Research: The golden time to prevent malicious code after the system is compromised
Recently, ransomware-spreading malicious agents have also started deploying tactics to collect and exploit victims' data, then use them as leverage to force them to pay ransom with the threat of information leakage. The information is stolen, making the recovery much more difficult. However, this strategy also exists loopholes.
There was enough time to establish a defense
As mentioned, ransomware miners usually deploy malicious payloads after at least 3 days, in 75% of all ransomware incidents that FireEye investigates, so this is also considered a golden time for organizations. deploying preventive measures, helping minimize the possible damage. It is even possible to prevent ransomware deployment if the organization's cybersecurity team has sufficient knowledge and level of security to deal with the same security.
In some successful containment cases, it was discovered that ransomware payloads were pushed into the victim's system, but could not be deployed as usual.
Basically to hack into a victim's network, ransomware exploiters often use some methods like RDP (in the case of LockerGoga malware), phishing emails with malicious links or attachments. (Ryuk) and download malware (Bitpaymer and DoppelPaymer) as original vectors of infection.
The moment the malware was deployed
According to information that the FireEye team pointed out, in most cases (76%) ransomware started encrypting data on victims' systems outside office hours, specifically "on weekends or before 8:00 am / 6:00 pm every weekday, "and may change flexibly according to the victim's schedule.
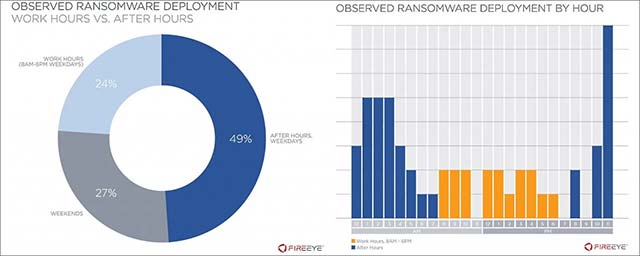
This tactic allows an attacker to avoid the scanning operations of the system security team, ensuring that incident response measures will not be implemented in time to prevent the attack.
In order to protect the system against ransomware attacks according to the above motif, FireEye recommends that organizations block the infection vector by implementing multi-factor authentication measures, planning a test. regular systems, and using security solutions and email systems capable of detecting common malware strains like Trickbot, Emotet and Dridex.
In addition, organizations should implement network segmentation techniques, regular backups, restrict local administrators, use unique passwords, and especially improve security knowledge. Secret of system personnel.
You should read it
- ★ 7 kinds of ransomware you didn't expect
- ★ Disable malicious HiddenTear Ransomware with HT Brute Forcer
- ★ STOP - Ransomware is the most active in the Internet but rarely talked about
- ★ Shade ransomware, the nightmare of 5 years ago is showing signs of returning
- ★ Lukitus Guide to preventing extortion malicious code