The emergence of application delivery technology is controlled by software and what it can do for your network
The flexibility of cloud computing has prompted IT to seek opportunities to replicate its flexibility in infrastructure and operation. Automation initiatives have optimized many layers of stack computer data structures, but application delivery services are still a problem when network staff feel "cut in the leg "by heterogeneous architectures.
Virtual devices for load balancing, which is considered a solution for software-controlled infrastructure, have been born since virtualization, having inherited most of the architectural challenges. of old solutions, including limited scalability, lack of management, centralized coordination and performance constraints. While what we need is the application distribution architecture based on software control principles, there is a logical separation between data plane and control plane provided for application services. .
This model, with the central controller that manages a distributed software load balancing group, between the data center and even many cloud environments, can bring many benefits:
- Both data plane and control plane can run on leading Intel architecture servers, providing cost-effective network services.
- Data plane can be deployed on physical servers, virtual machines, containers, enabling consistent application deployment across multiple cloud environments.
- Because virtual services are no longer limited to devices, they can be distributed on the balance of data plane load.
- Data plane can collect application data continuously, send to the controller to analyze and view user performance and experience in real time, effectively use the strategic position of load balancing (in path of application traffic) to get more important information about the application.
Due to the importance of data-based development for fast network application and troubleshooting teams for operating teams, important information about the application will help IT managers make decisions. Create new or replace services. For example, an online retailer can use the system to create a dashboard for CIO after a big sales event like Black Friday or Cyber Monday, providing an overview of their web application, including Including the average number of transactions, peaks, shopping cart abandons, the most popular types of devices used by customers to access applications, total end users by region and more. In this way, architecture has expanded the capabilities of services, beyond load balancing to reach a complete application service suite. Let's explore application services in a modern application context.
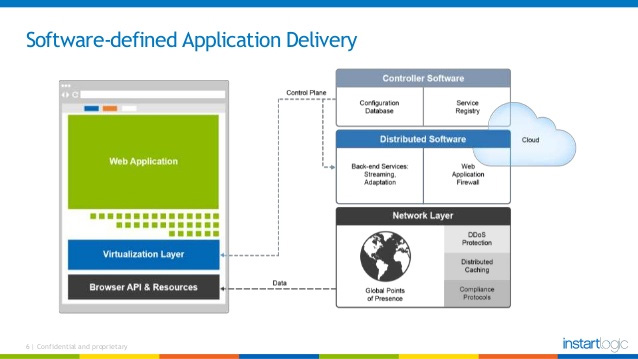
Software-driven distributed architecture platform introduced by Instart Logic
New application distribution architecture
When businesses are more focused on applications, they have come up with strategies to deploy applications and update faster using architectures like Microservices. Container technology (container technology) facilitates the creation of microservice-based applications, by helping developers to "tear off" large applications into smaller blocks. For example, each microservice such as catalog, payment, inventory management or security, belongs to a larger application, can run on multiple containers and each container is a network endpoint managed and deployed effectively. Containers help speed up development and extend the capabilities of the application, but complicate the supply, maintain, and update applications.
With dozens or hundreds of containers managed through the cloud, you need a flexible approach, controlled by software to distribute load balancing and proxy services in the microservice group. Setting proxies on each host or server allows monitoring and controlling interactions between microservices, enabling application developers to see application components and improve debugging capabilities on the application.
Centralized control and the ability to review interactions in the application also allow the creation of security policies for each part of the service to better meet security requirements. In addition, a centrally managed proxy service will help identify new services, updates introduced for each application, such as a new payment system, by providing DNS services. to the container based on the application, because the controller can integrate the API, using the container management framework such as Kubernetes or Mesos.
The software-defined application delivery architecture (architecture) architecture consolidates many L4-L7 services, adding and removing multiple point solutions to handle IPAM, DNS, performance monitoring Application, microsegmentation and East-West firewall. More importantly, this architecture can handle most existing network functions such as REST API, enabling programmable application services, configurations that can automate common network management tasks. such as delaying the update, providing the application.
The flexibility in choosing application infrastructure and architecture is changing the way modern businesses apply information technology to their operations. When businesses focus on applications, IT staff will be subject to greater pressure to complete the application deployment goal and bring it to market at the right time. The traditional application delivery mechanism no longer meets the needs of modern cloud-based applications, including personal data centers and cloud platforms. The application distribution architecture under the control of the software, on the other hand, can provide flexibility, scalability, performance monitoring and automation of regular IT jobs that businesses need to Solving new challenges constantly appearing.
You should read it
- ★ Amazon boss deployed delivery service to compete with UPS and FedEx
- ★ Viettel suddenly launched the app called MyGo, competing with Grab, be, Go-Viet
- ★ Amazon will soon deploy an unmanned aircraft delivery project
- ★ How to deposit into Lalamove
- ★ Vadi: Vietnamese application of traffic map and newspaper