Troubleshoot service errors in Windows Server 2008 R2 - Part 1
In this article, I will show you some of the basics of troubleshooting system service errors, including verifying error messages and checking information in the system. event recording .
Troubleshooting a service error is a simple task. However, with the help of some techniques, we can find out the cause of the problem and fix the server quickly. In this article, I will show you some of the techniques used to troubleshoot some of those service errors.
Before start
Before we get started, we note that all the images shown in this series are done on Windows Server 2008 R2. The exact steps may vary slightly between different operating system versions, but the basic concepts remain the same.
Error verification
The first thing we need to do when we see the service error message is to verify the error correctly. This is because there are some cases where the application reports an error but the service is actually still active. Similarly, when Windows boots a lot, we see an error message indicating that one or more of the services failed. However many of these announcements are false.
To verify service errors, we need to open the Service Control Manager by selecting the Services command from the Administrative Tools menu. Service Control Manager will list all services installed on the machine, as well as services with current status. You can see the Service Control Manager in Figure A below.

Figure A: The Services interface displays all system services.
If the error message received is related to a service, you can find the service within the Service Control Manager (services are sorted alphabetically) and check if the service is working. or not. If you receive a generic error message stating that one or more of the services failed when launching, you need to find what services are currently running.
As you can see in the image above, you will see that not all services are active. This is normal because Windows provides four different launch types for services (some older Windows versions only offer three types of startup). These types include:
Automatic - Services with this type of startup will automatically start when Windows is started.
Automatic (Delayed Start) - Automatic services are configured with a certain delay, it will be automatically launched after all other automated services have completed. Start-up services of this type use a lower priority to ensure the server can respond to all services.
Manual - These configured services will not start unless they are started by a user (you) or an operating system or an application.
Disabled - If a service is disabled, it will not start even if you try to launch it. Some services will be disabled for a number of security reasons, but there are some instances where malware may disable some system services. If you need to launch a service that has been disabled, you can do so by changing the launch type to Manual or Automatic (or Automatic Delayed Start) and then launching the service.
If you are trying to determine whether the necessary services are running, you just need to look in the list of services and make sure that all services have an Automatic launch or Automatic Delayed Start. If a configured service runs automatically but is not started, some other services may cause the error.
Launch service manually
If you see a service that should be working, but it is not, the first thing you need to do is try to launch the service using manual methods. To do so, simply right-click on the service and select the Start command from the menu that appears. Normally, the service will launch without problems.
Check the event log
So what happens if you try to launch a system service but fail? The first thing that I suggest to you in this situation is to check the Event Viewer. In many cases there will be multiple event log entries that appear when the service fails. These log entries are valuable in helping you identify the root cause of the problem.
The location where the event log entry is created depends entirely on the type of service you are experiencing. There are three main types of event logs that can contain information about the service you are having trouble with. These three types include:
- System Log - System Log includes events related to the Windows operating system. If there is a problem in launching the service related to Windows operating system, System Log is the best place for you to find information.
- Applications and Services Logs - Newer versions of Windows include a set of records known as Application and Services Logs. Applications and Services Logs include logs for applications such as Internet Explorer, Microsoft Office, and Windows PowerShell.
- Application Log - Most applications usually do not create detailed records under the Applications and Services Logs section but instead the log information related to the application is written to the Application.
Although event logs are a valuable resource for troubleshooting service failures, finding information sometimes encounters many difficulties. This is because there are many event log entries that you have to search and select. So if you have problems finding information related to the service, the way we introduce it here is to use the Find feature of Event Viewer (in the Actions panel). This feature works like a search engine and allows you to search by phrase related to the problem encountered, as shown in Figure B.
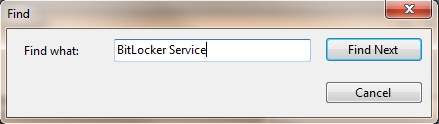
Figure B: You can search for event logs for a particular phrase
When searching for a log entry related to a problem, just double click on the entry to see it. Sometimes the log entry can tell you exactly what the problem is. For example, the log entry in Figure C indicates that the service has been disabled. This problem is only corrected by re-enabling the service. Even so sometimes the situation is not so simple. In some cases we need to get the event ID number to look up on the Internet. Microsoft provides a number of TechNet articles with comprehensive solutions for certain event IDs.

Figure C: Sometimes event log entries can tell you exactly which service failed to start
Conclude
In this first part we have provided you with some basic problems in troubleshooting service errors. In part two, I will introduce you to more detailed and advanced issues.
You should read it
- ★ If you want to get more updates in the future, Windows Server 2008 must be installed on version KB4493730
- ★ Find out about Managed Group Services Accounts in Windows Server 2012
- ★ Steps to prepare for installing Windows Server 2008
- ★ Some new points in the network connection of Windows Server 2008 R2
- ★ Configure Windows Server 2008 to remotely access SSL VPN Server (Part 3)