What is high memory and Low memory in Linux?
When running the show module status command from CLI or cat / proc / meminfo command on the module, the output lists the values for High memory and Low memory:
total: used: free: shared: buffers: cached: Mem: 1049051136 765775872 283275264 0 158441472 376979456 Swap: 1036115968 0 1036115968 MemTotal: 1024464 kB MemFree: 276636 kB MemShared: 0 kB Buffers: 154728 kB Cached: 368144 kB . HighTotal: 131072 kB HighFree: 3064 kB LowTotal: 893392 kB LowFree: 273572 kB So you know what High memory and Low memory are in Linux? Find out with TipsMake.com through the following article!
What is high memory and Low memory?
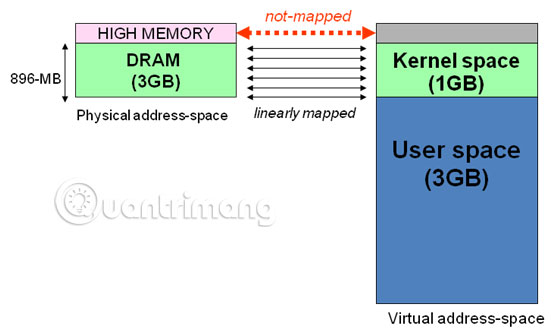
- High memory is the memory part that user-space programs can handle. High memory does not affect Low memory.
- Low memory is the memory part that the Linux kernel can handle directly. If the kernel must access High memory, the kernel must first map to its own address space.
How is high memory and Low memory used?

On a 32-bit Linux operating system, the CPU can handle up to 4GB of memory. Memory is divided into Low memory (also known as Normal memory), which is mapped directly into the kernel's address space, and High memory, without direct kernel mapping. In other words:
- The kernel itself (including its operating modules, for example Check Point kernel modules) can only use Low memory.
- The user processes on the system (anything that is not a kernel) are capable of using both Low and High memory.
Situations that can occur with High memory and Low memory
Due to the Low memory limit, OoM (Out of Memory killer) can be called even if there is a lot of free memory. This situation occurs when Low memory is exhausted and the kernel needs to allocate more memory. However, an unusual situation can happen is that there are many high memory vacancies but all Low memory is empty. More commonly, both High and Low memory are close to zero.
High memory usually starts at over 896MB. However, on Blue Coat X-Series chassis, the limits will vary.
Please note that on 64-bit operating systems, since there is too much virtual memory address space, Low memory should be equal to Total memory . When running the show module status command from CLI, the High memory and Low memory values will not appear.
Slot 14: SDRAM 1 Size 1048576(KB) SDRAM 2 Size 1048576(KB) SDRAM 3 Size 1048576(KB) SDRAM 4 Size 1048576(KB) SDRAM Total Size 4194304(KB) Reserved Memory 602536(KB) Total Memory 3591768(KB) Used Memory 453144(KB) Free Memory 3138624(KB) Shared Memory 0(KB) Buffers Memory 139340(KB) Cached Memory 187200(KB) Memory Utilization 3.52% Running cat / proc / meminfo on modules, HighTotal and HighFree will always be 0 :
# cat /proc/meminfo MemTotal: 3591768 kB MemFree: 135968 kB Buffers: 378312 kB Cached: 1754432 kB SwapCached: 68 kB Active: 965532 kB Inactive: 2080476 kB HighTotal: 0 kB HighFree: 0 kB