What is ECMO? In which case does the patient need ECMO intervention?
ECMO is a method of oxidation through the outer membrane of the body. Doctors will use a circulatory system to perform oxygen exchange on the outside of a patient with severe circulatory or respiratory failure to support and maintain vital functions.
Extracorporeal circulation is a technique to use artificial cardiopulmonary devices to temporarily replace heart and lung function when patients need to perform surgeries to repair or replace cardiovascular or vascular structures. Large blood in the body.
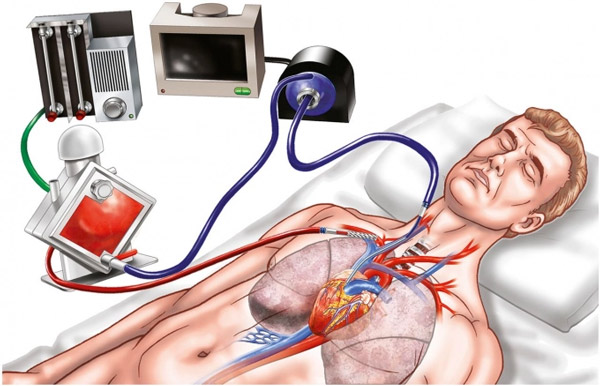
External body circulation is a semi-closed system consisting of a combination pump system and a gas exchange system. They are connected to the reservoir of cannula, cannula and heart of the patient so they can completely replace the patient's pulmonary function.
This system will create physiological changes in the body and be actively controlled thereby leading to self-regulating and self-protective reactions of the patient.
Extracurricular circulation may partially or completely replace the operation of the cardiopulmonary system but place multiple cannula at different positions simultaneously with temporary discontinuation of circulation.
When does the patient need ECMO intervention?
Patients with serious medical conditions, who are at risk of stopping circulatory or life-threatening breathing, are candidates for ECMO. Specifically when patients fall into 1 of the following cases:
- When the patient was given oxygen assisted ventilation but the lungs still could not afford to supply oxygen to the body. For example, in severe cases of pneumonia with respiratory distress, acute pulmonary edema accompanied by severe respiratory distress .
- When a patient is supported with mechanical ventilation but the lungs cannot eliminate carbon dioxide, the heart's pumping activity is insufficient to supply blood to the body.
- The patient has a heart and lung disease and is waiting for an organ to be transplanted.
You should read it
- ★ 6 ways to detoxify your body from Fluorine, toxins in tap water and toothpaste
- ★ There are 8 signs that mean your body is lacking serious vitamin C
- ★ Successfully created human kidney tissue from stem cells
- ★ 5 unexpected benefits of tears have been scientifically proven
- ★ 5 bone-destroying foods you should know to limit