Distinguish & compare Intel CPUs
Manufacturers always launch many products in many different segments to meet the needs of customers. But for a beginner to learn, understanding all the segments to choose the right product for you is not easy. Today, Thuthuatphanmem.vn will help you distinguish and understand all about Intel CPUs.

I. Intel Celeron
Intel Celeron is the lowest segment of the Intel CPU family. It is greatly cut to save costs. Intel Celeron CPU is Intel's basic processor for very simple computing tasks, such as Email, Internet and document creation.

Celeron CPU series has so far only 2 cores / 2 threads, the best Celeron CPU currently is G4920 with a clock speed of up to 3.20GHz, Cache capacity still stops at 2MB. Despite being a low-cost segment, Celeron is still equipped with Intel Graphics
In some light tasks, Pentium and Celeron have not made much difference. But when running in strong applications requiring strong CPU such as gaming, graphics, video, Celeron will be much weaker than his brother Pentium. But in return Celeron has a very power-saving advantage.
II. Intel Pentium
A bit more powerful than Celeron is the Pentium, but Pentium still has the task of hitting users with a small budget but wants high performance. To reduce the cost of Pentium CPUs, omit modern technologies such as Turbo Boost or Hyper-threading, but in return, Intel Pentium is compatible with many motherboards from many different manufacturers.

Regular Pentium CPUs have 2 cores / 2 threads (for high-end Pentium codes are 2 cores / 4 threads) (typical Intel Pentium G4560 CPUs, which have almost the same power as I3 6100). With clock rates from 1.1 GHz and up to 3.8 Ghz (Pentium G5500). Pentium Cache capacity from 2MB and up to 4MB with high-class codes like G5500. 8th generation Intel has been improved a lot when Pentium has the same power as 1 7th Generation Intel Core CPU. It is a very bargain gift for users.
III. Intel Core
Intel Core is the "golden chicken" of Intel because Intel Core production is the largest in the Intel family. In the Core line, Intel continues to divide into products to meet user needs are Core i3, Core i5, Core i7.

- Intel Core I3 : 8th Generation Core I3 is a big revolution of Intel, formerly Core I3 only 2 cores / 4 threads and clocked slightly better than Pentium. When the 8th generation Core I3 was released, it had 4 cores / 4 threads, that power was equal to the old Core I5. But Core I3 still cuts down on Hyper Threading multithreading technologies, but there's no Turbo Boost to automatically overclock the processor when running heavy tasks.
- Intel Core I5 : Core I5 is an intermediate product. Up to the 8th generation, the Core I5 has 6 cores / 6 threads (from the 7th generation and below only has 4 cores / 4 threads). Accompanied by advanced technologies such as Turbo Boost, Hyper Threading. In addition, Core I5 series also has some code that allows OC (overclocking) to bring the CPU clock to higher level for better performance. For example: I5-8600K. i5-9600K .
- Intel Core I7 : It is the improved version of Core I5 and brings in all the modern technology. 8th Gen Core I7 CPU has 6 cores / 12 threads, clocked up to 4.60 GHz (Turbo Boost). 8th Generation Cache capacity has reached 12MB.
- Intel Core I9 : This is a newly launched product line and it is also the last generation of Intel Core current. Core I9 launches to meet the heavy work such as gaming, graphics processing, video editing, streaming, . of users. The current Core I9 CPU series is I9-9900K with 8 cores / 16 threads, Cache capacity of 16MB, clocked at Turbo Boost to 5.00GHz. Looking through such parameters certainly Core I9 will not disappoint users.

IV. Intel Xeon
Intel Xeon is the CPU for workstations (still used for personal computers). Intel Xeon meets the needs of users who require CPU to work continuously and persistently. Xeon CPUs work more stably than Intel Core i, thanks to ECC RAM technology, which automatically recovers errors during data transfer between CPU and RAM, so it does not get a blue screen error when rendering or is use.
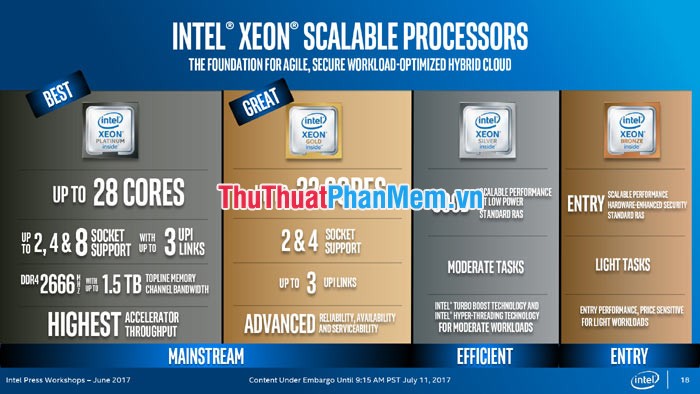
Intel Xeon CPUs have an extremely large thread count, such as Xeon Platinum 8176 with 28 cores / 56 threads, cache capacity of 38.5Mb. Intel Xeon CPUs outperform the Core series, but in return the Xeon clock is lower because of its stability. CPU Xeon can also combine 2 CPUs on the motherboard to maximize its power. The motherboard supports Dual Socket, the user can install 2 Xeon CPUs, thus a compact computer but bringing in a lot of power. In return, the cost of the most expensive Xeon CPU in the Intel family.