Hash Table data structure
What is Hash Table?
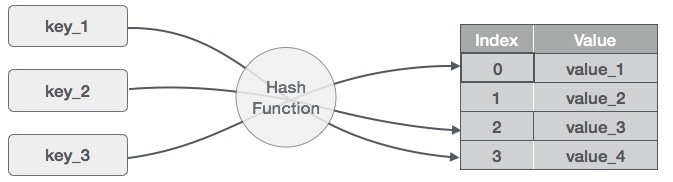
The Hash Table data structure is a data structure that stores data in a federated manner. In Hash Table, data is stored in array format, in which data values have their own index values. Accessing data becomes faster if we know the index of the data to find.
Therefore, with this type of Hash Table data structure, insertion and search operations will take place very quickly, regardless of the size of the data. Hash Table uses arrays as an intermediate repository and uses hash techniques to create indexes where elements are inserted.
Hashing techniques
Hashing is a technique to convert a range of key values into a range of index values of an array. We are using the remainder operator to obtain a sequence of key values. Suppose there is a HashTable of size 20, and below are the elements that need to be stored. Element in format (key, value).
(1.20)
(2.70)
(42.80)
(4.25)
(12.44)
(14.32)
(17.11)
(13.78)
(37.98)
Linear Probing Technique (Linear Probing)
We see that it is possible that the hashing technique used to create an index already exists in the array. In this situation, we need to search for the next blank position in the array by looking in the next cell until we find an empty cell. This technique is called Linear Probing.
SttKeyHash Only array itemAfter technique Linear Probing, array index1 1 1% 20 = 1 1 1 2 2 2% 20 = 2 2 2 3 42 42% 20 = 2 2 3 4 4 4% 20 = 4 4 4 5 12 12% 20 = 12 12 12 6 14 14% 20 = 14 14 14 7 17 17% 20 = 17 17 17 8 13 13% 20 = 13 13 13 9 37 37% 20 = 17 17 18Basic operations on Hash Table
Here are some basic operations that can be performed on the Hash Table data structure.
Search activity : search for an element in the HashTable data structure.
Insert operation : insert an element into the HashTable data structure.
Delete operation : delete an element from the HashTable data structure.
Data Element (DataItem) in HashTable
Data elements include: data and key. Based on this key we can perform search operations in the HashTable data structure.
struct DataItem { int data ; int key ; }; Method of Hash Table data structure
Specify a method to estimate the Hash Code of the key of the data element.
int hashCode ( int key ){ return key % SIZE ; } Search activity in Hash Table
Each time an element is searched: estimate the hash code of the transmitted key and then determine the element's location using that hash code value as an index in the array. Use Linear Probing to get the element if no element is found with the estimated hash code value.
struct DataItem * search ( int key ){ //lấy giá trị hash int hashIndex = hashCode ( key ); //di chuyển trong mảng cho tới khi gặp ô trống while ( hashArray [ hashIndex ] != NULL ){ if ( hashArray [ hashIndex ]-> key == key ) return hashArray [ hashIndex ]; //tới ô tiếp theo ++ hashIndex ; //bao quanh hash table hashIndex %= SIZE ; } return NULL ; } Insert operation in Hash Table
Each time an element is inserted: estimate the hash code of the transmitted key and determine the element's location using that hash code value as an index in the array. Use Linear Probing for the blank position if the element is found with the estimated hash code value.
void insert ( int key , int data ){ struct DataItem * item = ( struct DataItem *) malloc ( sizeof ( struct DataItem )); item -> data = data ; item -> key = key ; //Lấy giá trị hash int hashIndex = hashCode ( key ); //di chuyển trong mảng cho tới khi gặp ô trống hoặc bị xóa while ( hashArray [ hashIndex ] != NULL && hashArray [ hashIndex ]-> key != - 1 ){ //tới ô tiếp theo ++ hashIndex ; //bao quanh hash table hashIndex %= SIZE ; } hashArray [ hashIndex ] = item ; } Delete operation in Hash Table
Whenever an element needs to be deleted: estimate the hash code of the transmitted key and then determine the element's location using that hash code value as an index in the array. Use Linear Probing to get the element if no element is found with the estimated hash code value. Once found, store a fake element here to keep the hash table's performance.
struct DataItem * delete ( struct DataItem * item ){ int key = item -> key ; //lấy giá trị hash int hashIndex = hashCode ( key ); //di chuyển trong mảng cho tới khi gặp ô trống while ( hashArray [ hashIndex ] != NULL ){ if ( hashArray [ hashIndex ]-> key == key ){ struct DataItem * temp = hashArray [ hashIndex ]; //gán một phần tử giả tại vị trí bị xóa hashArray [ hashIndex ] = dummyItem ; return temp ; } //tới ô tiếp theo ++ hashIndex ; //bao quanh hash table hashIndex %= SIZE ; } return NULL ; } According to Tutorialspoint
Previous article: Interpolation Search algorithm (Interpolation Search)
Next lesson: Alignment algorithm in data structure & algorithm