The difference between Tethering and Hotspot
According to the American Heritage Dictionary, tether is a term used to refer to a string that holds an animal in a given radius. In the context of mobile technology, connecting a mobile phone to a laptop with a USB cable is called tethering. Tethering can be done by various means like WiFi, Bluetooth or USB. Tethering often allows sharing this device's internet connection with another device. All modern mobile operating systems have Internet sharing capabilities. Windows, Android and iOS have built-in features to allow connection via USB, Bluetooth and WiFi. When an Internet connection is made via WiFi, it is also called a mobile hotspot.

Tethering refers to connecting the phone to a computer with a USB cable to act as a USB modem.
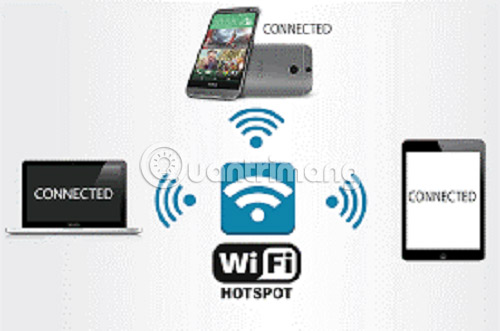
Hotspot is the act of creating a WiFi network in which the phone acts as a modem / router.
Distinguish Tethering and Hotspot
- The Tethering approach
- Protocols and connection requirements
- Models provide Tethering and Hotspot
- Cost
- Connect
- Advantages of Mobile Hotspot compared to Tethering
The Tethering approach
- Mobile hotspot is the most popular approach to tethering. It is very easy to install and the presence of WiFi modules on most devices makes it unnecessary to add any additional components.
- Tethering via Bluetooth is relatively difficult to set up and the speed is also lower than WiFi. Currently, Bluetooth tethering is not widely used, although it appeared before WiFi became widely available.
- Tethering uses USB very fast and consumes less power because the device can be charged via USB. However, there are not many devices that support this USB connectivity. In addition, it will need special drivers or software on both sides and may require additional configuration.
Protocols and connection requirements
Tethering often uses NAT (Network Address Translation) to share the Internet. In this case, only the device connected to the Internet (the device is connected to the Internet) has IP public. Other devices connected by tethering have private IP and a technique called NAT is used to identify different devices under the view of a single public IP.
Mobile hotspots are provided by different telecommunications service providers including an adapter or device that allows computer users to connect to the Internet from anywhere. Mobile hotspots are promoted as an alternative to the usual method of logging into a local or other wireless network from a PC. Although mobile hotspots can be used for a variety of devices, they are often combined with laptops because laptops are hybrid devices that can be carried around, but often include mobile WiFi.
Today, in addition to hardware, there are many wifi broadcast software. For example, Connectify Virtual Router or similar tools built into the operating system allow Internet sharing by turning WiFi modules on laptops or mobile phones into virtual hotspots.

Models provide Tethering and Hotspot
The other difference between tethering and hotspot is in the models provided. Most telecom operators that offer mobile hotspot will sell the box or adapter at a fixed price and provide a monthly fee for mobile hotspot service. With tethering, just simple cable connectors to connect an existing mobile wireless device to a laptop without paying any monthly fee. However, mobile hotspots still seem to be a popular choice for convenience.
The difference in cost
When planning to use one of these services, the potential costs involved are also considered. If using tethering to access the Internet, users may have to pay for each kB of data transmitted over the mobile network. If you use the internet regularly, this amount can be very large. For comparison, with a traditional hotspot, users can use the Internet freely, without having to worry about the amount of data being accessed. Hotspot owners will pay monthly service fees to Internet service providers.
Typically, a mobile hotspot does not include contracts and fees. Use how much to pay, so users only have to pay for the data they use and recharge when needed. Operators with the best coverage and speed often have the most expensive costs and may require contracts. If you choose providers that offer the best price, sometimes users have to trade between coverage and speed.
Connect
WiFi hotspots are found in public places as well as in private places. Today, many public places in the world such as airports, shops, restaurants, hotels, hospitals, libraries, public phone stations, railway stations, schools and universities have hotspots. Many hotspots offer free Internet access, others require fees. Hotspot can be set up at home by connecting the wireless router to the Internet via ADSL or 3G. This is the most common method used today to share Internet connection at home on many different devices.
Advantages of Mobile Hotspot compared to Tethering
Mobile Hotspot has many advantages over tethering.
- Data bandwidth : When you have to perform tasks that consume a lot of data bandwidth, users may fall into a usage situation that exceeds the data transfer limit. Using hotspots is the best option in this situation.
- Phone battery life : Using a hotspot means never draining your battery just to get it done. This is beneficial for long-term use, since users do not have to trade off the phone's lifespan just to stay connected.
- Using multiple devices : Users can safely share the connection between multiple devices. Although many devices can be connected to the phone, the more Internet devices the worse the experience. Most hotspots will limit the number of devices connected, but you can still connect more than one or two devices without performance issues.
- Continuous : Tethering is easy to miss calls often, especially when used for a long time. This is usually attributed to the firmware used. Similarly, even unlimited data programs of different vendors (depending on the provider), can also be adjusted after a certain time (ie it is essentially just for high-speed access in a certain capacity level, then decrease to normal speed). Hotspots are more reliable with the added advantage of using how much to pay.
- Choosing between data and conversation capabilities : This varies depending on the operator, but with Verizon Wireless and Sprint, the connection (via 3G, not through LTE) conflicts with phone conversations. Although the phone may ring, the signal will be disconnected as soon as the user answers and vice versa.
- Diversifying suppliers : If you regularly travel, you can choose any provider that offers better service in your destination. Even when you're at home, you can now choose the best-performing provider.