What is 'social jet lag' syndrome? The harm of this syndrome to human health like?
In a perfect world, it is indispensable for a routine that can easily be found in biology textbooks such as: After a long day of studying and working, we will go to bed at 22:00 and get up after about 8 hours, do gentle exercise, take a shower and have breakfast, then go to school, the workplace with a refreshing spirit and body full of life.
This is definitely a great schedule that perhaps any one of us would long for. However, modern life, hustle with billions of other 'unnamed' jobs makes us even know that eating and sleeping in moderation is good for health but still can not obey.
- 'Keeping an eye' on the screen before bed does not harm the mental health of teenagers!
 Many people tend to sleep and wake up later on holidays without knowing it's social jet lag
Many people tend to sleep and wake up later on holidays without knowing it's social jet lag
Weekends or public holidays are different, we have enough time to follow the schedule above, but most choose to live even more 'negatively' than weekdays. We go to bed later, spend the next morning to 'make up for sleep' and think this is a reward 'worth' after working days like a machine. For example, we often allow ourselves to sleep later on Friday nights, wake up later on Saturday mornings because we don't need to go to work and feel it makes sense to do so, still sleeping 6 or 8 language. In reality, however, you accidentally touched a syndrome called 'social jet lag'.
Social jet lag can basically be interpreted as a time zone deviation due to social impact. In other words, this is the phenomenon that occurs when there is a difference between the body's biological clock and the daily circadian rhythm due to the irregularities that occur in daily life. Thus, the change of sleep schedule on weekends as mentioned above is considered as a typical example of Social jet lag syndrome.
- Surprise with the pain medication can cause obesity, poor sleep
 Social jet lag can be interpreted as a time zone deviation due to social impact
Social jet lag can be interpreted as a time zone deviation due to social impact
Till Roenneberg, a veteran biological time researcher from the Institute of Medical Psychology at Ludwig-Maximilian University in Munich, Germany, coined the term Social jet lag in 2006 to describe the effect that changes drastic changes in sleep patterns can appear on the human body. Till Roenneberg noticed that many adults tend to sleep a lot on weekends to make up for lack of sleep on weekdays, or to accommodate late-night parties with friends the night before. .
As we all know, the body's daily circadian rhythms have a cycle of about 24 hours, the time when the body's most productive or resting functions are determined by the biological clock. This 'watch' will be shaped according to the daily routine of every person and any circumstances that go against it will have a negative impact on health. For example, if you stay up late and wake up late every weekend, at that time, you won't feel many negative changes to your body, but just the next day, you will see many symptoms. more discomfort such as lack of alertness, drowsiness, or body aches These symptoms may even last for days to come.
- Predictable death through blood test, accuracy up to 83%
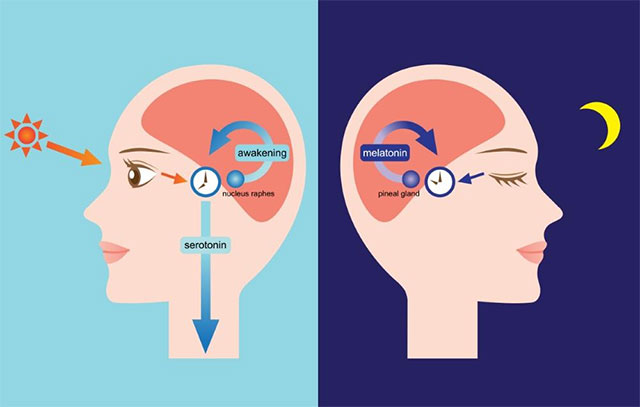 Human circadian rhythms have cycles of about 24 hours
Human circadian rhythms have cycles of about 24 hours
However, these are just 'external' symptoms that we can easily recognize, in fact, social jet lag also contains many other complicated changes hidden deep inside the body when we detect them. So things have become especially serious.
Healthy, mature people often think that they can compensate for their sleep by going back to the circadian clock. However, Till Roenneberg's research found that abnormal changes during sleep actually only disturbed other circadian rhythms of the body, such as the ability to regulate body temperature and repair. cell repair, regeneration, aging and metabolism.
A study conducted by Duke University Medical Center analyzed the sleep patterns of nearly 2,000 volunteers between the ages of 54 and 93 to determine whether social jet lag syndrome really affects too. Negative to their health or not. The researchers found that people who regularly slept on time on weekends were more likely to have higher blood sugar levels. In addition, body mass index and blood pressure are also significantly affected, leading to the possibility of stroke or heart attack for the elderly, a history of hypertension and cardiovascular diseases. .
- Google AI can diagnose a patient's cardiovascular condition by scanning an image of the retina
 Social jet lag is closely related to cardiovascular disease
Social jet lag is closely related to cardiovascular disease
However, the authors of the research project also note that their findings do not show a cause-effect relationship. "We cannot conclude that irregular sleep leads to health risks, or whether health conditions affect sleep quality. Perhaps all of this has an interaction. "Dr. Jessica Lunsford-Avery, assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral science from Duke University Medical Center, said.
'We suspect there is a factor linked to obesity that interrupts sleep regularly. Or, as some studies show, perhaps poor quality sleep can also interfere with the body's metabolism, which can lead to weight gain, and it's a vicious circle. ', Dr. Jessica Lunsford-Avery adds.
The findings further reinforce the findings of previous studies that abnormal sleep patterns may be linked to obesity and other health problems.
- Not dieting, this is the new method of preventing obesity
 Teenagers who experience frequent social jet lag are at greater risk of being overweight
Teenagers who experience frequent social jet lag are at greater risk of being overweight
Another study, conducted this year and published in the journal JAMA Pediatrics, also found that teenagers encountered social jet lag with a big difference between their weekly and weekend sleep schedules. risk of being overweight. In particular, this phenomenon occurs more strongly for women, but scientists have not been able to explain the reason.
In another new study published in the journal Current Biology, researchers found that the level of social jet lag is directly related to an increase in body mass index (BMI). ) - an important marker in the diagnosis of obesity.
Additional studies have found a similar link between changes in sleep patterns and chronic health conditions. A study published in the JAMA Neurology found that older adults with a more volatile schedule, especially at the time of their sleep, were also at an increased risk of beta-amyloid protein accumulation, which is a precursor. of Alzheimer's disease. In addition, another study by the American Institute of Sleep Medicine found that a person's average chance of developing cardiovascular disease increased by 11% after each social jet lag.
- Highly educated people are less likely to develop Alzheimer's disease
 Social jet lag increases beta-amyloid protein accumulation leading to Alzheimer's disease
Social jet lag increases beta-amyloid protein accumulation leading to Alzheimer's disease
The link between circadian rhythms and cancer has led the World Health Organization to declare night shift (a form of social jet lag) is the cause of cancer in humans. Thus, it can be concluded that the long-term social jet lag is an excellent 'catalyst' for cancer, besides other basic factors such as cell catabolism, genetic modification, and quality. food and habitat.
In short, social jet lag syndrome has a negative impact on the human body. It is closely related to cardiovascular disease, obesity, hypertension, Alzheimer's, and especially cancer. So what can you do to minimize the health risks associated with social jet lag?
- Sensory compensation mechanism and the magic of the brain
A balanced and healthy life can only be achieved when sleep is respected. School administrators, employers and ourselves, as individuals living in a civilized and modern world, should know how to balance life activities with sleep , instead of 'clicking on your tongue' for work, but the fun invades sleep, then 'sleeps off' in your free time and thinks this is harmless.
But to say it again, most of us do not want to change jobs, neglect learning or lose social relationships. Therefore, the best thing we can do is to keep our sleep schedule as consistent as possible, minimizing any disturbance between sleep during the week and at weekends. This is completely within the control of most of us.
- 5 habits young people need to remove immediately so that "goldfish brain" does not cause serious harm to health
 Follow a regular sleep schedule for optimal health
Follow a regular sleep schedule for optimal health
According to the recommendations of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine, an adult should sleep between 7 and 8 hours a night, and observing a regular sleep schedule will be a prerequisite for optimal health.
- It may seem simple but this habit is silently killing your brain day by day
You should read it
- ★ Kill yourself because of the habit of sleeping late
- ★ Plan to remove sugar from your daily meals in just 3 weeks
- ★ How to prevent and control high blood pressure?
- ★ Hypertension in pregnancy can affect long-term cardiovascular health
- ★ Soaking rice overnight can reduce the risk of heart disease and cancer