How does Thunderbolt actually work?
However, everything you need to know about Thunderbolt ports is easier to understand when broken down into simple, concise sections.
What is a Thunderbolt port?
Thunderbolt is a high-speed communications interface developed by Intel. First introduced in 2011, Thunderbolt technology combines multiple functions into a single port: it can transfer data, transmit video and audio signals, and even power devices. This makes it popular for connecting external displays, high-speed storage drives, and docking stations.
One of the standout features of Thunderbolt is the use of the USB-C connector from version 3 onwards. This means the same port can handle everything from high-definition video to fast file transfers, while also supporting daisy-chaining multiple devices, perfect for KVM switches and docking stations.
Are Thunderbolt and USB-C the same?
When looking for USB, there are two things to consider: Interface and protocol. Interface refers to the physical shape of the USB port and connectors, while protocol describes the features and capabilities of the USB connection.

While the latest versions of Thunderbolt use the same USB-C connector, they are not the same as USB-C. USB-C refers to the interface or physical shape of the port and cable, while Thunderbolt is the protocol that uses the interface to provide more advanced features.
In addition to Thunderbolt, other protocols can be used with USB-C, such as DisplayPort (DP), which provides connectivity to support 16K video; Power Delivery (PD), which allows for up to 240W of power, and standard USB protocols, such as USB 3 and USB 4.
The great thing about the Thunderbolt USB-C port is that it essentially combines the features of DisplayPort, Power Delivery, and the latest USB standard, plus features that are unique to Thunderbolt. This simplifies things, as a single Thunderbolt logo on a device already indicates support for some level of DP, PD, and high-bandwidth data transfer. Thunderbolt ports are essentially USB-C ports with the latest features. They offer faster data transfer speeds, better video performance, and additional features like serial, which USB-C can't do on its own.
The Difference Between Thunderbolt 3, 4, and 5
Now that you know that USB-C is a version of the USB interface, what about Thunderbolt? Are there different versions of this protocol?
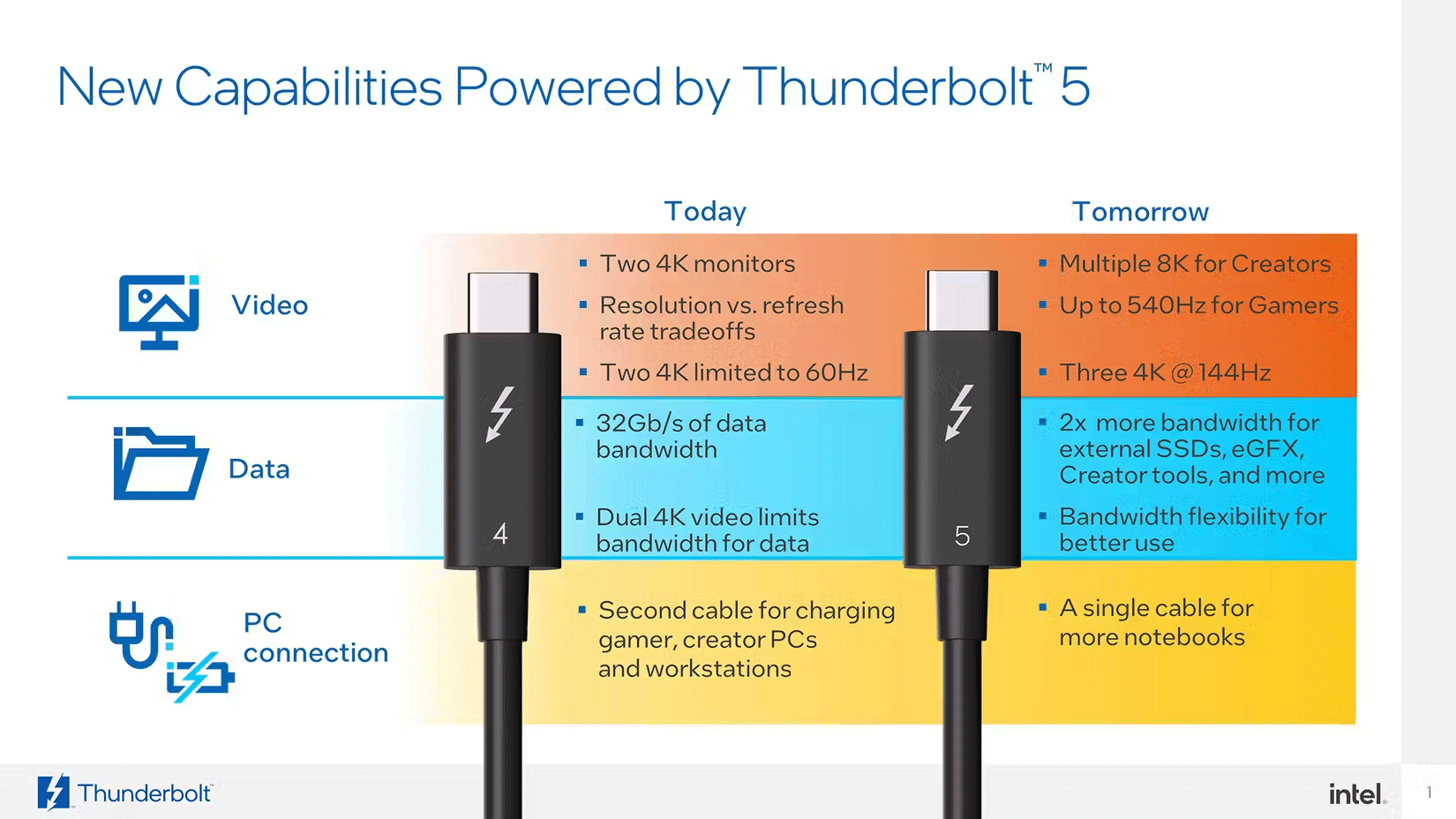
At the time of writing, most Thunderbolt devices use either the Thunderbolt 3 or 4 protocol. Thunderbolt 5 is also on the way, and is expected to be widely available by mid-2025. Thunderbolt 5 was released in 2023, but the first Thunderbolt 5s were available in mid-2024. You can identify which version of Thunderbolt a device or connector supports by the number indicated near the Thunderbolt logo. However, some devices may not indicate a version number. You'll have to look at the supplied spec sheet or search online.
Each new version of Thunderbolt improves speed, video capabilities, and security. Let's break down the key differences between Thunderbolt 3, 4, and the upcoming Thunderbolt 5.
| Features | Thunderbolt 3 (2015) | Thunderbolt 4 (2020) | Thunderbolt 5 (2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum speed | 40 Gbps | 40 Gbps | 80 Gbps (bi-directional), up to 120 Gbps in special cases (unidirectional) |
| Video support | Dual 4K or single 5K display | Dual 4K or single 8K display | Supports higher resolution displays, up to 3 4K displays or 2 8K displays |
| PCIe data transfer | 16 Gbps | 32 Gbps | 64 Gbps |
| Power Delivery | Up to 100W | Up to 100W | Up to 240W |
| Daisy-Chaining (Peer-to-Peer Connection) | Yes, up to 6 devices | Yes, up to 6 devices | Yes, up to 6 devices for better performance |
| Security | Basic | Add DMA protection | PCIe tunneling |
While Thunderbolt 4 didn't offer a speed boost over Thunderbolt 3, it did improve security, reliability, and video capabilities. However, Thunderbolt 5 promises a huge jump in performance, especially in bandwidth for video and graphics-intensive tasks.