Contructor and Destructor in C ++
Class Contructor in C ++
A contructor class is a special member function of a class that is executed whenever we create new objects of that class.
A constructor will have the same name as the class and it does not have any return type, including void type.Constructors can be very useful for setting initialization values for specific member variables.
The following example explains the concept of constructor in C ++:
#include using namespace std ; class Line { public : void setChieuDai ( double dai ); double layChieuDai ( void ); Line (); // Day la constructor private : double chieudai ; }; // phan dinh nghia cac ham thanh vien, bao gom ca constructor Line :: Line ( void ) { cout << "Doi tuong da duoc tao!" << endl ; } void Line :: setChieuDai ( double dai ) { chieudai = dai ; } double Line :: layChieuDai ( void ) { return chieudai ; } // Ham main cua chuong trinh int main ( ) { Line line ; // thiet lap chieu dai cua line line . setChieuDai ( 6.0 ); cout << "Chieu dai cua duong la: " << line . layChieuDai () << endl ; return 0 ; } Compiling and running the above C ++ program will produce the following results:
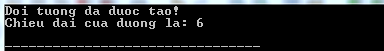
The constructor is parameterized in C ++
A default constructor in C ++ does not have any parameters, but if you need it, a constructor can have parameters. This helps you assign the initial value to an object at the time of creating it, as in the following example:
#include using namespace std ; class Line { public : void setChieuDai ( double dai ); double layChieuDai ( void ); Line ( double dai ); // Day la phan khai bao constructor private : double chieudai ; }; // phan dinh nghia cac ham thanh vien, bao gom constructor Line :: Line ( double dai ) { cout << "Doi tuong dang duoc tao, chieudai = " << dai << endl ; chieudai = dai ; } void Line :: setChieuDai ( double dai ) { chieudai = dai ; } double Line :: layChieuDai ( void ) { return chieudai ; } // ham main cua chuong trinh int main ( ) { Line line ( 10.0 ); // lay chieu dai da duoc khoi tao ban dau. cout << "Chieu dai cua line la: " << line . layChieuDai () << endl ; // thiet lap chieu dai mot lan nua line . setChieuDai ( 6.0 ); cout << "Chieu dai cua line la: " << line . layChieuDai () << endl ; return 0 ; } Compiling and running the above C ++ program will produce the following results:

Use the initialization list for initialization fields
In case the constructor is parameterized, you can use the following syntax to initialize fields.
Line :: Line ( double dai ): chieudai ( dai ) { cout << "Doi tuong dang duoc tao, chieudai = " << dai << endl ; } The above syntax is equivalent to the following syntax:
Line :: Line ( double dai ) { cout << "Doi tuong dang duoc tao, chieudai = " << dai << endl ; chieudai = dai ; } If with a class in C, you have multiple X, Y, Z, . fields to be initialized, then you can use the same syntax and distinguish the fields by commas, as follows:
C :: C ( double a , double b , double c ): X ( a ), Y ( b ), Z ( c ) { . } Destructor class in C ++
A destructor is a special member function of a class that is executed whenever an object of that class is out of scope or whenever the delete expression is applied to a pointer to the object of the class. there.
A destructor will have the same name as the class and be preceded by the ~ symbol and it can: not return a value and not receive any parameters. Destructor can be very useful to free resources before exiting the program, for example: closing files, freeing memory .
The following example explains the concept of destructor in C ++:
#include using namespace std ; class Line { public : void setChieuDai ( double dai ); double layChieuDai ( void ); Line (); // Day la phan khai bao constructor ~ Line (); // Day la phan khai bao destructor private : double chieudai ; }; // phan dinh nghia ham thanh vien, bao gom constructor va destructor Line :: Line ( void ) { cout << "Doi tuong dang duoc tao" << endl ; } Line ::~ Line ( void ) { cout << "Doi tuong dang bi xoa!" << endl ; } void Line :: setChieuDai ( double dai ) { chieudai = dai ; } double Line :: layChieuDai ( void ) { return chieudai ; } // ham main cua chuong trinh int main ( ) { Line line ; // Thiet lap chieu dai cua line line . setChieuDai ( 6.0 ); cout << "Chieu dai cua line la: " << line . layChieuDai () << endl ; return 0 ; } Compiling and running the above C ++ program will produce the following results:
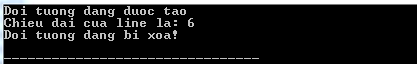
According to Tutorialspoint
Previous article: Access Modifier for class in C ++
Next: Copy constructor in C ++