How to use cURL command in Linux
No matter what you use your computer for, at least once you need to download a file and opening the browser may seem overkill. This will be the time cURL really plays its role.
As its name suggests, cURL is a command-line tool to transfer data by URL. One of the simplest uses is to download a file via the command line. cURL is an extremely powerful tool depending on how you use it. Even if you are familiar with using the command line, it is difficult to fully exploit the full potential of cURL.
Instructions for using cURL command in Linux
- Basic functions of CURL
- Track HTTP Headers
- Save cURL results to a file
- Download multiple files at once
- The download process has stopped
- Use basic HTTP authentication
Basic functions of CURL
One of the most basic things you can do with cURL is to download a website or file. To do this, simply use the curl command followed by a URL. Eg:
curl https://www.google.com In most situations, using the command this way will help you get a terminal that contains the full raw (raw) HTML data (in the most ideal case) or unreadable characters (in case worst). If you want to save it to a file, you can use standard Unix redirection features to do this.
curl https://www.google.com > google.html Track HTTP Headers
Browsers often fix this for you, but the Internet is different. When you enter a URL, you will probably be redirected one or more times before reaching the landing page.
For example, say you are trying to visit TipsMake.com website. Enter the following command that will help you get a redirect notification:
curl http://quantrimang.com You can track these HTTP location headers by using the following -L flag:
curl -L http://quantrimang.com 
It doesn't look great in the terminal, but it's also an option to know.
Save cURL results to a file
There are several ways to save URL content into a file. The -o option allows you to decide the file name, while the -O option uses the file name in the URL to save. To select your own file, use the following option:
curl -o filename.html https://example.com/url Often you will want to save a file with the same name it uses on the server. To do that, use the -O option .
curl -O https://example.com/filename.html 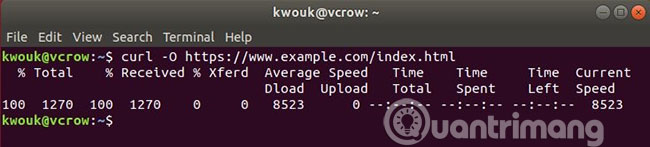
Download multiple files at once
If you need to download several files at once, cURL will help you easily do this with the -O option .
curl -O https://example.com/file1.html -O https://example.com/file2.html 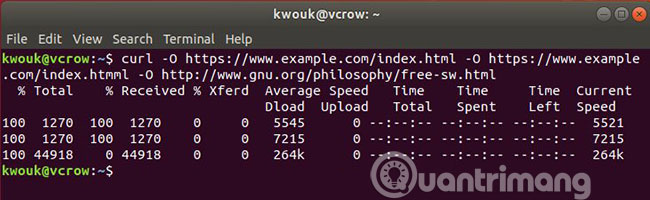
When downloading this way, cURL will try to reuse the connection instead of creating a new connection each time.
The download process has stopped
No fun when the download process stopped midway. Fortunately, cURL makes it easy to continue downloading without having to start over. The syntax is a bit strange, because you need to add -C - to the command.
Suppose you started downloading with the following command:
curl -O https://example.com/bigfile.zip After that, you stopped it by pressing Ctrl + C. You can continue with the following command:
curl -C - -O https://example.com/bigfile.zip Use basic HTTP authentication
Basic HTTP authentication will not work with things that require usernames and passwords. But if the server uses basic HTTP authentication, cURL will be able to work with this feature. To download a file with username and password authentication, you can use the following command:
curl -u username:password -O http://example.com/filename.html 
This command also works with FTP servers, because cURL supports many different protocols.
There are many things you can do with cURL. Sometimes you can feel all the functions that cURL offers can be too much. If you feel that cURL is too complicated, you can choose a simpler alternative: GNU wget.
Although cURL provides all the options you want, wget actually provides the best default options for you. If you are not sure what is the right choice, read the detailed comparison of TipsMake.com cURL and wget to make a decision.