What is Starlink? How does satellite internet work?
So, what is Starlink? When will Starlink be available to regular consumers? And how does satellite Internet work?
What is Starlink?
Starlink is a satellite constellation project that will place thousands of small satellites in low Earth orbit (LEO), 550 km from us. This array will transmit the Internet signal from the satellite to the transceivers on the ground, from there broadcasting locally or transmitted directly to your Starlink router.
Starlink is not the same as cell phone or 5G signal. It allows a home, business or remote location to connect to the Internet via satellite.
At the time of writing, 800 Starlink satellites are orbiting the planet. SpaceX plans to deploy at least 12,000 satellites, with plans up to 30,000 to ensure global Internet coverage via Starlink (some sources say the total is up to 42,000).
How does satellite internet work?
Satellite Internet works similarly to cable Internet, except with a few more moving parts (literally!). Here is a brief summary:
1. You go to TipsMake to update the latest technology news. Request your data to be transferred from your computer to a satellite Internet dish attached to your home (or a nearby location).
2. Satellite Internet dish transmits a data request to a satellite orbiting the Earth. In turn, the satellite sends the request to the ISP.
3. Resending your data reverses the process, transferring data from your carrier to the satellite, then from the satellite to the satellite Internet dish, down to the router, and onto your computer.
That's the basic outline of how satellite Internet works.
How fast is Starlink Internet?
Starlink is advertising download speeds of up to 1Gbps when the service is fully operational. SpaceX is "targeting latency below 20 milliseconds, so someone can play competitively responsive video games" using the service.
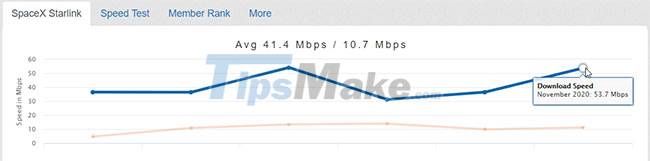
In August 2020, Starlink opened a beta launch program to a number of users across high latitude regions of the United States and Canada, such as Seattle, Chicago, and Portland. There are some very promising results in speed tests available to the public, through services like Ookla's Speedtest and TestMy, with a helpful Reddit list illustrating some of the best speeds (and pictures). the photo above shows the average speed).
- According to the listing, Starlink's confirmed fastest speed is 203.74Mbps, with a ping of 29ms.
- The fastest overall ping was 18ms.
- The fastest upload speed recorded was 42.58Mbps.
Obviously these are remarkable speeds, which will get better as more Starlink satellites are launched into the sky. Starlink beta testers have signed a non-disclosure agreement about the service, the speed tests provide some of the best insights into how the service performs.
Is Starlink Faster Than Fiber Internet?
The answer depends on your provider. Consumer fiber internet is currently leading the way at around 1Gbps. Currently, Starlink is not as fast as fiber, but faster than some alternative Internet technologies. With SpaceX's history of delivering large projects, expect Starlink to get faster and faster.
You should also note that Starlink is not trying to compete with fiber optic services either. Instead, Starlink is targeting users in rural and remote locations, providing those there with much faster internet than before (or at least at fast speeds and with less restrictions). ).
Who can use Starlink?
Once the Starlink satellites are fully orbited, the service will provide "near-global coverage for the densely populated world". Currently, only select users in North America can use Starlink.
There are also other considerations. For example, Starlink may provide coverage in your country, but whether you can use it is subject to country regulations.
Australia has laid out satellite Internet coverage in a completely clear way. But countries like China and Russia will require special regulation of the service, if they allow Starlink to operate there. Another alternative would be to ban the sale and use of Starlink ground terminals.
So the answer is no simpler than turning on Starlink's satellite receiver as soon as you have coverage.
Will Starlink benefit remote areas?
Starlink will cover global satellite Internet. For people living in remote areas, Starlink could completely change the way they use the Internet. However, how many benefits does Starlink provide?
A definite benefit of Starlink for remote locations is latency (response time). If you are in a remote area, building a long cable is expensive and comes with the potential disadvantage of high latency. Starlink data transmission will take place partially in the void of space, potentially reducing latency. At the very least, Starlink's response times should be great for remote locations.
How much will Starlink cost?
During Starlink's beta, officially known as the Better Than Nothing Beta, participants will have to pay $499 for the Starlink router and antenna, plus an additional $99/month for the subscription.
However, little is known about the final pricing structure for Starlink or even what any of the subscription plans may entail.
Is the Starlink satellite visible from Earth?
In mid-2020, Starlink hit the news. Everyone who has to stay at home because of the Corona virus will see a special sight in the night sky. SpaceX launched hundreds of new Starlink satellites in a short time. Before the satellites reach their LEO, you can easily spot them racing across the night sky, like a UFO train.
Once the satellites are in position, 550km above Earth, they will be hard to see with the naked eye. They are visible to telescopes, surprising astronomers and space enthusiasts alike.
How will Starlink affect astronomy?
Starlink's influence on astronomy is still being studied - but initial response from scientists and night sky observers has been poor. The main concern is that Starlink will pollute the LEO area with artificial light from the satellites.
An experiment by SpaceX, DarkSat, aims to reduce light pollution from satellites. SpaceX claims to have reduced light pollution on the test satellites by about 55% compared to regular Starlink satellites. However, this level is still "too bright for astronomers' super-sensitive instruments, which can observe stellar objects 4 billion times fainter than that threshold".
While Starlink only has 800 satellites in the sky, that's not a big deal. But when there is a fleet of 12,000 or up to 40,000 satellites, artificial light pollution can become a sore problem.
Is Starlink safe?
Starlink is secure in terms of data transmission. It's not 5G, which some people worry about. It's not like WiFi either. Starlink uses existing bands (Ka and Ku bands) that have long been used for satellite communications without problems.
Starlink will continue to send satellites into orbit. Satellite Internet users will rejoice at the prospect of faster, lower-cost Internet connections wherever they live and wherever they go. Prices are also likely to drop as hardware production ramps up.
You should read it
- ★ Starlink satellite accused of 'can be deadly'
- ★ How to Use Satellite Internet
- ★ Elon Musk posted a Twitter post, showing off the Internet provided by the Starlink satellite system was working
- ★ Despite concerns from astronomers, SpaceX launched 60 additional Starlink internet satellites into space
- ★ SpaceX lost 3 Starlink satellites after a month launched into space