Spanning Tree in data structure and algorithm
What is a Spanning Tree?
A spanning tree is a subset of Grahp G that has all vertices enclosed by the minimum number of edges. Therefore, a spanning tree will not form a cycle and it cannot be interrupted in the middle.
From the above definition we can conclude that each periodic Graph G will have at least one spanning tree. A broken Graph G will not have any spanning trees.
Below is an example of an example of a Ghp and its spanning trees:
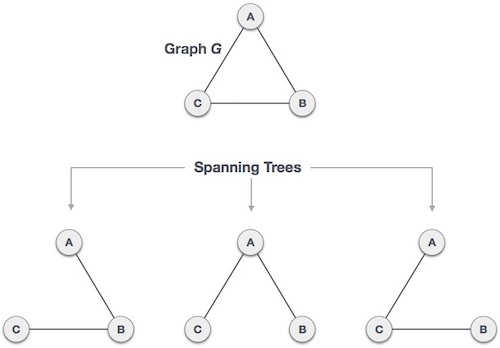
Above we have 3 spanning trees of a periodic graph. A periodic graph can have up to n n-2 spanning trees, where n is the number of nodes. In the above example, n is 3 so 3 3−2 = 3 spanning trees.
Common properties of the spanning tree (Spanning Tree)
We now understand that a Graph can have more than one spanning tree. The following are some of the properties of the cyclic Graph G tree given:
A periodic Ghp can have more than one spanning tree.
All spanning trees of a Graph G have the same number of edges and vertices.
The spanning tree does not have any cycles.
Removing an edge from a spanning tree will cause the Grahp to be non-periodic.
Adding an edge to the spanning tree creates a cycle.
Mathematical properties of the spanning tree (Spanning Tree)
The spanning tree has n-1 edges, where n is the number of nodes (vertices).
From a periodic Graph, by deleting the maximum of e-n + 1 edges, we can construct a spanning tree.
A recurring grahp can have up to n n-2 spanning trees.
Application of the frame tree (Spanning Tree)
Basically, the spanning tree is used to find the shortest path to connect all nodes in a Graph. Common applications of spanning trees are:
- Civil network planning
- Computer network routing protocol
- Cluster Analysis
We explore the following simple example to understand these applications. Imagine an internet in the city as a large graph and now the plan is to deploy network lines so that the shortest wire length can still connect all the nodes. city. That is an example explanation for the application of the spanning tree.
Minimum Spanning Tree (MST)
In a Weighted Graph, a minimum spanning tree is a spanning tree that has the smallest weight of all these Grahp spanning trees. In real life, the weight here can be distance (distance), congestion, traffic load, or any value that can be represented as edges.
Algorithms for the smallest spanning tree
Because of the page length limitation, I will not present the following two algorithms in this chapter. Please click on the following two links to further explore the two most important spanning tree algorithms:
- The smallest spanning algorithm of Kruskal
- The smallest arithmetic algorithm of Prim
According to Tutorialspoint
Previous article: AVL tree in data structure and algorithm
Next lesson: Heap data structure
You should read it
- ★ Not only people but even animals do not dare to array to the unique tree species on this planet
- ★ Feng shui tree behind the house brings luck and fortune
- ★ Ideas to decorate a unique Christmas tree
- ★ The oldest tree in the world 'old' 9550 years old
- ★ The mystery of the 'ghost tree' poisoning itself in exchange for nutrients