The ultimate guide to Google Ads
This guide will provide detailed information on how to get started advertising on Google. This article will cover platform-specific features and show you how to optimize your campaigns to get the best results with your ads.
What is Google Ads?
Google Ads is a pay-per-click (PPC) advertising platform where advertisers pay for each click (or impression) on an ad.
Google Ads is an effective way to attract the right traffic or customers to your business, because they're looking for products and services like yours. Google Ads helps increase website traffic, get more queries, and increase store visits.
Over time, Google Ads will also help analyze and optimize those ads to reach more people.
Why advertise on Google?
Google is the most used search engine, receiving millions of user searches every day. Not to mention, the Google Ads platform has been around for nearly two decades, giving it experience and credibility in the paid advertising space.
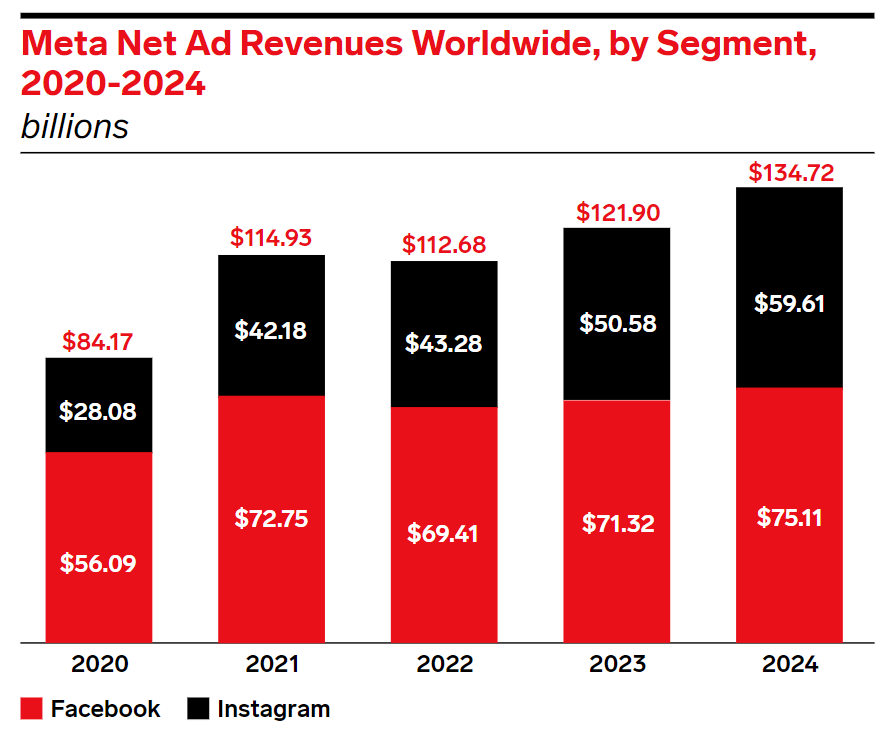
Insider Intelligence forecasts Facebook will generate 58.5% of Meta's global advertising revenue, totaling $121.90 billion.
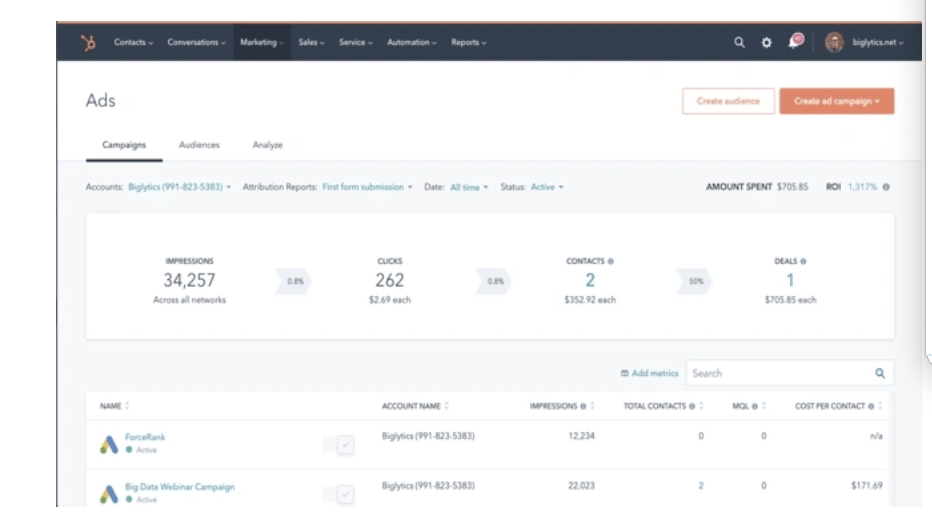
Hundreds of thousands of companies use Google Ads to promote their businesses. Even if you rank organically for a search term, your results are still pushed to the page below your competitors that use ads.
Google Ads terms you need to know
1. Ad Extensions
Ad Extensions allow you to add additional information to your ad at no additional cost. These extensions belong to 1 of 5 categories: Sitelink, Call, Location, Offer or App.
2. AdRank
AdRank determines ad placement. The higher the value, the better the ranking, the more people will pay attention to the ad, and the higher the probability of users clicking on the ad. AdRank is determined by maximum bid multiplied by Quality Score.
3. Bidding
Google Ads is based on a bidding system in which you, the advertiser, choose the maximum amount you are willing to pay for a click on your ad. The higher the bid, the better the position. There are 3 options for bidding: CPC, CPM or CPE.
- CPC or cost-per-click is the amount paid for each click on an ad.
- CPM or cost per mile is the amount paid for one thousand times an ad is viewed by a user without clicking on the ad.
- CPE or cost per engagement is the amount of money paid when someone takes a predetermined action with an ad.
The article will review the bidding strategies below.
4. Campaign Type (campaign type)
Before you start a paid campaign on Google Ads, you'll choose between seven campaign types: Search, display, video, shopping, app, smart or max performance.
- Search ads are text ads displayed between search results on Google results pages.
- Display ads are typically image-based and shown on websites in the Google Display Network.
- Video ads range from 6 to 15 seconds in length and appear on YouTube.
- Shopping campaigns appear on Google search results and the Shopping tab.
- App campaigns use information from apps to optimize ads on websites.
- Smart campaigns help Google find the best targeting for maximum effectiveness.
- Maximize performance is a new campaign type that allows advertisers to access all of their Google Ads ad space from a single campaign.
5. Click-Through Rate (CTR) - Click rate
CTR is the number of clicks received with an ad as a ratio of impressions. A higher CTR shows that the ad is quality, relevant to search intent, and targets relevant keywords.
6. Conversion Rate (CVR) - Conversion rate
CVR measures form submissions as a proportion of total landing page visits. Simply put, a high CVR means that the landing page delivers a seamless user experience that matches the promise of the ad.
7. Display Network
Google Ads can be displayed on search results pages or websites in the Google Display Network (GDN). GDN is a network of websites that dedicate space on their websites to Google Ads - these ads can be text or image based and are displayed alongside content relevant to the target keyword. The most popular Display Ad options are Google Shopping and app campaigns.
8. Impression
Every time an ad is displayed on a SERP, it will receive an impression (the number of times the ad is viewed by the user without clicking on the ad). Impression accounts for half of the CTR rate mentioned above.
You can use this insight to see how many people who see your ad click through to the landing page and optimize your ad to get a higher CTR.
Remember that it is virtually impossible to convert all impressions into clicks and achieve a 100% CTR. People may click on the SERP (zero-click search), click on a competitor's ad, or even click on an organic search result instead of clicking on your ad.
9. Keywords
When a user enters a query into the search field, Google returns a series of results that match the searcher's intent. Keywords are words or phrases that match what searchers want and will satisfy their query. Choose keywords based on the query you want to show with your ad. For example, a searcher who types 'how to clean gum from shoes' will see results for advertisers targeting keywords like 'gum on shoes' and 'clean shoes'.
10. PPC
Pay-per-click, or PPC, is a type of advertising in which the advertiser pays for each click on the ad. PPC is not specific to Google Ads but is the most popular type of paid campaign. It's important to understand the ins and outs of PPC before launching your first Google Ads campaign.
11. Quality Score (QS)
Quality Score measures ad quality by click-through rate (CTR), keyword relevance, landing page quality, and historical performance on SERPs. QS is the deciding factor for AdRank.
How does Google Ads work?
There are 3 parties involved in the Google Ads process: Searchers, advertisers and the Google Ads platform. Everyone has a role to play in making Google Ads work, where advertisers and businesses can make money and customers see (and can buy) products and services that meet their needs. their.
Here are the details on what happens with Google Ads:
1. Advertisers bid on keywords in Google Ads
Keyword bidding is how advertisers tell Google which keywords they want their ads to appear on the SERPs. Keyword bids can range from a few dollars to hundreds of dollars per keyword. Advertisers typically set the daily budget used for individual keyword bids.
Plus, regardless of your business size or available resources, you can tailor your ads to fit your budget. Google Ads tools allow staying within monthly limits and pausing or stopping ad spend at any time.
2. Potential customers search for keywords on Google
Next, the potential customer searches for the keyword the advertiser bid on. On the SERP, they will see ads for products or services that are most relevant to their query. The order of ads they see depends largely on ad rank.
3. Google displays ads for that keyword based on ad rank.
Between the time a user types a search into the Google search bar and the moment the SERP for that keyword appears, Google works quickly in the background to perform a process called ad ranking.
Within seconds, Google ranks advertisers number one by the total number of available ad spaces on the SERP. The platform uses the Quality Score for the keyword and the amount an advertiser bid for that keyword to determine who gets the number one, number two, number three, etc. spot.
4. Potential customer clicks on one of the websites listed on the SERP
When customers see an ad for a searched keyword, they may decide to click on an ad that they believe best matches their search intent.
From there, they can decide to make a purchase or click back on the SERP and choose a different ad or organic SERP result to click on. They can also choose to end their search without clicking or making a purchase.
Factors affecting Google Ads
Many factors influence your ability to create effective and high-performing Google Ads, including:
Ad Rating
AdRank determines ad position. It is determined by a formula that considers Quality Score and the amount bid for a keyword.
Quality Score is based on the quality and relevance of the ad, and Google measures that by how many people clicked on the ad when it was displayed - i.e. CTR. CTR depends on how well the ad matches the searcher's intent, which can be inferred from three aspects:
- How relevant are the keywords?
- Whether the ad copy and CTA meet the searcher's intent.
- Landing page user experience.
Quality Score is where you should focus the most attention when setting up your first Google Ads campaign - even before increasing bids. The higher the QS, the lower the cost of purchasing the keyword and you'll get better placement without paying more.
Location
When you first set up Google Ads, you'll choose the geographic area where your ads will be shown. If there is a store, it must be within a reasonable radius around the physical location. If you have an e-commerce store and physical products, the location must be located where you deliver.
Location settings play an important role in rankings. For example, if you own a yoga studio in San Francisco, someone in New York searching for 'yoga studio' won't see your results, regardless of your AdRank. That's because Google aims to show the most relevant results to searchers.
Key word
Keyword research is also important for both paid advertising and organic (non-paid) search. Keywords need to match the searcher's intent as much as possible. That's because Google matches ads to search queries based on your chosen keywords.
Each ad group you create in your campaign will target a small set of keywords (between 1 and 5 keywords is optimal), and Google will show ads based on those selections.
Match Types
Match Types provide choices about keywords - they tell Google whether you want an exact match to a search query, or whether your ad should be shown to anyone with a closely related search query. . There are 4 types to choose from:
- Broad match is the default setting that uses any words in the keyword phrase in random order. For example, 'goat yoga in Oakland' will match 'goat yoga' or 'yoga Oakland'.
- Modified broad match allows certain words to be "locked" in a keyword phrase by indicating them with a '+' sign. At the very least, the matches will include that "locked" word. For example, '+goats yoga in Oakland' might yield results containing 'goats', 'goats like food' or 'goats and yoga'.
- Phrase match will match queries that include the keyword phrase in the exact order, but may include additional words before or after the phrase. For example, 'goat yoga' might yield results containing 'spotted goat yoga' or 'goat yoga with puppies'.
- Exact match maintains the keyword phrase because it is written in the correct order. For example, 'goat yoga' won't show up if someone types 'goats yoga' or 'goat yoga class'.
If you're just starting out and don't know exactly how to search, switch from Broad match to a narrower approach so you can test which queries yield the best results. However, because your ads will rank for many queries (some of which are unrelated), you should closely monitor your ads and modify them as new information becomes available.
Title and description
The content displayed in your ad will determine whether users click on your ad or your competitor's. Therefore, ad content must match the searcher's intent, match the target keyword, and address the user's pain point with a clear solution.
Let's look at an example to make this clearer!

Searching for 'baby swim lessons' returned this result. Content is concise and uses limited space wisely to convey the message and connect with the target audience.
Swim Revolution has been known to put keywords in their headline, so users know right away that this ad matches what they're looking for. Furthermore, the description tells why this is the best option for swimming lessons as it addresses the user's concerns - as a parent looking to enroll their child in classes swim.
They use words like 'skills', 'fun', 'confidence' and 'comfort in the water' to ease parents' anxiety when taking their baby to the pool. These phrases demonstrate that we will get what we want from this class.
This display ad content will help get clicks, but whether they convert into actual signups depends on the quality of the landing page.
Ad Extensions
If you are running Google Ads, you should use Ad Extensions for two reasons. They are free and give users another reason to interact with ads. These extensions fall into one of the following 5 categories:
- Sitelink extensions expand your ad - helping you stand out - and provide additional links to your website to give users more compelling reasons to click.
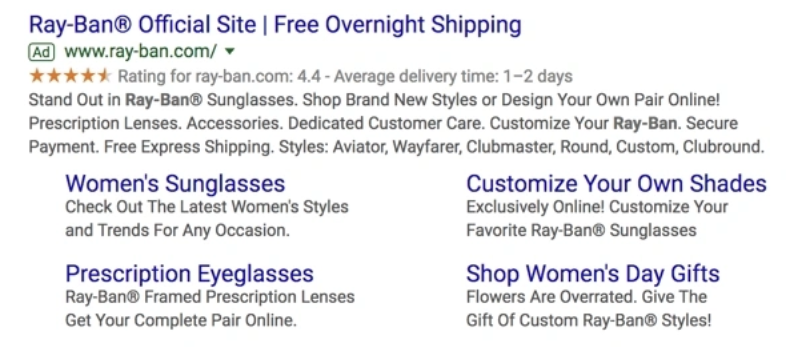
- Call extensions allow phone numbers to be incorporated in your ads, giving users an additional (and immediate) way to contact you. If you have a professional customer service team, include your phone number.
- Location extensions include your location and phone number in your ad so Google can provide searchers with a map to find you easily. This option is great for businesses with stores and works well for the '. near me' search query.
- Offer extensions work if a current promotion is running. It can entice users to click on your ad instead of others, if they see that your options are more discounted than your competitors.
- App extensions provide links to app downloads for mobile users. This eases the pain of doing a new search to find and download apps in the AppStore.
Retarget Google Ads
Retargeting (or remarketing) in Google Ads is a way to advertise to users who have previously interacted with you online but haven't turned into physical buyers. Tracking cookies follow users across the web and target these users with your ads. Remarketing is effective because most leads have to see your marketing multiple times before becoming actual customers.
How to use Google Ads
Getting started with Google Ads is simple but requires a few preparation steps. Here's a step-by-step guide to setting up your first Google Ads campaign.
1. Use the Google Ads planning template
Don't have to start from scratch when using Google Ads. Using Google Ads PPC Kit will take the guesswork out of the platform and give you a head start on the competition.
Whether you're using a template or creating your own plan, take the next steps to get started with your Google Ads campaign.
2. Set up a Google Ads account
First, visit the Google Ads home page. In the top right corner, click 'Start Now'.
You will be instructed to sign in with your Google account or set up a new account.
3. Choose a business name and website
After logging in, you will be taken to a page providing your business name and website. The domain you provide is where anyone who clicks on your ad will be taken.
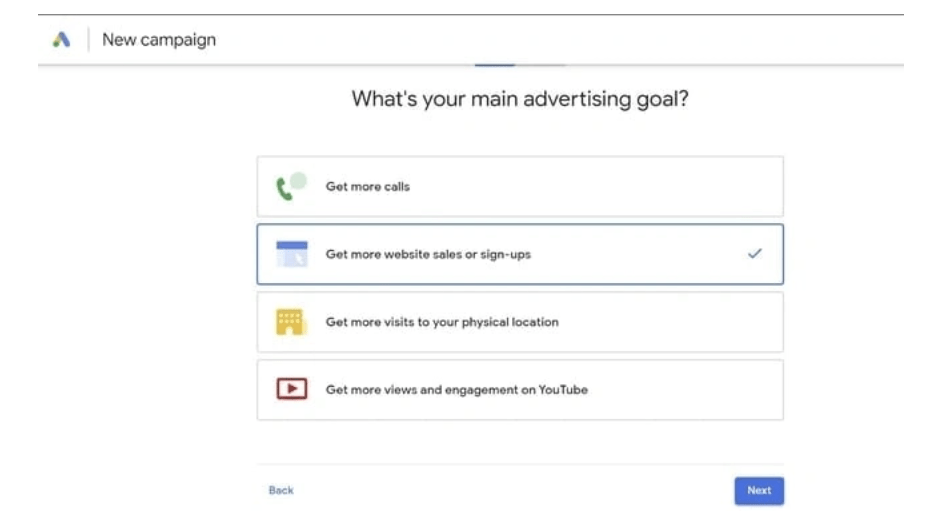
4. Choose your advertising objective
Next, choose your primary advertising objective. There are 4 options: Get more calls, get more website sales or registrations, get more visits to physical locations, get more views and engagement on Youtube.
5. Create ads
The next step is to create the ad. This requires creativity and can be a bit difficult.
Thankfully, Google provides advice on what to write. Of course, the most important thing is to write an ad that can attract and convert viewers into real customers.

6. Add keyword themes
On the next page, you can choose keywords that match your brand. Google will suggest some topics. If you are new to keyword research, you should choose the research that Google has suggested to start. After selecting the correct keyword, click 'Next'.

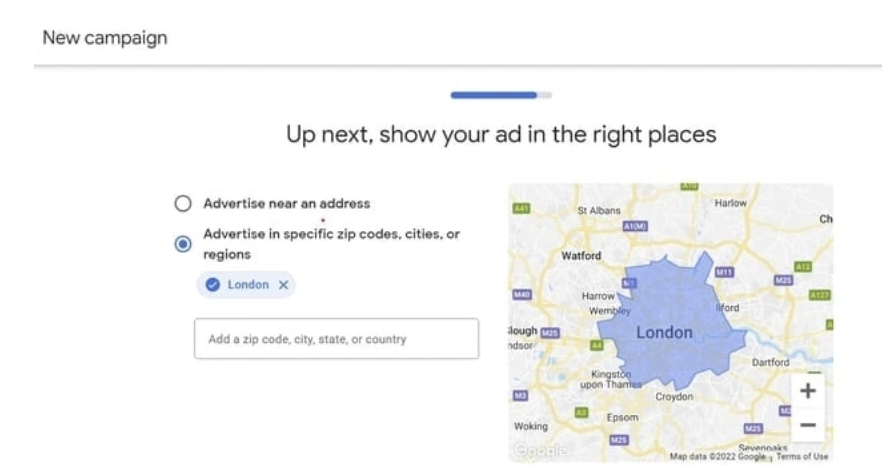
7. Set ad position
The next page allows you to choose where you want your ad to appear. It can be near the physical address or anywhere else.
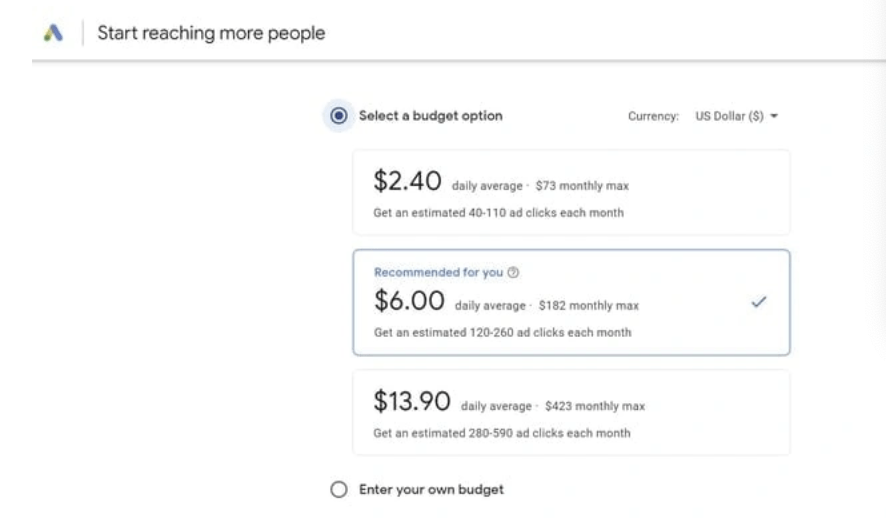
8. Choose a budget
Here, you'll use the budget options provided by Google or enter a specific budget.
9. Confirm payment
Finally, provide your payment information.
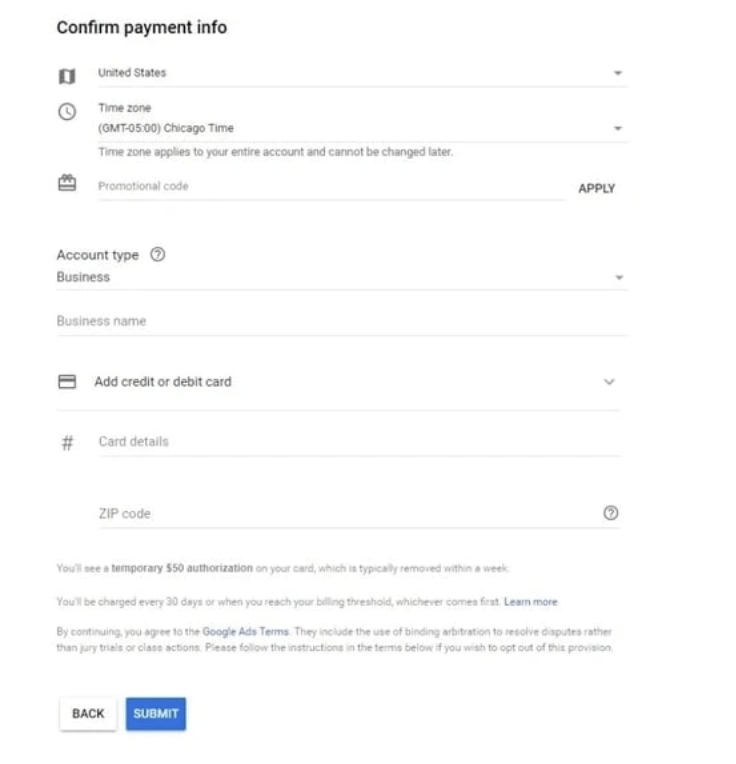
As you can see, setting up a paid advertising campaign on Google is relatively easy (and quick), mainly because the platform will provide detailed instructions and helpful hints along the way. presently. If prepared well, setup should take no more than 10 minutes.
The next thing to do is make sure the ad is set up optimally and is easy to track.
10. Link Google Analytics account
You probably have Google Analytics set up on your website to track traffic, conversions, goals, and any other metrics. If so, link your Analytics account to Google Ads. Linking these accounts makes tracking, analysis, and reporting across channels and campaigns much easier because these events can be viewed in one place.
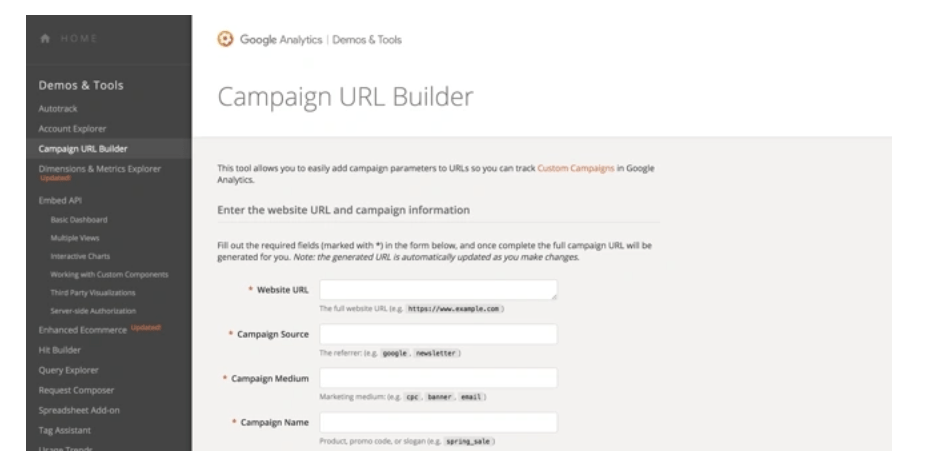
11. Add UTM code
The Urchin Tracking Module (UTM) code is used by Google to track any activity associated with a specific link. UTM codes will show which offers or ads led to conversions to track the most effective parts of your campaign. UTM codes make optimizing Google Ads easier because you know exactly what's actually working.
However, the trick is to add the UTM code at the campaign level when setting up Google Ads, so you don't have to do this manually for each ad URL using Google's UTM generator.
12. Set up conversion tracking
Conversion tracking shows exactly how many customers or leads were acquired from an advertising campaign. No setup required. However, without it, you'll have to guess at your ad's ROI.
Conversion tracking shows sales (or other activities) on your website, app installs, or calls from ads.
13. Integrate Google Ads with CRM
It's important to keep all data in one place for easy tracking, analysis, and reporting. If you already use your CRM to track contact data and lead flow, integrating Google Ads with your CRM allows you to track which advertising campaigns are working for your audience so you can Continue marketing them relevant offers.