Queue data structure (Queue)
What is the queue data structure (Queue)?
Queue (Queue) is an abstract data structure, is something similar to queues in everyday life (queuing).
Other than the stack, the queue is open at both ends. One end is always used to insert input (also known as incoming rows) and the other end is used to delete data (leaving the row). The queue data structure follows the First-In-First-Out method, ie the first entered data will be accessed first.
In real life, we have many examples of queues, such as cars on one-way roads (especially when traffic is blocked), in which the first car will exit first. Some other examples are queuing up students, queuing up for tickets, .
Demonstration of queue data structure (Queue)
Now you probably imagine what a queue is. We can access both ends of the queue. Below is a queue representation in the form of data structures:

Similar to the stack data structure, the queue data structure can also be deployed using Arrays (Array), Link list (Linked List), Pointer (Pointer) and Structure (Struct ). For simplicity, the next section will learn more about queues deployed using one-dimensional arrays.
Basic operations on queue data structure
Activities on the queue data structure may involve queuing initialization, using data on the queue and then deleting data from memory. The list below is some basic operations that can be performed on queue data structures:
Enqueue () : add (or store) an element into the queue.
Operation dequeue () : delete an element from the queue.
In order to use queues effectively, we also need to check the status of the queue. For this purpose, here are some other support features of the queue:
The peek () method : takes the element at the top of the queue, without deleting this element.
IsFull () method : check if the queue is full.
IsEmpty () : check if the queue is empty or not.
In the queue data structure, we always: (1) dequeue (delete) the data pointed by the front pointer and (2) enqueue (enter) the data into the queue by the help of the rear pointer .
In the next section we will learn about the support features of the queue data structure:
The peek () method of the queue data structure
As in the stack data structure, this function helps us look at the data at the top of the queue. The algorithm of the peek () function is:
b ắ t đầ u h à m peek return queue [ front ] k ế t th ú c h à m
Deployment of the peek () function in C language:
int peek () { return queue [ front ]; } The isFull () method in the queue data structure
If when we are using a one-way array to deploy the queue, we only need to check if the rear pointer has reached MAXSIZE to determine if the queue is full. In the case of queue deployment by using Round Linked List, the algorithm for isFull () function will be different.
The following is the algorithm of isFull () function:
b ắ t đầ u h à m isfull if rear equals to MAXSIZE return true else return false endif k ế t th ú c h à m
Algorithm deployment of isFull () function in C language:
bool isfull () { if ( rear == MAXSIZE - 1 ) return true ; else return false ; } IsEmpty () method in the queue data structure
The algorithm of isEmpty () function:
b ắ t đầ u h à m isempty if front l à nh ỏ h ơ n MIN OR front l à l ớ n h ơ n rear return true else return false k ế t th ú c if k ế t th ú c h à m
If the value of the front is less than MIN or 0, then the queue has not been initialized yet, so the queue is empty.
Here is the code deployment in C language:
bool isempty () { if ( front < 0 || front > rear ) return true ; else return false ; } Operate enqueue in queue data structure
Because the queue data structure maintains two data pointers: front and rear, so the operation of this type of data structure is quite complicated when compared to the stack data structure.
Here are the steps to enqueue (insert) data into the queue:
Step 1 : check if the queue is full.
Step 2 : If the queue is full, the process fails and is exited.
Step 3 : If the queue is not full, increase the rear pointer to point to the next available memory location.
Step 4 : Add the data element to the position where the rear cursor is pointing to the queue.
Step 5 : return success.
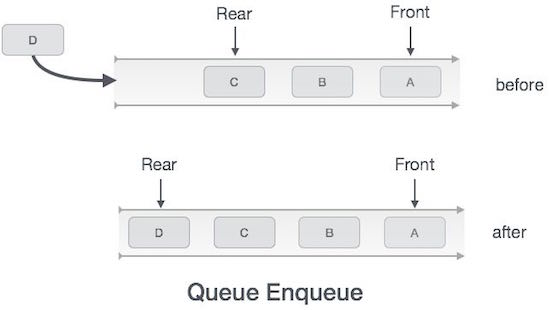
Sometimes we also need to check if the queue has been initialized to handle unexpected situations.
Algorithm for enqueue operation in queue data structure
b ắ t đầ u enqueue ( data ) if queue l à đầ y return overflow endif rear ← rear + 1 queue [ rear ] ← data return true k ế t th ú c h à m
The algorithm deployment of enqueue () operation in C language:
int enqueue ( int data ) if ( isfull ()) return 0 ; rear = rear + 1 ; queue [ rear ] = data ; return 1 ; k ế t th ú c h à m
To monitor the full code deployment of the above activities in C language, please click on chapter: Queue in C.
Operation dequeue in queue data structure
Accessing data from the queue is a two-step process: access the data where the front cursor is pointing and delete the data after accessing it. Here are the steps to perform dequeue :
Step 1: check if the queue is empty.
Step 2 : If the queue is empty, the process fails and is exited.
Step 3 : If the queue is not empty, access the data where the front cursor is pointing.
Step 4 : Increase the front pointer to point to the location containing the next element.
Step 5 : return success.
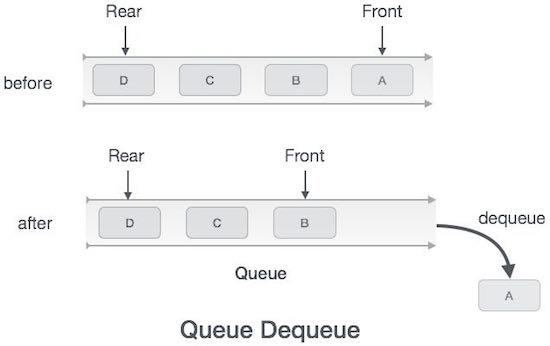
Algorithms for dequeue operation
b ắ t đầ u h à m dequeue if queue l à tr ố ng return underflow end if data = queue [ front ] front ← front + 1 return true k ế t th ú c h à m
Dequeue () operation deployment in C language:
int dequeue () { if ( isempty ()) return 0 ; int data = queue [ front ]; front = front + 1 ; return data ; } To monitor the full code deployment of the above activities in C language, please click on chapter: Queue in C.
Store queues
According to Tutorialspoint
Previous article: Stack data structure (Stack)
Next article: Linear search algorithm (Linear Search)