Strftime () function in Python
In this article, TipsMake.com will show you how to convert date, time and time objects into strings corresponding to the given format and specific examples to make it easier to visualize and capture functions. .
The strftime () function in Python returns a string representing the date, time, and time values using date, time, and datetime objects.

Example 1: Use strftime () to convert datetime to string
The following program converts a datetime object containing the current date and time into different string formats.
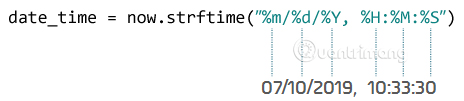
from datetime import datetime now = datetime.now() # current date and time year = now.strftime("%Y") print("year:", year) month = now.strftime("%m") print("month:", month) day = now.strftime("%d") print("day:", day) time = now.strftime("%H:%M:%S") print("time:", time) date_time = now.strftime("%m/%d/%Y, %H:%M:%S") print("date and time:",date_time) Run the program, the result is:
year: 2019 month: 07 day: 10 time: 10:37:16 date and time: 07/10/2019, 10:37:16 You can see, the variables date, time, and datetime here are in the form of string, only the now variable in the form of datetime object
How does strftime () work?
In the above program,% Y,% m,% d . are format codes. The strftime function () takes that format code as an argument and returns a string formatted based on it.
1. The datetime class is imported from the datetime module because the object of the datetime class can access the strftime function ().

2. The datetime object contains the current date and time stored in the now variable .

3. The strftime () function is used to create strings according to the format we passed.

4. The string you pass into the strftime function () may contain a lot of formatting codes.
Example 2: Use timestamp value
from datetime import datetime timestamp = 1562733155 date_time = datetime.fromtimestamp(timestamp) print("Thoi gian tuong ung:", date_time) d = date_time.strftime("%m/%d/%Y, %H:%M:%S") print("Output 2:", d) d = date_time.strftime("%d %b, %Y") print("Output 3:", d) d = date_time.strftime("%d %B, %Y") print("Output 4:", d) d = date_time.strftime("%I%p") print("Output 5:", d) Run the program, the result is:
Thoi gian tuong ung: 2019-07-10 11:32:35 Output 2: 07/10/2019, 11:32:35 Output 3: 10 Jul, 2019 Output 4: 10 July, 2019 Output 5: 11AM List of code formats
The table below shows all the formatting codes that you can pass to the strftime method ().
%a Abbreviated name of the week Sun, Mon, . %A name of the week in the week that is written in full Sunday, Monday, . %w Day of the week, value form 0, 1, ., 6 %d Day of the month, numeric value (value 0 as a buffer before the 1-digit date) 01, 02, ., 31 %-d Date of the month, value type 1, 2, . ., 30 %b Abbreviated month name Jan, Feb, ., Dec %B Full month name, January, February, . %m Month of the year, numeric form (value 0 as previous buffer month with 1 digit) 01, 02, ., 12 %-m Month of the year, value form 1, 2, ., 12 %y 2-digit year value (value 0 as buffer 1 digit before the year) 00, 01, ., 99 %-y Year 2 digit values 0, 1, ., 99 %Y Full year value 2013, 2019 . %H Hour in a 24 hour system (with a value of 0 as a buffer before 1 digit) 00, 01, ., 23 %-H 24 hour system time, value form number 0, 1, ., 23 %I 12 hour system time, numerical value form (value 0 as buffer before 1 digit) 01, 02, ., 12 %-I 12 hour hours 1, 2, . 12 %p Local time is AM or PM. AM, PM %M Minutes, numeric values (value 0 as 1-minute pre-minute buffers) 00, 01, ., 59 %-M Minutes, numeric values 0, 1, . , 59 %S Seconds, numeric values (value 0 as a buffer before the 1-digit second) 00, 01, ., 59 %-S Seconds, numeric values 0, 1, ., 59 %f Micro seconds, numeric value (value 0 as a 1-second pre-pad buffer) 000000 - 999999 %z UTC compensation time in + HHMM or -HHMM format. %Z Time zone name %j Date of the year, numeric value (value 0, 00 as a buffer before the date has 1 and 2 digits) 001, 002, ., 366 %-j Year of the year, form values of 1, 2, ., 366 %U Number of weeks in the year (Sunday is the first day of the week). All days in the new year before the first Sunday are considered as during the week of 00, 01, ., 53 %W Number of weeks in the year (Monday is the first day of the week). All days in the new year before the first Monday are considered in week 0. 00, 01, ., 53 %c Returns the date and time Sep 30 30:06:05 2013 %x Returns on 09 / 30/13 %X Returns 7:06:05 %% '%' character literally. % Example 3: Common format codes: Returns date and time:% c,% x,% X
from datetime import datetime timestamp = 1562733155 date_time = datetime.fromtimestamp(timestamp) d = date_time.strftime("%c") print("Output 1:", d) d = date_time.strftime("%x") print("Output 2:", d) d = date_time.strftime("%X") print("Output 3:", d) Results returned:
Output 1: Wed Jul 10 11:32:35 2019 Output 2: 07/10/19 Output 3: 11:32:35 Previous post: Datetime in Python
Next lesson: strptime () function in Python