Why split into blood groups?
We all know that there are 4 basic groups, A, B, O and AB. But why, humans have to divide into such blood groups?
- Instructions on how to read blood test results
- Artificial beef has blood, smell, taste like real meat
Finding and dividing blood groups is a great discovery of medicine and contributes to saving millions of lives every year.

The tragic history of blood transfusions
During the Renaissance, humans could die from hemorrhage and blood transfusion was something extremely crazy.
By the 1600s, a French doctor conducted a blood transfusion for a madman, but instead of using human blood he used the blood of a young calf. And of course, the tragic consequence happened, the transfusion began to sweat, vomit, urinate black water, and die very quickly after the next blood transfusion.
This failed experiment has made blood transfusions a scary obsession for 150 years. Until 1817, James Blundell, a British doctor, decided to use blood transfusion techniques for bleeding women instead of sitting and watching them go.
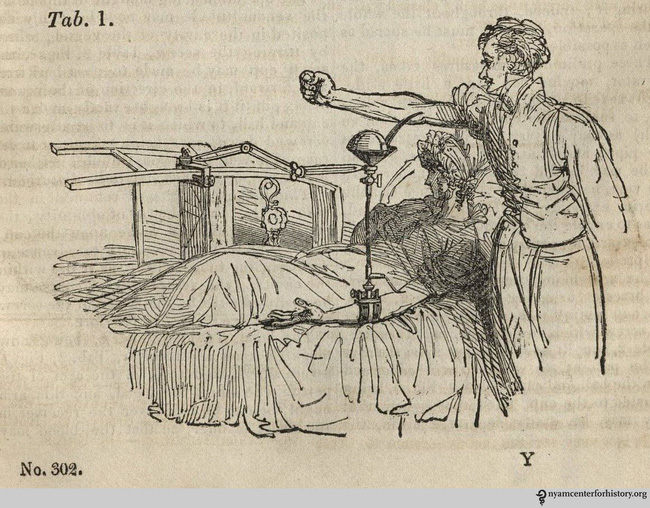
Image of Blundell's experimental description.
Blundell believes that only human blood can be transmitted to people. He took human blood to the patient, but unfortunately, the transferee died. But Blundell did not give up, in the following years, he continued to conduct 10 similar experiments but only 4 survived.
Blundell was right about human blood being transmitted to humans, but that was not enough to carry out blood transfusion techniques to save lives. In fact, a person can only receive blood from certain people.
Breakthrough Medical Achievement
Karl Landsteiner, an Austrian physician, discovered that, when blood transfusions, red blood cells of the mixture begin to form agglutination. The strange thing is not only in the patient's blood, but when mixing the blood of a healthy person, there is a case of that phenomenon.

Karl Landsteiner, who found blood groups.
To investigate this strange phenomenon, Karl Landsteiner began collecting blood samples from everyone in the laboratory, then split each sample into two parts: red blood cells and serum. To observe the phenomenon of agglutination, he proceeded to mix this erythrocyte with the other serum. After many experiments, he divided the samples into 3 groups: A, B and C (C is the O blood group now) and discovered certain rules: group of red blood cells and group plasma. When mixed together, it will not be agglutinated, but when mixing Group A erythrocytes with group B serum, the cells will clot.
In 1930, Karl Landsteiner was awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine for his work to find blood.
The cause must transmit the right blood type
According to modern science, the cause of agglutination when wrong transmission is because each red cell contains its special antigen.
- Red blood cell A contains antigen A.
- Red blood cells B have antigen B.
- O erythrocytes have no antigens.
- AB cells have both antigens A and B.
When the antigen enters another body, it stimulates the immune system to produce antibodies.
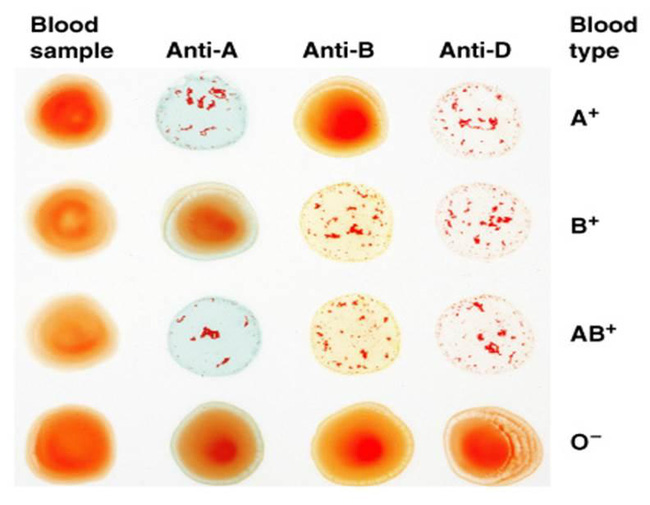
- Blood A contains Anti B antibodies.
- Blood B contains Anti A. antibodies.
- O blood contains both Anti A and Anti B antibodies.
- AB blood does not contain antibodies.
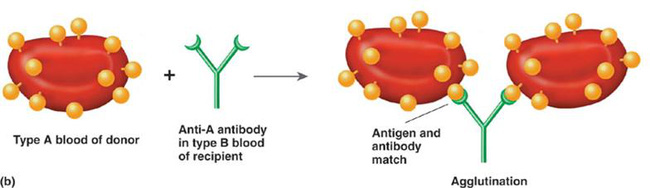 When A antigen encounters Anti A antibody, agglutination will occur.
When A antigen encounters Anti A antibody, agglutination will occur.
If the wrong type of blood is transmitted, the body will produce anti-antigen reactions (the blood that is passed on), causing the patient to die. For example, if blood A passes to B blood, antigen A will encounter an Anti A antibody that will cause agglutination and the patient will die.
Know what blood group to do?
Inheriting the research results of Dr. Landsteiner, scientists have continued to research and provide safe blood transfusion schemes to save millions of lives around the world.
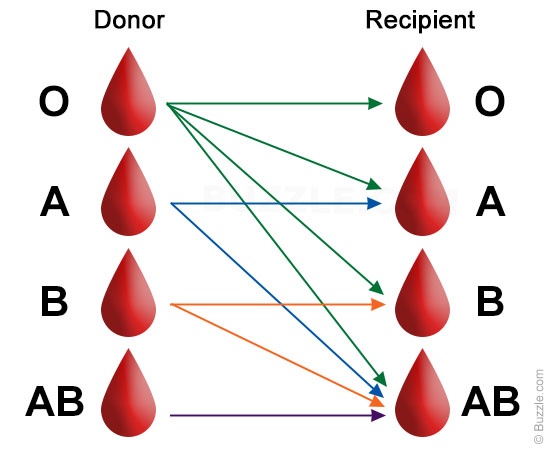 Diagram of safe blood transfusion.
Diagram of safe blood transfusion.
Currently, scientists are studying the relationship between blood type with certain types of diseases, thereby giving the best treatment method. For example, O-type people are less likely to have malaria than others because immune cells are more likely to recognize red blood cells if they are O-red.
In addition, knowing blood type helps us explain why the blood group exists for millions of years. The pathogen will grow extremely fast when selecting common blood groups and gradually destroy the host. And the rarer blood groups with protective mechanisms should gradually become dominant and survive over time.