What is DNS Amplification Attack?
DNS Amplification is a kind of mirror attack that manipulates publicly accessible DNS, making them a target for large numbers of UDP packets. Using a variety of techniques, the culprit can "inflate" the size of these UDP packets, making the attack so powerful that it destroys even the most powerful Internet infrastructure.
Description of the attack
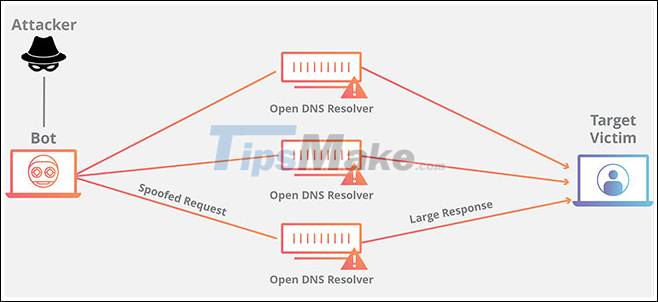
DNS Amplification, like other amplification attacks, is a kind of reflection attack. In this case, mirroring is achieved by eliciting a response from the DNS resolver to a spoofed IP address.
In a DNS Amplification attack, the culprit sends a DNS query with a fake (victim's) IP address to an open DNS resolver, causing it to respond to that address with a DNS response. With many fake queries being sent, and with several DNS resolvers responding simultaneously, the victim's network can easily be overwhelmed by the uncontrolled number of DNS responses.
Counterattacks are even more dangerous when amplified. 'Amplification' here refers to the fact that the server's response does not match the packet request originally sent.
To amplify a DNS attack like this, each DNS request can be sent using the DNS EDNS0 protocol extension, allowing for large DNS messages, or using DNSSEC's encryption (DNS security extension) to increase the size. message. Spoof queries of type 'ANY' (any), which return all known information about the DNS zone in a single request, can also be used.
Through these and other methods, a DNS request message about 60 bytes in size can be configured to send response messages over 4000 bytes to the destination server - resulting in a gain of 70. :first. This significantly increases the amount of traffic that the target server receives and speeds up the server's resource exhaustion.
Furthermore, DNS Amplification attacks often forwards DNS requests through one or more botnets - significantly increasing direct traffic to the targeted server (s) and inducing anonymous tracking. The attacker's character is much more difficult.
Methods of minimizing the impact of DNS Amplification attack
Common ways to prevent or mitigate the effects of DNS Amplification attacks include tightening DNS servers, blocking specific DNS servers or all recursive relay servers, and limiting the speed.
However, these methods do not eliminate sources of attacks, nor do they reduce the load on the network and switch between the name server and the open recursive server. Additionally, blocking all traffic from open recursive servers can thwart legitimate DNS communication attempts. For example, some organizations maintain open recursive servers so that employees working on mobile devices can resolve from 'trusted' name servers. Blocking traffic from these servers may interfere with their access.