Why is seawater salty?
All the water on our planet, from rainwater, pond water, sea water . contains chemical compounds called 'salt' by scientists. However, only seawater is always salty, but others do not. Why is there such a difference, find out through the article below.
The origin of the ocean
The Earth consists of 5 oceans: the Pacific Ocean, the Atlantic Ocean, the Indian Ocean, the Arctic Ocean and the Antarctic Sea. According to scientists' estimates based on ancient biological fossils found on the sea floor, the ocean is about 500 million years old.

Regarding the origin of the great king, many scientists have come up with different theories but no theory can explain all aspects of the problem.
Among them, the hypothesis that both the atmosphere and the ocean are accumulated gradually from the time of geological tectonic through the process of "gas" of the Earth received the most agreement of scientists. .
According to this theory, steam and other gases escaped from Earth's molten magma after rising high, cooled to cloud cover above. As the Earth cools below the boiling point of water, rain begins to appear and lasts for centuries to come. This rainfall covers almost the entire surface of the Earth, and creates the first primitive ocean. At this time, thanks to gravity, the water is retained, not falling off the Earth.
The origin of salt
Seawater is a complex mixture of decomposing marine organisms and mineral salts. The magma on the Earth's crust is cooled by weathering and dishwashing. When mountains are formed, minerals from the land are swept by rainwater and streams to the sea and accumulate into a large amount like today.
Stones and sediments beneath the seabed also contribute to the creation of some salts in the ocean. In addition, salt in the ocean comes from the types of solids and gases inside the Earth's heart escaping through craters in the ocean.
Large amounts of fresh water from the rivers flow into the sea, so why is seawater not diluted by freshwater?
Day and night, the huge amount of fresh water from the big rivers in the world such as Amazon, Mississippi, and Mekong, . always poured into the Pacific and Atlantic oceans . So why is the sea water still salty but not made? diluted? The reason is that salt is just one of the elements that make up the salty taste of the ocean.
The ancient sea contained only a small amount of salt, not salty as it is today. But about a hundred million years ago, the water created from the first rains poured down the young Earth broke the geological layers and dragged the minerals into the sea. This makes the sea water more salty. It is estimated that every year rivers and streams from the US flowing into the sea carry 225 million tons of dissolved solids and 523 million tons of sediments. If you count all the rivers on Earth, the amount of mineral salts pouring into the sea each year reaches 4 billion tons.
Let us know that, under the effect of heat from the Sun, almost pure steam in the sea rises high, but mineral salts still remain in the sea. This steam is carried by the winds to other places. Water vapor will condense when cold air is high and falls to the ground to form rain. Rainfall on land will converge on streams and rivers and eventually flow into the sea. This amount of fresh water will dissolve the salt in the sea, making the salt water salty. This cycle keeps going on like that.

Water cycle.
Composition of seawater
After years of research, scientists have not been able to fully understand the chemical composition of seawater. The main reason is because of the large size of the Ocean, which accounts for 70% of the Earth's surface, the marine environment has a system of extremely complex chemical compounds that some of them continually change. according to the period of time.
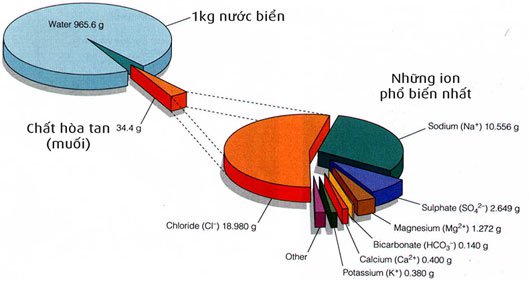
Composition of seawater.
Currently, scientists have only discovered 72 chemical elements in seawater, a number so small compared to the amount of compounds that actually exist in the ocean. Some scientists believe that all natural elements of the Earth exist in seawater, even when they are combined in both dissolved forms, or precipitate into sediments. standing in the seabed. Even when precipitated, under the influence of continuous processes in the marine environment these compounds are still capable of changing the chemical composition.
How salty is sea water?
According to chemists, there are more than 50 million tons of substances dissolved in the oceans on Earth. If it is possible to remove salt in seawater and bring it to the surface and spread it across continents, it will create a layer of 152m thick, equivalent to a 40-storey building today.
Of the 28 liters of seawater containing about 1 kg of salt, according to researchers' calculations, seawater is about 220 times more salty than freshwater in the lake.

However, the salinity of the seawater changes in different areas on Earth, it depends on factors such as evaporation level, amount of purchase, level of melting ice, water flow from rivers and streams, Snow, wind, wave movement into ocean currents.
The most salty seawater .
The sea area with the most salinity belongs to the Red Sea and the Persian Gulf area, the two areas with the highest evaporation rate of seawater, with 40 o / oo, the thousandth unit (o / oo) to measure about salinity.

Red Sea is the most salty sea in the world.
Compared to large oceans, the ocean has the largest salinity level of the Atlantic Ocean, with an average salinity of about 37.9 o / oo. In the North Atlantic Ocean, the Sargasso Sea is the region with the highest salinity because the temperature in this area is quite high and lies far from the mainland so it does not receive fresh water from rivers and streams.
Seawater has the lowest salinity of the Arctic and Antarctic waters, 2 areas with low temperatures, continuous rain and melting ice.
Coastal coves such as the Baltic Sea (salinity of 5 to 15 o / oo), Black Sea (salinity below 20 o / oo) . have lower salinity than average because of supplementing water sources New sweet mass of several billion tons per day.
The salinity of the seas along the coastal regions of the countries also varies according to geographical location and time of year.
In general, the average salinity of seawater across the Earth is about 35 o / oo. This is the result estimated by scientist William Dittmar in 1884, after analyzing 77 seawater samples in different parts of the world.
Composition results of 77 seawater samples.
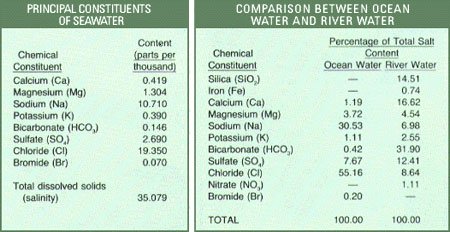
How are the composition of river and sea water different?
William Dittmar's analysis shows that seawater includes many different compounds. Sodium and chlorine (combined into NaCl) are the main factors that make up the salty taste of seawater, accounting for 85% of seawater solutes. In the ocean, the amount of Chlorine is 46 times that of Calcium.
In the river water contains a quantity of silicate and iron compounds, in the sea water is not available. In addition, 50% of dissolved solids contained in river water are Calcium Bicarbonate, 2% less than seawater.
The proportion of major constituents of seawater is almost constant, NaCl, Magnesium, Sulfate, Calcium and Potassium account for 99% of water-soluble solid compounds, although the salinity and total salt content of seawater differ. Between the world.
Other non-common elements, such as aluminum, copper, tin, . dissolved gases such as oxygen, CO2, nitrogen, have a difference between different sea waters.
You should read it
- ★ Water glasses that you drink every day can contain many harmful substances such as chlorine, pesticides, arsenic ...
- ★ Create sponge that can boil water
- ★ About 90% of Vietnamese eat excess salt, 4 hazards when Vietnamese eat too salty
- ★ It turns out this is the reason why seawater is often blue but the waves are white
- ★ Instructions for using water swab machine