Discover the 'unbeatable' 2D material: Light as plastic and stiffer than steel
Polymers are versatile materials, of which plastic is perhaps the best known example. Under a microscope, polymers often look like squiggly threads, one-dimensional chains of units called monomers, but they can be assembled into three-dimensional shapes through manufacturing methods such as injection molding.
However, getting the polymers to bond together to form two-dimensional sheets is surprisingly difficult. Although some research teams have had some success, the resulting materials often have flaws, reducing their strength or other desirable properties.
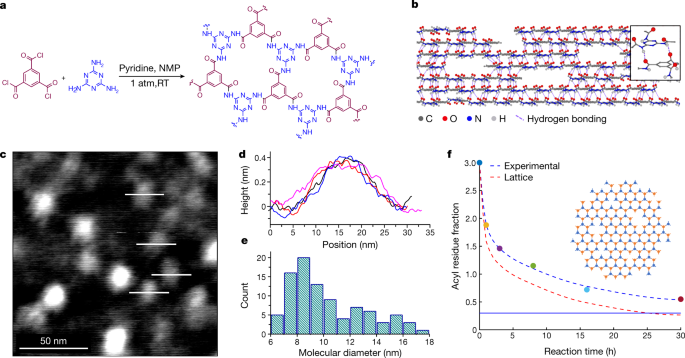
But for the new study, MIT scientists say they have developed a new manufacturing method that allows polymers to form 2D sheets while preserving their strength. The team started with melamine as the monomer, which has a structure of carbon and nitrogen rings. In a solution exposed to the right conditions, these molecules grow sideways into discs, then stack, with hydrogen bonds holding the layers together.
'Instead of creating a spaghetti-like molecule, we can create a plate-like molecular plane where we make the molecules connect themselves in two dimensions,' said Michael Strano, author main of the study said. 'This mechanism occurs naturally in solution, and after we synthesized the material, we were able to easily stretch it into thin films with outstanding strength'.
The team calls the material 2DPA-1 and it has some impressive properties. Although it is extremely thin and light, the polymer has twice the flexural strength of steel and requires six times more force to deform it than bulletproof glass. It is also completely impervious to gases and liquids.
With these capabilities, 2DPA-1 can create a lightweight, durable, watertight coating for vehicles, electronic devices like smartphones and the like, or even be used as a material build.
'We don't usually think of plastic as something that you can use to support a building, but with this material you can create new things,' says Strano. unusual and we're excited about that."
The team says that the manufacturing method is easily scalable and can be adapted to make other types of materials.