How does a chatbot simulate a conversation with a human?
Chatbots have been a strange but useful online tool for a while. The emergence of AI-based language models, such as GPT-4 and the ChatGPT chatbot it supports, has given the human-bot-human interface a new lease of life. But how do AI chatbots simulate human-like conversations?
What are Chatbots? How do chatbots work?
Before ChatGPT, Claude, and Google Bard, there were more rudimentary chatbots. They are called rule-based chatbots or Decision Tree chatbots.
Rule-based chatbots do not adapt to situations or understand context and cannot simulate human logic. Rather, they have a series of rules, templates, and dialog trees set by the developer that they must adhere to.
Rule-based chatbots follow predefined conditions when prompted. Keywords are an important factor here. The user's input is scanned by the chatbot for specific words to help it understand what is being asked. Without the ability to understand context, rule-based chatbots must rely on clues like these to provide useful responses.
Many businesses use rules-based chatbots as a buffer between customers and human representatives. If you've ever tried contacting your electricity or mobile provider, you may have been asked to explain your query to a chatbot first. Additionally, a chatbot can appear when you visit a website to ask a question.
Rule-based chatbots cannot answer complex, multi-layered questions. They are designed to answer short and simple queries, such as "Change my account details" . A question containing many variables may be out of scope for a rules-based chatbot, either because it is not trained to interpret natural language or because its knowledge database is limited.
Rule-based chatbots cannot improve without manual intervention during the development phase. This is because they cannot learn from previous interactions.
AI chatbots are also given rules. For example, ChatGPT cannot swear or give advice about criminals. However, the way AI chatbots operate and interact goes beyond what any rules-based chatbot can handle.
How does AI Chatbot work?
ChatGPT is not the beginning of Chatbot AI. Before ChatGPT went mainstream, some less advanced chatbots still used AI to interact with users.
Take Eviebot for example. Launched in 2008, Evie uses AI to interact with users. As a learning AI chatbot, Evie can build her conversation skills by recording what other users have previously typed. In fact, Evie uses the same AI system as Cleverbot, another chatbot that went mainstream in the late 2000s and early 2010s.
But this chatbot is a far cry from the modern versions we use today.
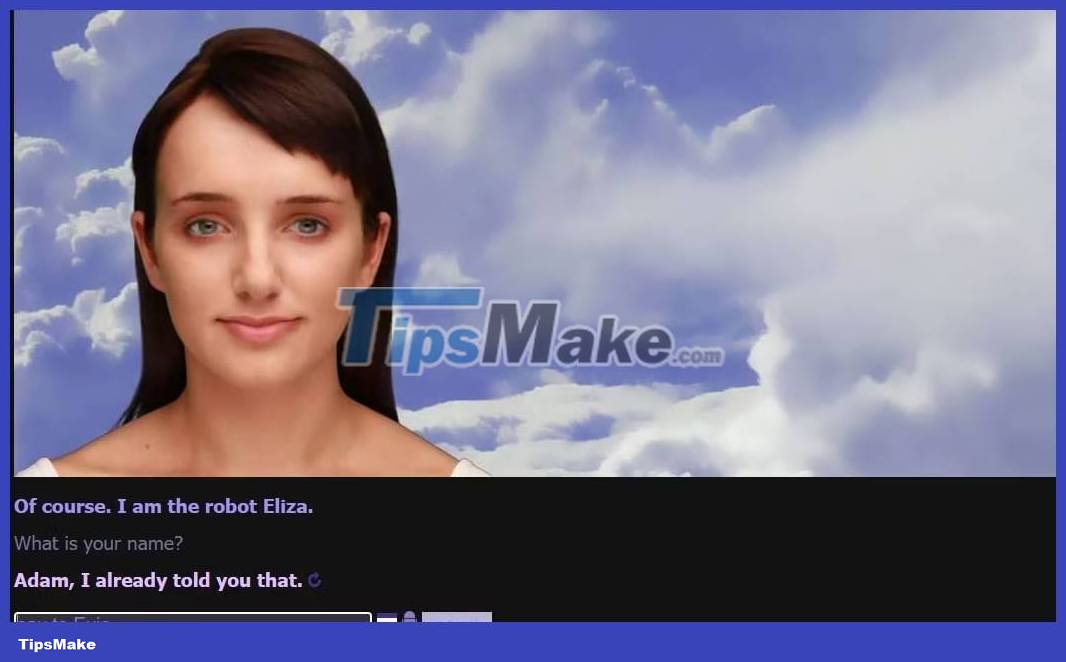
As you can see in the screenshot above, Evie is not good at answering questions correctly or remembering conversation history. Within seconds, the chatbot said its name was Eliza but then changed it to Adam in the next response.
Also, Evie is not a great source of information. When we asked Evie how big the sun was, she replied: "Bigger than my future." Although humorous, Evie is not good at providing users with factual information, no matter how popular they are. If you're looking for a more fun or quirky chatbot experience, Evie might be the right choice for you.
Sites like Cleverbot and Evie are certainly entertaining but they are not suitable for practical use. By the end of 2022, the world is starting to see how useful AI chatbots can be.
How does a chatbot simulate a conversation?
The question remains: How do AI chatbots like ChatGPT simulate accurate conversations with humans?
In November 2022, OpenAI released a publicly accessible version of its GPT-3.5 large language model called ChatGPT. This is the first AI chatbot to demonstrate the ability to simulate very human-like conversations.
First, the "GPT" element in the tool's name stands for "Generative Pre-training Transformer", which is a type of large language model (LLM). You may have seen both of these terms used a lot going into 2023, but what do they really mean?
LLM is an AI learning model used by all the major AI chatbots you see today. It is powered by an AI algorithm that uses Deep Learning methods to operate at an extremely complex level. All LLMs are trained with very large datasets, giving them a huge pool of knowledge to solve problems and answer queries. ChatGPT-4, for example, was trained with between 1 trillion and 1.7 trillion parameters and terabytes of data (though OpenAI hasn't revealed exactly how many).
GPT is a specific type of LLM that includes artificial neural networks with deep learning capabilities. GPTs are pre-trained models with a huge database of information to learn from. In the case of ChatGPT, this includes text from books, magazines, articles, etc. But even with all this data, how can ChatGPT talk to users in a human-like way? ?
During the development of ChatGPT, it was trained using reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF). This type of training uses reinforcement to transform ChatGPT into the desired chatbot. With a reward and feedback model, ChatGPT can understand which feedback is useful or "good" and which is not. This method also allows ChatGPT to better capture conversation context, meaning it can respond to prompts more effectively.
ChatGPT's natural language processing also plays a large role in how it responds to users, including recognizing specific language and emotional patterns. During training, the algorithm was provided with examples of human conversations to better understand how humans communicate. The algorithm can even note signals, like hellos and goodbyes, to track the stage of the conversation.
How are AI Chatbots Developing?

OpenAI has released some limited information about GPT-5, the next version of LLM. What's especially interesting about GPT-5 (apart from a more up-to-date knowledge base) is that it is said to incorporate artificial general intelligence (AGI) into the algorithm. Given that AGI could theoretically simulate human cognition, this could be a game changer.
ChatGPT has taken the world by storm and continues to do so, but AI chatbots don't end with OpenAI. Companies around the world are working to improve their AI chatbots to simulate conversations with people, with some AI chatbots taking things to a physical level.
Take Desdemona as an example, a robot model that uses AI to communicate.
Created by Hanson Robotics and SingularityNET, Desdemona is the "little sister" of the famous robot Sophia, which has made headlines for its impressive human-like features and temperament.
Unlike Sophia, Desdemona focuses on music and is even part of a band with other human musicians. The AI algorithm takes from the available music library, allowing Desdemona to sing along to famous songs. Robot even performed live with her bandmates.
But Desdemona can also talk and converse with people. In 2022, Desdemona was interviewed by YouTube creator Discover Crypto. In it, the creator of her AI algorithm, Ben Goertzel, also answered some questions about AI and its future.