as a report on corporate financial health.
Assets (Assets)
In the above situation, assets are resources you own, including farmland, apples and tools and tools.
Current assets: Current assets are assets expected to be sold or used up in the near future, usually within a year or a business cycle. Typical assets currently include cash, cash equivalents, accounts receivable, warehouses, and parts of prepaid accounts that will be used within a year and short-term investments.
Long-term assets (Non-current assets): Long-term assets are those with time to use, rotate, recover for more than 12 months or in many business cycles (accompanied by great value) and It is often difficult to convert into cash. Currently, in enterprises, factories, equipment and other facilities, infrastructure are called fixed assets - a form of long-term assets.
Intangible assets: Intangible assets are assets that cannot determine the exact value of money and physical form. Intangible assets include production process registration papers, copyright registration papers, technology technical documents (laboratory notes, technical know-how .), good works copyright, copyrighted computer software, digital database, internal integrated network control software, industrial design, product copyright registration, brand know-how, drawings and charts engineering, design, ownership .
The value of these assets will increase or decrease over time. In the above situation, the apples will lose value very quickly because they are likely to rot in a few weeks.
Debt (Liabilities)
Understand this, debt is something that you borrow from other people and pay them, including loans (Loans), deferred payments (Acferred payments) and Accrued expenses.
Accrued expenses: Accumulated expenses are expenses incurred in the accounting period but have not been recognized. These are expenses that have been incurred, not yet paid but in the future will have to be paid when the payment period arrives. Some types of accrued expenses such as wages (when the payday does not fall at the end of the accounting reporting period), the interest on the debt or tax payments.
Current liabilities: Current liabilities are debts of the company or debt obligations determined within a period of 1 year (fiscal year). Short-term liabilities on the company's balance sheet include short-term liabilities, payable accounts, accumulated debts and other types of debts.
Non-current liablities: Long-term liabilities are those that can be repaid over a year, including long-term loans for development investment, long-term debt payable, issued bonds, and other deposit, deposit, backup account .
Income statement
The business result report reflects the cumulative results of business operations within a specified time frame. This report indicates whether or not a business is profitable - that is, whether the net income (actual profit) is positive or negative and is often considered to be a profit report. The business results report is represented by a simple expression as follows: Revenue - cost = profit.

Cost categories (Expense)
1. Cost of goods sold (Cost of goods sold - COGS)
Cost of goods sold is the value reflecting the amount of goods sold by the enterprise over a period of time. It reflects the consumption of goods as well as participation in determining the profitability of that business in a business cycle. Cost of goods sold includes the cost of all items that are directly or indirectly related to the production or purchase of goods / services sold.
For an example of an apple farm listed at the beginning of the article, the cost of goods sold here is the cost of buying the seeds, the salaries of the workers and the cost of preserving the apples until they are sold.
2. Operating expenses (Operating expenses - Opex)
Operating costs for trading companies are those that occur during the normal operation of the company, not the cost of selling goods. Typically, operating costs are usually the cost of sales or administrative expenses, such as office rent, taxes and insurance for both sales and management purposes.
- Distribution costs - transportation (Distribution expenses): It is the amount of money that businesses spend to make sure that the apple (the situation mentioned at the beginning of the article) is delivered to the customer, including truck hire, loading and unloading, delivery fees to supermarkets, distributors and agents. .
- Chi selling and marketing (Selling - Marketing expenses): These are expenses to run marketing campaigns, salaries paid to marketing staff and sales teams.
- Technology expenses: areexpenses for research, development, creation, implementation, deployment and maintenance of technology.
- Administrative expenses (Administrative expenses):Costs are related to the organization, including the salary of the management department and the expenses related to the operation.
3. Cost (Capital expenditures - Capex)
Costs - Costs are the funds used by the company to upgrade or acquire physical assets such as real estate (houses - land), factories for production or equipment. This type of cost is used to develop production and maintain business operations, from building roof repairs to building a new factory.
4. Financial cost (Finance cost)
Financial expenses are fees that borrowers have to pay when they borrow money from a bank or a credit institution, including loan interest, transaction fees, commission fees, late payment fees, product charges. years such as annual credit card fees and annual insurance credit fees in case lenders require insurance before making a loan decision.
5. Tax (Tax expense)
Tax expense is the total current income tax expense and deferred income tax (or current income tax income and deferred income tax) when determining the profit or loss for a period.
Revenue (Revenue or sales / gross income / top-line)
Revenue is the total amount of money earned by the company after a defined period of business. If selling 1 million apples in a year, that is annual revenue. It is also called "top line" because the calculation data is in the first line of the Income Statement.

The Revenue is also often confused with a different index called the Gross merchandise value (GMV) - the total transaction value of goods sold in the market within a specified period of time.
For example, if other farmers sell your apples and you get 10% of the money they earn. Now, if you sell 1 million apples and others sell 2 million, your net revenue is 1 million + 2 million x 10% = 1.2 million.
Gross profit (Gross profit / sales profit / gross income)
Gross profit (Gross profit) = revenue (Revenue) - cost of goods sold (COGS)
Gross profit margin (Gross profit margin) = Gross profit (Gross profit) / revenue (Revenue) x 100
Gross profit measures the performance of your business, depending on the industry. For example, if your apple farm's gross margin is 20% while the apple industry is 15%, this means you are doing business more effectively than many other competitors in the industry.
Non-operating income (Non-operating income)
Profits from other activities include profits from investments, dividends and foreign exchange trading.
Measuring profitability (profitability)
Profitability is one of the most important indicators to assess the health situation of the company.
1. Earnings before interest and tax (EBIT)
Earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) is a measure used to assess the company's ability to earn profits, with income minus costs, but not deducting (paying) interest and income taxes. EBIT is referred to as "operating income", "operating profit" or "operating income".
The formula for calculating EBIT is:
EBIT = Income - Operating costs
2. Net income
Net income (Net income) is calculated from the total income adjusted for operating costs, depreciation, interest, taxes and other costs related to the business activities of the enterprise. This data is shown in the income statement, a business report of a business, which is the calculation data in the last line so it is also called by the English name "the bottom line". . This index is also used to calculate earnings per share (EPS).
Cashflow statement (Cashflow statement - CFS)
Cash Flow Statement is a financial report that provides information about economic operations that affect the monetary situation of the business. The statement of cash flow is prepared on the basis of balancing cash receipts and payments, reflecting the formation and use of the amount of money arising in the reporting period.
Operations (Operations): are the activities that generate the main revenue of the enterprise and other activities that are not investment or financial activities.
Investment activities : are activities of procurement, construction, liquidation, and sale of long-term assets and other investments other than cash equivalents.
Financing: Activities that create changes in the size and structure of equity and loans of businesses.
Net cash and cash equivalents: Net increase / decrease in the period.
Net change in cash and cash equivalents: Difference in cash and cash equivalents in the period.
Evaluation of financial statements
So you have some basic information related to the financial statements. Now, start evaluating them.
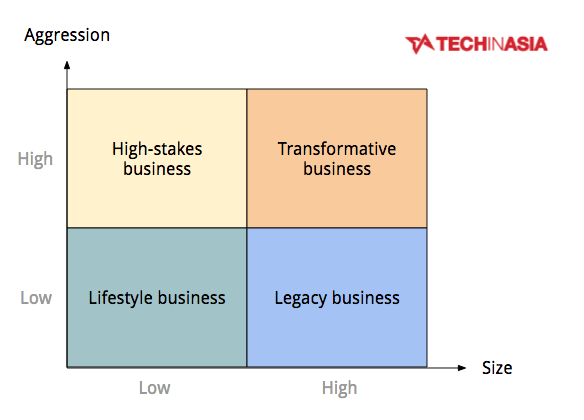
Size: enterprise scale and Aggression: the level of "overwhelming" the market
Business Lifestyle
Better businesses are also known as small and medium sized enterprises (SMEs), both in terms of business, labor and organizational structure. A good SME enterprise usually has net profit, stable cash flow and more assets than debt. Companies in marketing or law are mostly in this group.
Legacy businesses
Legacy businesses are quite similar to SME in that if they work well, they usually maintain net profit, stable cash flow and more assets than debt. However, these businesses hold a monopoly position on the business path they have identified, typically mining companies, restaurants, newspapers .
High stakes business
These are small-scale enterprises but are very excited to invest with the desire to expand their organization. They do not pay much attention to profits, cash flow or assets but pursue the goal of revenue growth. This makes the selling and marketing costs quite large despite the high business stakes ensuring that the unit economics (index on a certain unit, such as the cost of adding a customer) is reasonable. In addition, these companies also invest heavily in growth by accepting loans or calling for capital - which leads to more often debt than assets. Startups (startups) are the most representative representatives of this model.
Transformative business
These are big businesses that succeed in their niche and continue to invest heavily with the goal of expansion or innovation. They are fast-moving because of continuous improvements in equipment, product quality and investment in human resources. Amazon is a typical.
summary
Financial statements are a snapshot of the health of a business. However, there are other important, indispensable aspects such as culture, vision and leadership that you cannot ignore if you want to have the most accurate view of the overall performance of a company. any.