The interesting mystery behind how to put code names and numbers of famous Linux distributions, you know?
Have you ever felt deeply impressed with the code name of a favorite Linux release, and wondered about the meaning and the mysteries behind that codename?
The newly released Linux Mint 18 code-named Sarah, while the upcoming Ubuntu 19.10 will be called Eoan Ermine. Ubuntu's list of code names continues like this, true to the tradition of this platform, filled with extremely impressive names and makes it difficult to confuse.
- The silent contributions of Linux for human life
The secret from how to set the code name and number of Linux distributions
- Why need to learn about code naming?
- Ubuntu version numbering rules and code naming
- The version number rules and code names of Linux Mint
- The rule for versioning and codename of elementary OS
- Debian version numbering and code naming rules
- OpenSUSE version numbering and naming rules
- The way of naming the code is an 'art' and the person naming the code is 'artist'
Why need to learn about code naming?
Questions about the codename of software releases, operating systems in general are not new questions. However, fans of Linux are often known to be curious and curious about new things, so you may want to know the logic behind code naming of an Ubuntu or Debian release is the common desire of many others, and the pursuit of knowledge, in every situation, deserves to be welcomed.

- Zorin OS 15, a user-friendly version of Linux operating system, for those who are tired of Windows or Mac
On the other hand, after all, the code name was, is, and still is an indispensable part for every release, and the team of developers is also working hard to create impressive, memorable names. So our understanding of them is also a great way to respond to the efforts of developers, right?
With all the extremely practical and full of 'humanity' reasons, right now, we will together learn the logic behind how to code the names of some of the most popular Linux distributions, as well. as the true meaning behind each impressive name. Seems like it will be interesting!
- 5 distributions based on the best Arch Linux
Ubuntu version numbering rules and code naming

As one of the most widely used Linux distributions (and of course owning the most fans in the Linux family), it is undeniable that the great contributions Ubuntu brings to the community. In particular, this platform is also known for strict adherence to the release route and possessing impressive code names for each update.
Ubuntu follows the release cycle twice a year, with a release in April and the remaining version will be released in October. There is an interesting story behind the naming convention for releases. as well as the code name of Ubuntu. Let's first come to the conversation of Mark Shuttleworth (sponsor of Ubuntu operating distribution projects) and Robert Collins (Ubuntu's veteran developer), discussing the release of the first version. of this platform:
lifeless : How long will it take before we can launch the first version?
sabdfl : Let's see, I need to 'polish' some places, quite complicated, up to 6 months.
lifeless: 6 months! I don't think it takes time to 'makeup'.
sabdfl: Ok, then we'll name this release as Warty Warthog!
In the conversation, lifeless nickname is Robert Collins and sabdfl, Mark Shuttleworth, and Warthog is a pretty bad boar and possesses a 'smooth' skin. In his sentence, Mark Shuttleworth mentioned that it took a lot of time to 'polish' this release, so he thought of taking the name of a pig with rough skin to set name for it. The name, though not very good, created curiosity and impression for Ubuntu users at the time.
- Ubuntu 19.10: Roadmap for release & planned features
 Pig Warthog species
Pig Warthog species
The month and year of release play a very important role in the version number of Ubuntu releases. An Ubuntu release usually has a version number that conforms to the XX.YY format. In which XX is the issuing year and YY is the issue month. For example, we get the version of Ubuntu 16.04 in the 4th month (April) of 2016, or Ubuntu 15.10 that is released in the 10th month (October) of 2015.
So far, there is only one exception to the Ubuntu releases in April or October during the 11 years of development of this operating system, which is the case of Ubuntu 6.04. The release of this version has been delayed for 2 months (from April to June) and that's why it was named Ubuntu 6.06, instead of XX.04 or XX.10 as usual.
** You may not know: Ubuntu 6.06 is also the only release delayed for 11 years.
So that's the version number issue, now it's time to code Ubuntu code. You may notice that any Ubuntu release has a 2-letter code name, starting with the same letter. For example, Ubuntu 14.04 is called Trusty Tahr (starting with T), or like the first version: Warty Warthog (starting with W).
- Official: Ubuntu 19.10 includes Nvidia driver in ISO
The codename of the Ubuntu versions is made up of 2 words, the first word is adjective and the second word is noun, which is specifically an endangered animal, or sometimes mythical creatures like Unicorn or Werewolf (Werewolf). As in the example above, Trusty is an adjective which means trustworthy, trustworthy, while Tahr is a short horned mountain goat that lives in Central Asia, and is considered at risk. High extinction.
Another interesting fact is that these code names are usually incrementally alphabetically in each release (except for a handful of first versions). Thus, we have Ubuntu 14.04 as Trusty Tahr, Ubuntu 14.10 is Utopic Unicorn, Ubuntu 15.04 is Verv Vervet, etc.
Perhaps now you have a good understanding of the numbering and code naming of Ubuntu versions. If we have to summarize all releases of this platform, we will have a list as follows:
 List of Ubuntu releases and code names
List of Ubuntu releases and code names
Thus, in addition to leaving an unforgettable impression, Ubuntu releases also help us improve a lot of English vocabulary, and it is important to introduce the information about animals to the community. rare, endangered species that we may not have heard of, thereby raising the awareness of protecting the natural environment as well as the wild animals.
Here's a video that explains Ubuntu's code naming convention for you to refer to:
- Is CentOS or Ubuntu the best web hosting server operating system?
The version number rules and code names of Linux Mint

- These Linux distros are used in IoT devices
Ubuntu's distant cousin 'fired new cannons': Linux Mint, is a very popular Linux distribution around the world and owns a relatively large fan base. The first version of Linux Mint was Ada, launched in 2006. The latest stable version (17.3) is Rosa.
Linux Mint is built on the Ubuntu platform. Linux Mint has more features that Ubuntu does not have as many pre-installed software, including non-open source software like Java and Adobe Flash; and some software created by Linux Mint, like mintInstall, mintUpdate, mintNanny, .
That introduction is enough, now we come to the main problem. Since the distribution is based on Ubuntu, every few months after the new Ubuntu release is released, another release of Linux Mint will appear, based on that Ubuntu release.
Unlike Ubuntu, the version numbers for Linux Mint are usually not set in months and years, but simply increase. As such, we have Linux Mint 15 then Linux Mint 16, Linux Mint 17, etc. These are the major releases. Sub-releases (similar to service packs in Windows), are numbered incrementally. Therefore, we have Linux Mint 17.1, 17.2, 17.3 and so on
It's about version numbers, but now let's talk about code names. Each release of Linux Mint, either child or main, has its own codename. And like Ubuntu, they are also placed in ascending order of the alphabet.
A more interesting thing about the Linux Mint code name is that they are usually named after the female name, ending with the letter 'a', and most are derived from mythical Abrahamic religious stories (religions by tradition Abrahamic's system includes: Judaism, Christianity, and Islam, with the number of believers making up more than half of the world's population. That gives us names like Linux Mint 17 Qiana, etc.
- Compare the most popular Linux distributions today
 Abrahamic religion
Abrahamic religion
The codename of the major releases will be placed in ascending alphabetical order, while the code names of the sub-releases will also have the same starting letter but the overall name will be changed, such as Linux Mint 17.1 is Rebecca, 17.2 is Rafaela and 17.3 is Rosa - the same begins with the letter 'R' but is different from the name.
To summarize all Linux Mint releases so far, we have the following list:
 List of Linux Mint releases and code names
List of Linux Mint releases and code names
'Sarah' is the only exception in the list that does not end with an 'a' letter.
- 8 best open source NAS operating systems for Linux
The rule for versioning and codename of elementary OS

- 11 best Linux distributions for programmers
Above we talked about Ubuntu and Linux Mint, let's continue with another member of this big family, elementary OS.
elementary OS is also an Ubuntu-based Linux distribution. This is the leading distribution to showcase the Pantheon desktop environment, and was developed by elementary LLC.
On the main issue, elementary OS has a version number that matches the ascending structure as 0.X. Thus, we have the first stable version of this operating system of 0.1, then 0.2 and the current stable version is elementary OS 0.3.
As for the codename, releases of elementary OS are often named after a mythological god, usually names taken from Roman or Nordic myths. This brings elementary OS with extremely impressive code names such as Jupiter, Luna, Freya (formerly ISIS) and perhaps soon to be Loki.
There are absolutely no alphabetic constraints here, we have a list of elementary OS releases as follows:
- 0.1 - Jupiter
- 0.2 - Luna
- 0.3 - Freya
Debian version numbering and code naming rules

- Your Linux system can be hacked just by opening a file in Vim or Neovim Editor
For now, let's go to the 'grandfather' of the Ubuntu family, Linux Mint and elementary OS. Debian As one of the earliest Linux kernel-based operating systems (Ubuntu is also derived from Debian), it was first published on August 16, 1993 by Ian Murdock, and released the first version. September 15, 1993.
Debian owns an interesting naming system but is equally 'confusing'. In fact, Debian itself is named after the founder Ian and his girlfriend Debra. Sadly, the founder Ian Murdock died last year, but his name will be forever shared with Debian - one of the world's most loved open source operating systems.
Debian version numbers - like many other operating systems - are sorted incrementally. However interesting things again in the code name. There is a pretty 'cool' fact, that all Debian releases have the codename given to the characters of the famous cartoon film Toy Story. That explains why we have Debian Jessie or Debian Woody.
 Toy Story
Toy Story
Below is a list of all Debian releases and their code names:
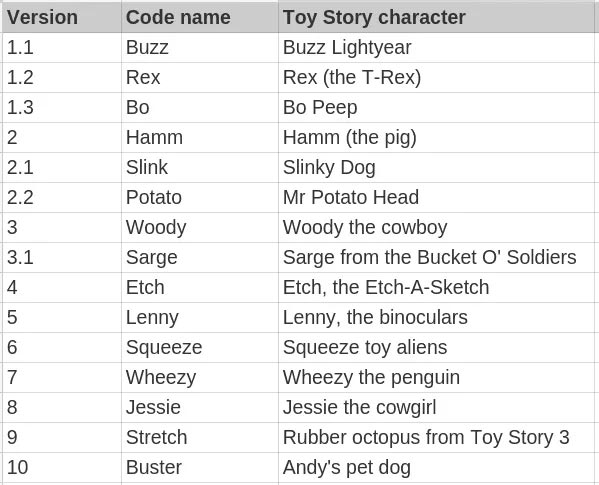 List of Debian releases and code names
List of Debian releases and code names
And if you've ever seen Toy Story, you probably can't forget the movie's villain: Sid - this hateful neighbor is a player who ruins toys. That's why all unstable Debian distributions are codenamed Debian Sid.
Toy Story has a lot of characters, so you don't need to worry about naming Debian!
OpenSUSE version numbering and naming rules

- The Korean government is going to use the Linux operating system instead of Windows because of the expensive cost
OpenSUSE is a Linux distribution sponsored by SUSE Linux Gmb and other companies. Originally developed on the platform of Slackware operating system, but gradually changed significantly. OpenSUSE is widely used all over the world.
The first OpenSUSE release was released in 2005 as OpenSUSE 10.1. It is not clear why the developers of this operating system have started with a name of 10 but not 1 (they probably like it). But since then, the major releases of OpenSUSE have followed the rule quite simply, which is to increase the version number for large releases before the decimal, and for small releases later decimal. Thus, we have OpenSUSE versions with release numbers: 11.3, 11.4, 12.1, 12.2, etc.
The original release of OpenSUSE was not codenamed. However, until the OpenSUSE 11.2 version or later, the code name was finally added.
The well-known identity of OpenSUSE is traditionally green, and this color is also an inspiration in code naming for its releases. That's why we have OpenSUSE Emerald (emerald, or jade), or OpenSUSE Teal (teal green) .
 Emerald - Jade
Emerald - Jade
List of OpenSUSE releases and code names:
- 11.3 - Teal
- 11.4 - Celadon
- 12.1 - Asparagus
- 12.2 - Mantis
- 12.3 - Dartmouth
- 13.1 - Bottle
- 13.2 - Harlequin
- Leap 42.1 - Malachite
- openSUSE 15.0 - Leap
Don't be confused if you've never heard of these green colors before. And if you think OpenSUSE will use all "code" in the future, it's possible! But maybe developers will have a way to solve it. That's right, we already have 50 shades of gray, so it could have been green!
The way of naming the code is an 'art' and the person naming the code is 'artist'
We can see how to set the version number and codename of different block versions are very diverse and interesting, demonstrating the creativity and sophistication of the development team. So do you think it's easier to remember a release through code names than version numbers? Do you think code names are necessary? Which Linux distribution code name do you like best? Leave your point in the comment section below!