People and AI are racing arms, this is why the CAPTCHA is getting harder and harder
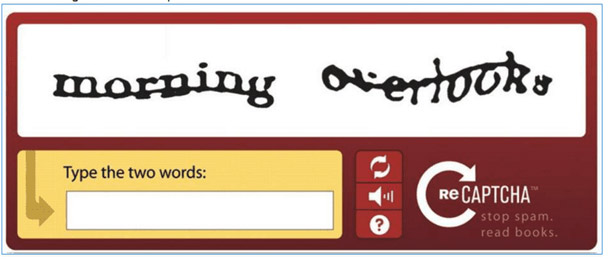
Years ago, to prove that you are not a robot, users only need a simple tick in the box. But today, you have to choose the right image of the car, the sign, the road mark, the store . to make it clear that you are a person.
But the difficulty of these tests has not stopped, the images you need to recognize are more difficult to see when the signs start to hide behind the trees, the morning dew hides the house far away, the store displays some foreign language is not English.
These tests are often called "CAPTCHA", abbreviated for Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart - Fully automated public Turing Tests to Decide Computers and People . In the past, this "increasingly difficult" plight has also appeared.

In the early 2000s, automated spam systems - spambots got stuck even with a simple text. But when Google partnered with researchers from Carnegie Mellon in 2010 and bought a reading program to digitize Google Books service, to prevent spambots, word-related tests must be more distorted and harder to read. . People must also evolve to adapt to the intelligence of computers.
CAPTCHA is a great AI teaching tool, as many test questions as you want, each is a temporary solution. The race between people and machines will end, sadly, people are not winners. In 2014, in a CAPTCHA reading competition between Google and Google's machine learning algorithms, people were only 33% correct, 99.8% of computers were correct.
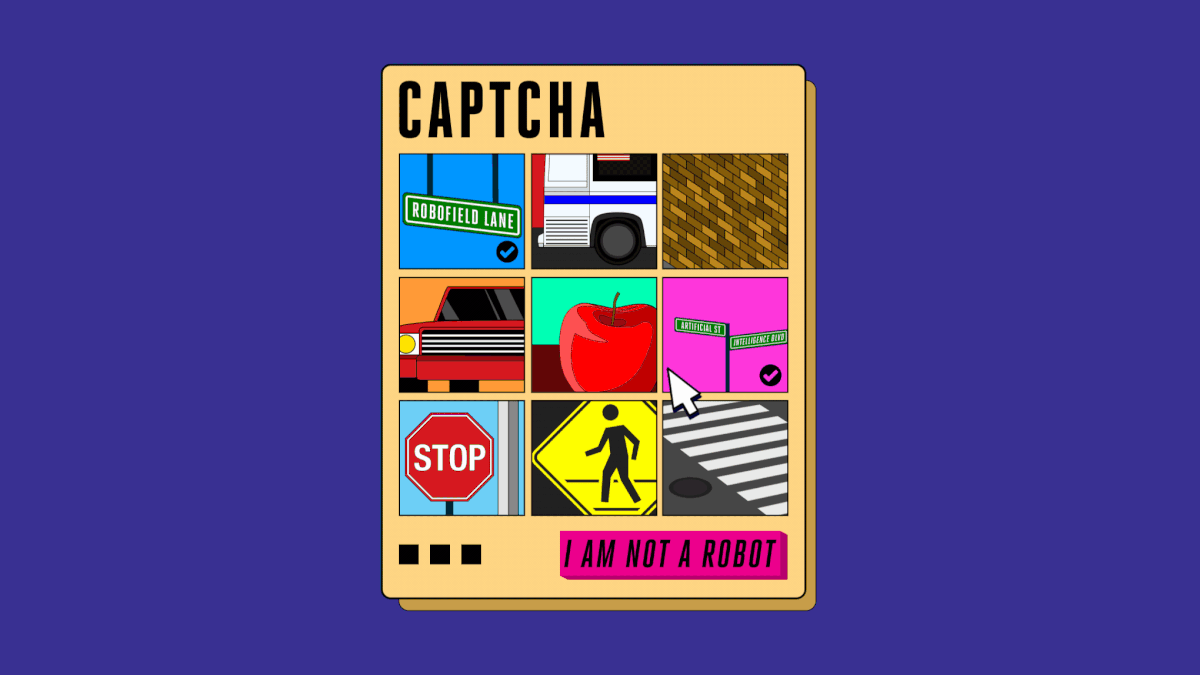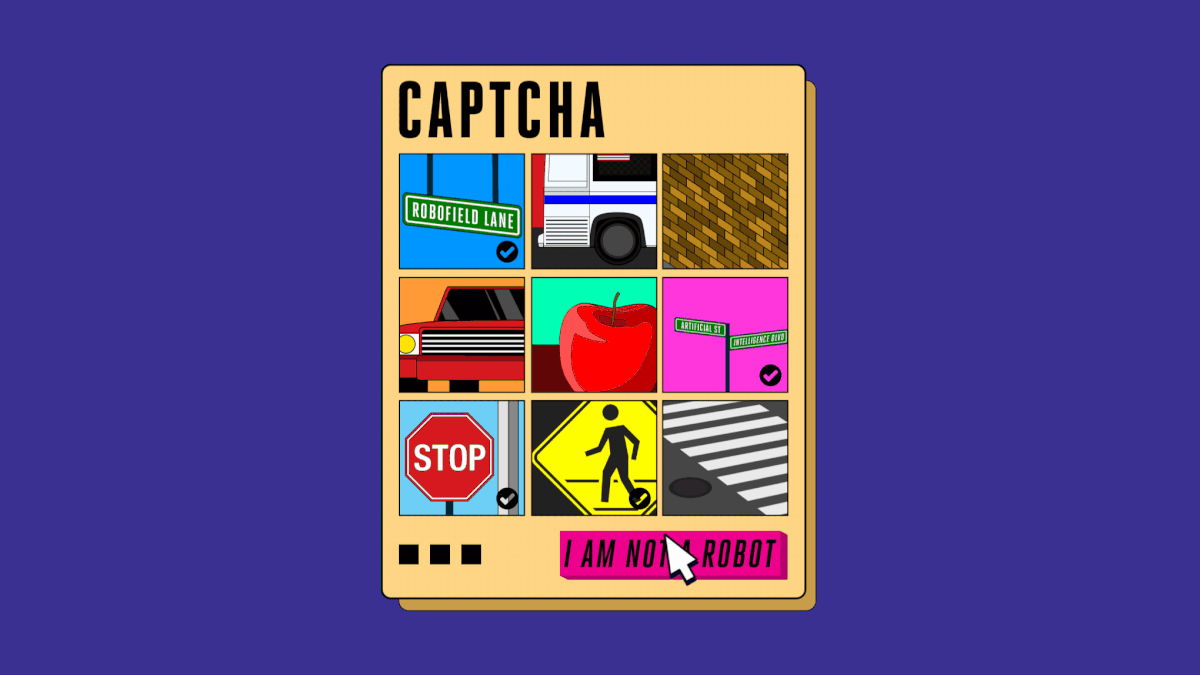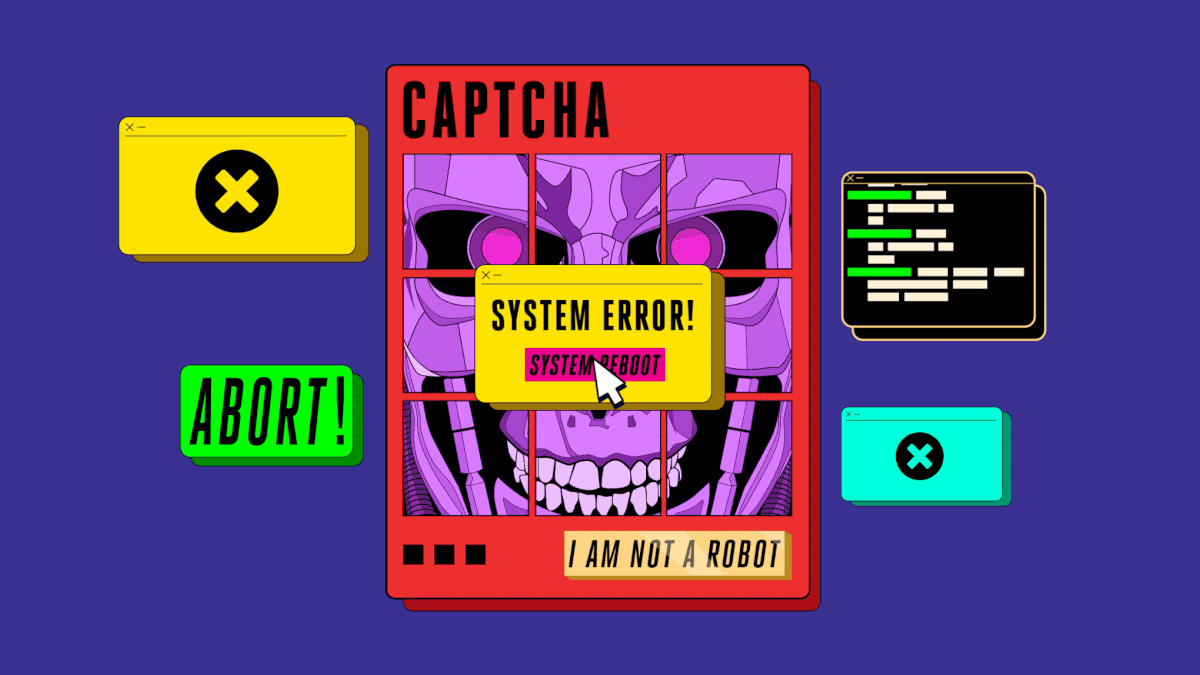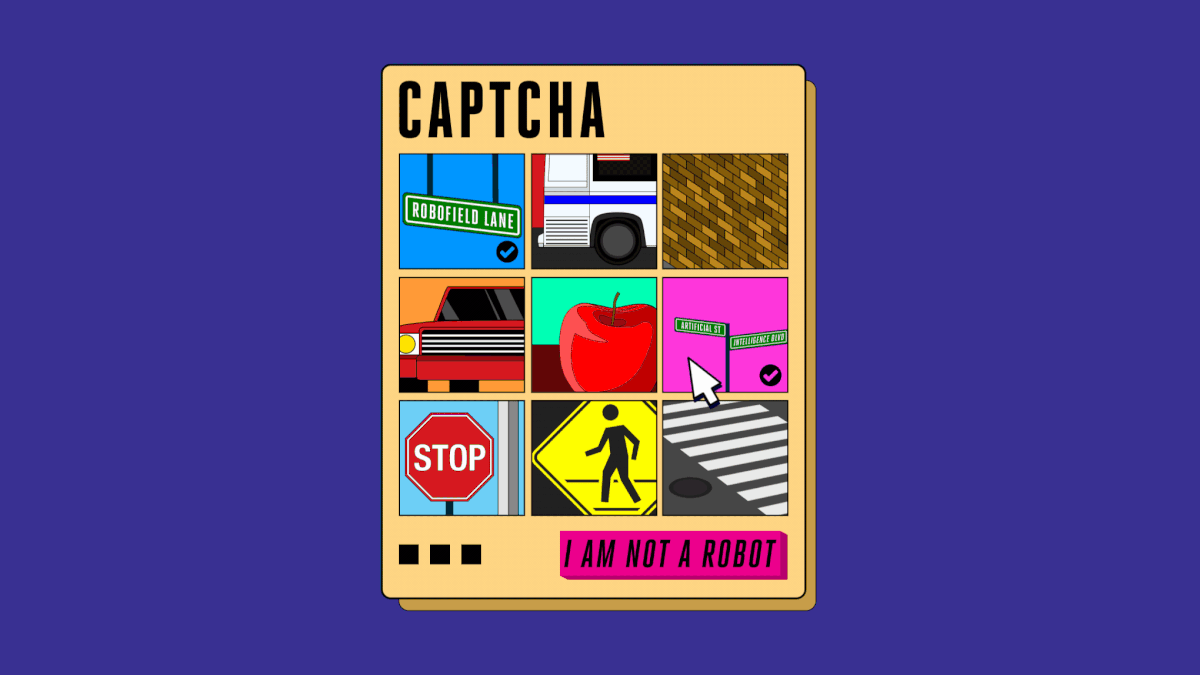
Seeing the problem, Google switched to using NoCaptcha ReCaptcha, reading data and observing user behavior. And to be able to prove that you're not a robot, just click on the box. But soon, automated systems also learned how to overcome these Google tests. Surely when you need to prove yourself as a person, you have seen the shop image appear. This is the last step in the race to see who will rise to dominate the CAPTCHA reading aspect, machine or person.
The one responsible for the CAPTCHA is getting tougher is Jason Polakis, professor of computer science at the University of Illinois. It was he who created the image recognition system available on the Internet in 2016 to decode the Google CAPTCHA test. His system achieves 70% accuracy. Some other researchers have achieved similar results when using Google's audio recognition software to overcome the Google sound CAPTCHA test.
According to Polakis, machine learning is good at human level, even more in terms of basic text reading, simple images and voice recognition.
In order to find out what people are good at, but difficult enough for machines, the researchers even thought about using facial recognition, gender or ethnicity. But this is a sensitive issue and may arise many problems later.

A number of other ideas have also been proposed as a cultural test using local lullabies to make CAPTCHA. This test not only targets bots, but also helps prevent people from filling out CAPTCHA manually to make money because they cannot know what a different culture child is singing.
Variated images are also used to make CAPTCHA. For example, stone carvings on ancient cave walls, which define the cartoon image of a pig wearing glasses, have no imagination, they are very 'ignorant' in this.
Many people also suggest new ideas such as integrating games into CAPTCHA. Users will have to choose the correct value or assemble the picture without instructions .
However, the bot can still pass such tests. The problem is not that bots are so smart, but because humans cannot find a test that can satisfy several billion variables. People here are only all human beings, each individual has a different experience.
Finally, although the computer's ability to process and recognize images is getting better, the CAPTCHA still has to come back to the old image processing test.
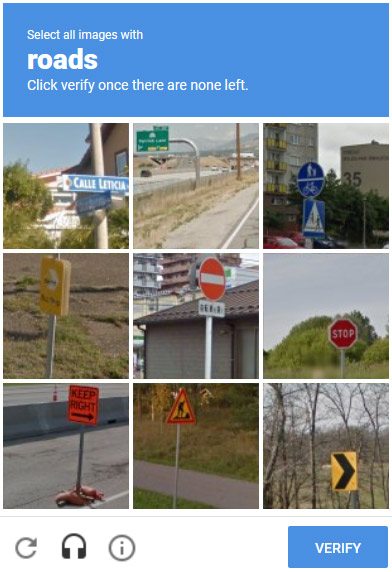
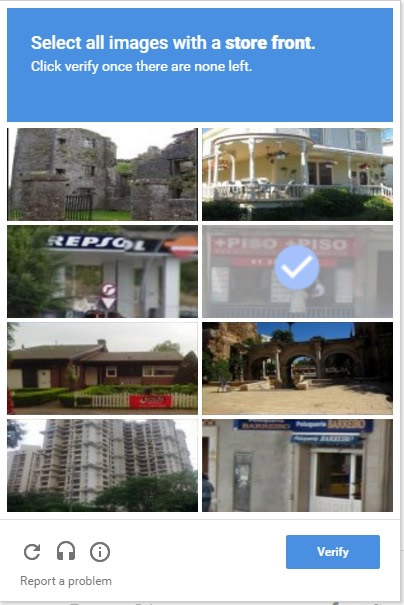
Answering the CAPTCHA tests has led many people to ask questions: what kind of nature can people identify, can they see how much they never learn? What will the machine feel when it exists in the form of "a person"?
In this case, human nature is determined through "evolution" along the length of development of the Internet.
Security researcher Ghosemajumder thinks that any CAPTCHA will eventually be disarmed by machines. He said, people cannot move the mouse to perform multiple operations at the same time, while a bot can interact with the site without touching the mouse, or using the mouse in an extremely accurate way. Therefore, people always have "chaos" very difficult to fake. This is what he calls "continuous authentication", observing every action of an Internet user to identify a sequence of automated actions.
Sharing the same thoughts with Ghosemajumder, Google's CAPTCHA team released the latest version of reCaptcha v3 at the end of last year, identifying a suspicious activity using the "arbitrary adaptive risk analysis mechanism. ".
In the chaos of web cookies, huge traffic from multiple sources, the unique characteristics of each browser . security researchers will have to determine which actions are normal to deduce actions. considered abnormal. However, when using this method, you will be suspected of being a bot if you use address hiding tools such as VPN or anti-tracking software.
In summary, CAPTCHA may need to evolve in the future, based on the mistakes users often make when browsing the web instead of picking the right image or text like this.
You should read it
- ★ unCAPTCHA breaks 450 reCAPTCHA in less than 6 seconds
- ★ Secrets behind the free program reCAPTCHA: Turn Internet users into 'free workers' to electronically 17,600 books a year
- ★ Google launched new reCAPTCHA v3
- ★ How to remove reCaptcha is quick and simple
- ★ Why can't the bot check the 'I'm not a robot' checkbox?