Scientists have found a way to boil water with sound
Researchers from the SLAC accelerator laboratory (USA) have recently successfully boiled water by sound. To be able to produce sound that can boil water at a temperature of 100,000 degrees Celsius for about a millionth of a second, the researchers used a combination of Linac (LCLS) and a powerful X-ray.
In fact, the researchers say, in fact, X-rays can produce sounds so loud that near the sound threshold they can boil water through a single wave oscillation.
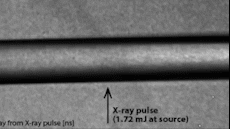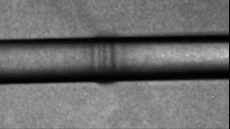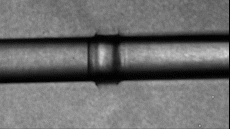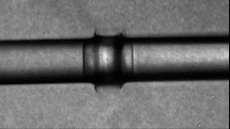
Sound is generated from a light source of Linac (LCLS) and an extremely powerful X-ray can evaporate water. Photo: Cnet.
When research on high-intensity sound waves produces maximum sounds that can affect biological specimens, scientists found that the ionisation process is extremely fast when the laser blocks the water. The water then heats up and evaporates, then creates a cylindrical shockwave propagating along the laser. These shock waves have a very large maximum pressure, equivalent to 270 dB, even greater than the noise when launching a rocket or the sound of a jet plane taking off.
If a normal person is exposed to sound levels that may have a perforation of the eardrum, the heart and lungs will also stop working.
This experiment was published by researchers in Phys Review Fluids.