How to prevent HIV AIDS
What is HIV/AIDS?
 Human immunodeficiency virus - HIV
Human immunodeficiency virus - HIV
Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome - AIDS is a chronic, potentially life-threatening illness caused by the Human Immunodeficiency Virus - HIV. By damaging your immune system, HIV interferes with your body's ability to fight disease-causing organisms. HIV is a sexually transmitted disease.
AIDS stands for Acquired ImmunoDeficiency Syndrome . AIDS is the final stage of HIV infection - the Human Immunodeficiency Virus . During this stage, the body's immune system is weakened, so the patient is susceptible to diseases such as infections, cancer .
4 stages of HIV/AIDS infection
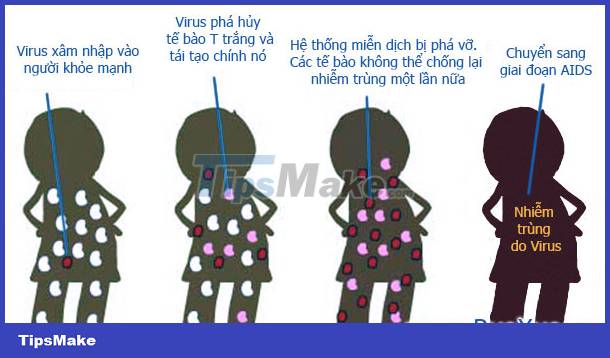 Stages of HIV AIDS
Stages of HIV AIDS
- Primary infection stage - Also known as the window period: the period lasts from 2 to 6 months, the body is completely normal. HIV test results are negative, so at this stage it is easy to infect others if you have unprotected sex.
- Asymptomatic HIV infection stage: From 5 to 7 years, the body is still healthy and normal. The test was positive.
- Near AIDS stage: Still no specific symptoms, test results are positive.
- AIDS Stage - Have the following symptoms:
- Loss of weight, loss of more than 10% of body weight.
- Fever, diarrhea, cough lasting more than 1 month.
- Occurrence of many diseases such as cancer, pneumonia, tuberculosis, dermatitis, body sores.
- Patients quickly die depending on care and treatment conditions.
3 routes of HIV/AIDS transmission
Sexual transmission of HIV/AIDS
The HIV virus is found in abundance in the genital fluid of an infected person. As a result, the HIV virus can enter the partner's bloodstream through the genitals. Sexual activity, whether it's intercourse or just contact with the genitals, is contagious.
Blood transmission of HIV/AIDS
HIV is found in abundance in the blood of infected people. Therefore, sharing needles, unsterilized medical equipment with an HIV-infected person, or transmitting the blood of an HIV-infected person can all cause HIV infection.
As for drugs, it does not cause HIV by itself, but drug addicts easily get HIV infection when sharing needles with addicts or needles at drug sales.
Mother-to-child transmission of HIV/AIDS
The percentage of children born with HIV to mothers infected with HIV is 25-30%. HIV can be passed from mother to baby through the placenta while the baby is in the womb, through the mother's blood and fluids at birth, or through breast milk while the baby is breastfeeding. Newborns infected with HIV usually do not live more than 3 years.
How to prevent HIV/AIDS
Based on the route of HIV transmission, there are the following preventive measures:
Prevention of HIV/AIDS sexually transmitted
- Live a healthy, faithful, monogamous life and both of you are HIV-free. Do not have promiscuous sex.
- In the case of sexual intercourse with an HIV positive person, it is important to practice safe sex to protect yourself by using a condom correctly.
- Early detection and prompt treatment of STIs also help to reduce the risk of HIV/AIDS transmission because the damage caused by STIs would be the ideal entry point for HIV.
Prevention of HIV/AIDS transmission through blood
- Do not inject drugs.
- Transfuse blood and blood products only when absolutely necessary, and only accept HIV tested blood and blood products.
- Use only sterile needles and syringes. Do not share syringes. Use sterilized instruments for surgery, tattooing, piercing, acupuncture.
- Avoid direct contact with the body fluids of an HIV-infected person
- Use separate personal items: razors, toothbrushes, nail clippers, .
Prevention of HIV/AIDS transmission from mother to child
- A woman infected with HIV should not become pregnant because the rate of HIV transmission to her baby is 30%, if she is already pregnant, she should not give birth.
- If you want to have a baby, you need to go to a health facility for advice on how to prevent HIV transmission to your baby.
- After birth, the baby should be given formula milk to replace breast milk.
T-cells - Most people know, the immune system - Immune System is an important defense barrier to help prevent bad agents from attacking the body with the main transport mechanism being the lymphatic system. Lymphocytes are divided into two types, T-cells and B-cells. Both types of cells are produced directly in the spinal cord and have a close relationship with each other. B-cells are responsible for producing antibodies to fight harmful invaders, including cancer cells. And T-cells are involved in various immune functions of the immune system. In particular, T-cells help secrete biologically active substances called Lymphokines, which help B-cells and T-cells to work better. Suppressor T-cells keep the immune system from overreacting and attacking other healthy parts of the body. Besides,
You should read it
- ★ Top 4 hearing aids for the best-selling hearing impaired today
- ★ 9 medicines and foods absolutely should not be used together
- ★ Symantec introduced a data protection solution
- ★ 6 basic mistakes when taking medicine make the disease forever
- ★ Disinfect COVID-19 epidemic respirator mask with a microwave