RegretLocker: A new strain of ransomware that targets Windows virtual machines
A new ransomware strain called RegretLocker has been found to use a host of advanced features to encrypt virtual hard drives and close open files on the target system to encrypt unauthorized data.
In fact, RegretLocker was first spotted in October, and is judged to be a formally simple ransomware strain because it doesn't contain lengthy ransom notices and specifically only uses email for communications. to the victim, not a regular Tor payment site.

RegretLocker's ransom notes
Once a file is successfully encrypted, RegretLocker adds a harmless sounding .mouse extension to the filename. But in fact, hidden inside it is an extremely unique encryption mechanism.

The file after being encrypted by RegretLocker
RegretLocker's dangerous encryption technique
When setting up a Windows Hyper-V virtual machine, a virtual hard disk is also created and stored in a VHD or VHDX file.
These virtual hard disk files contain raw disk images, include the partition table of the virtual drive and the partitions that are similar to regular drives, and can range in size from several GB to TB rows.
When ransomware encrypts data on your computer, encrypting a large file is ineffective because it slows down the speed of the entire process. In a ransomware sample discovered by MalwareHunterTeam and analyzed by Advanced Intel security engineer Vitali Kremez, RegretLocker used a relatively unique encryption technique, which is to mount virtual disk files for individual encryption.
ingredients quickly and easily. To implement this technique, RegretLocker uses the Windows Virtual Storage APIs OpenVirtualDisk, AttachVirtualDisk, and GetVirtualDiskPhysicalPath for the purpose of mounting the virtual disk.
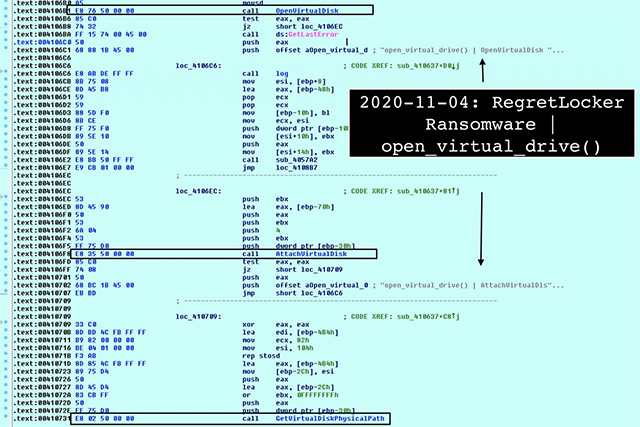
The malware mounts a VHD file
After the virtual drive has been mounted as a physical disk in Windows, ransomware can completely encrypt each individual drive, thereby significantly increasing encryption speed.
In addition to using the Virtual Storage API, RegretLocker was found to abuse the Windows Restart Manager API to terminate Windows processes or services that left files open during encryption.
When using this API, if the name of the process contains 'vnc', 'ssh', 'mstsc', 'System' or 'svchost.exe' then ransomware will not terminate that process. This exception list can be used to prevent important programs or programs used by hackers to access the target system from being accidentally stopped. The Windows Restart Manager API is currently only used by some popular ransomware such as REvil (Sodinokibi), Ryuk, Conti, ThunderX / Ako, Medusa Locker, SamSam, and LockerGoga.
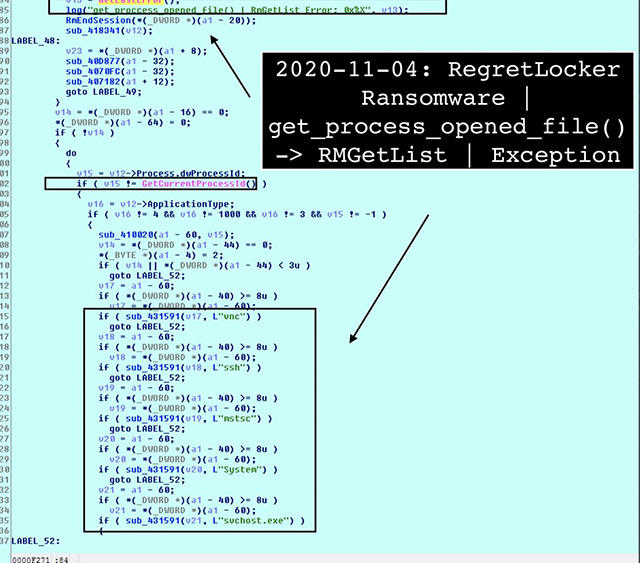
Windows Restart Manager Exceptions List
RegretLocker is not very active yet and is really popular right now, but this is clearly a dangerous ransomware strain that needs to be kept an eye out for now.
You should read it
- ★ Can data encryption protect you from Ransomware?
- ★ Ransomware (ransomware) is showing signs of explosion worldwide, paying is no longer the most effective option.
- ★ Ransomware can encrypt cloud data
- ★ New ransomware strain discovered using leaked Windows and Linux encryption
- ★ Ako ransomware is raging all over the world, what do you know about this ransomware?