What is VXLAN? An Overview of Virtualization Technology

One of the most popular virtualization technologies today is VXLAN (Virtual eXtensible Local Area Network). This technology helps connect data centers or manage many different physical networks. If you want to use VXLAN in your DC, follow the following article of TipsMake to better understand this technology.
What is VXLAN?
VXLAN (Virtual eXtensible Local Area Network) is a network virtualization technology developed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). They were created to solve the scalability problems of VLAN (Virtual Local Area Networks).

What is VXLAN?
VXLAN creates an extensible Layer 2 overlay network that can span Layer 3 network infrastructures via a 24-bit segment identifier. This is the VXLAN Network Identifier (VNI) which allows for up to sixteen million different network segments.
How does VXLAN work?
The VXLAN protocol encapsulates Layer 2 Ethernet frames in Layer 4 UDP packets, allowing the creation of virtualized Layer 2 subnets on a Layer 3 network. Each subnet is assigned a unique VXLAN Network Identifier (VNI).
The process of encapsulating and decapsulating packets is managed by the VXLAN Tunnel Endpoint (VTEP). The VTEP can be a standalone network device such as a router or switch, or a virtual switch on a host. The VTEP encapsulates Ethernet frames into VXLAN packets and transmits them over the IP network to the destination VTEP, where the packets are unwrapped and sent to the destination host.
For devices such as bare-metal servers that cannot function as VTEPs on their own, some hardware devices such as Juniper switches and routers support this process. VTEPs can also be deployed on hypervisors such as KVM to support virtualized environments, which is called software VTEPs.
What are the outstanding advantages of using VXLAN?
-
Improved scalability because VxLAN uses 24bit for VxLAN ID, there will be more than 16 million VxLAN ID.
-
High security due to network segmentation, especially for tenants.
-
Transport L2 data over L3 infrastructure without compatibility issues, thanks to the use of encapsulation.
-
Reduce packet transmission delay, can transmit packets on multiple paths without using STP, and also allows enabling ECMP.
-
Support building flexible virtualized network infrastructure with SDN (Software Defined Network) integration capabilities.
-
Separating the virtual network from the physical network makes network deployment, monitoring, and management more convenient.
Some limitations of VXLAN
-
Encapsulating Layer 2 in UDP packets adds overhead.
-
High complexity, especially when dealing with multiple segments and VTEPs.
-
Increasing MAC Address and VXLAN traffic can impact the performance of network devices and physical switches.
How is VXLAN different from VLAN?
How to deploy VXLAN
Deploying VXLAN involves configuring VTEP on network devices. VXLAN needs to be configured on the downlink interface for access services and the uplink interface for establishing VXLAN tunnels. Once deployed, packets can be forwarded to the network.
The VXLAN deployment process consists of three main steps: packet identification, VXLAN tunnel establishment, and packet forwarding. Before you begin, you need to ensure that the physical network is properly configured to support VXLAN:
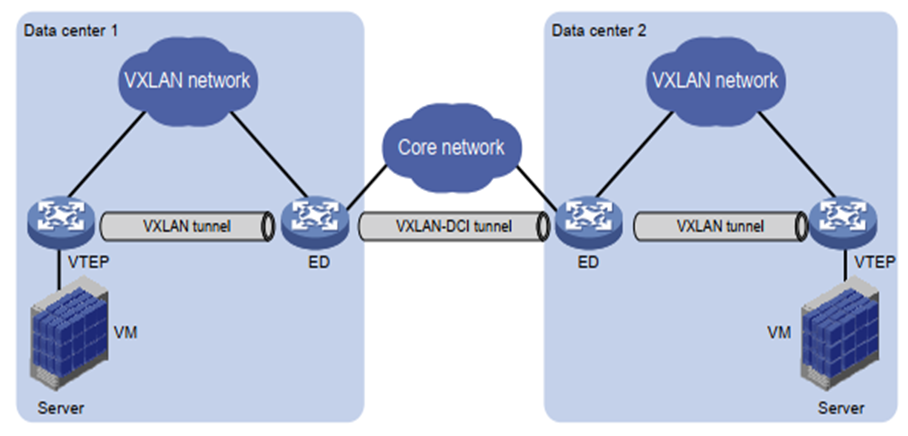
How to deploy VXLAN
-
Enable VXLAN on interfaces
-
Assign VNI and specify UDP port
-
VTEP IT address configuration
-
Remote IP addresses and enables VXLAN on the overlay interface.
Configuration needs to be adjusted to specific network hardware. Deployers can verify via commands such as `show vxlan tunnel` and `show vxlan peer`.
There are three methods to deploy VXLAN:
Host-based VXLAN
With this approach, VXLAN deployment is done directly on each server instead of on physical devices such as switches. One point to note is that the server operating system must support VXLAN and the related kernel modules or drivers.
Encapsulation and decapsulation are performed through a virtual switch that acts as a VTEP. Host-based VXLAN provides greater flexibility and control at the host level.
Port-based VXLAN
Port-based VXLAN deployments are performed directly on network gateway devices such as routers and Layer 3 switches. Encapsulation and decapsulation in port-based VXLAN are performed through switches or routers that act as VTEPs.
These devices are called VXLAN gateways. This method is commonly used to connect VXLAN-based virtual networks to non-VXLAN networks. VXLAN-based gateways provide flexibility and interoperability in routing.
Hybrid VXLAN
Hybrid VXLAN is a combination of port-based VXLAN and host-based VXLAN in the same network environment. Hybrid deployments are implemented with some VTEPs on hardware and some on virtual switches. The hybrid approach combines the advantages of both VXLAN deployments to provide flexibility, efficiency, and scalability.
Conclude
VXLAN is a powerful virtualization technology that extends the capabilities of virtual networks in the information technology era. Through this article, TipsMake hopes to help you understand what VXLAN is and how to effectively apply it in your network system.