Recycle space waste, impossible thought possible!
According to the latest statistics from the United States Aeronautics Agency (NASA), there are about 22,000 artificial objects orbiting the Earth, including active satellites as well as broken, inactive, and countless pieces of old missiles have been used in human space exploration for more than half a century. So not only littering the natural environment on the ground, we also leave plenty of 'imprint of the civilized world' outside the universe. And if the collection, sorting, and recycling of subterranean waste is not that simple, recycling of waste waste is more than a bargain, but not entirely impossible.
- NASA's space telescope finds three new planets with rare features
 Space waste floats more and more dense in Earth Orbit
Space waste floats more and more dense in Earth Orbit
Recycle space waste
- Why need to collect and recycle space waste?
- Status of waste situation in Earth Orbit
- Recycling waste in space
Why need to collect and recycle space waste?
According to scientists, the number of 22,000 objects mentioned above is too low compared to the current development of the cosmic industry. In addition, the densely packed cosmic garbage and the increasing number of rocket launchers on Earth Orbit have exacerbated concerns about unfortunate collisions occurring outside the space between ships. these pillars and floating objects - not only damage money, but also create more floating debris in space, seriously threatening the safety of other spacecraft and satellites doing mission.
A study conducted by NASA argued that 99% of the satellites working in space need to be removed from Earth orbit for up to 5 years to ensure the risk of collisions. in low space is always kept at a safe level. However, the bigger problem is that if it is impossible to communicate with the satellite, it will be difficult to control and remove the satellite from Earth Orbit.
- Celebrating 50 years of human footing on the moon, Google built a portrait of Apollo 11 astronaut software engineer from 107,000 solar panels
 The amount of waste is thick in Earth Orbit after more than 50 years of human exploration of space
The amount of waste is thick in Earth Orbit after more than 50 years of human exploration of space
More seriously, the space junk in the dense Earth Orbit will reduce the effectiveness of the weather forecast satellites, causing unnecessary disturbances to the meteorological industry. Besides, light reflected from these objects can affect the view as well as the images of the telescope. Radio astronomers are also skeptical that the frequency at which these satellites work may exceed the frequency they are using to study distant objects in space.
Clearly, it is extremely necessary and urgent to offer a long-term and sustainable solution to clean the space. From that idea, the Gateway Earth development team - a team of scholars from many prestigious universities around the world - has proposed turning this potential threat into an excellent resource through the project. Build space station to collect and recycle space garbage. It is expected that by the year 2050, the Gateway Earth - the space recycle station specialized in recycling garbage will officially come into operation, and its main task is nothing but recycling of old satellites and floating debris into Items that can be used.
- The newly discovered black hole contains anomalous characteristics, challenging most astronomical theories today
Status of waste situation in Earth Orbit
There are two main Orbit layers that satellites often operate:
- Low Earth orbit (low Earth orbit - LEO) is about 200 km to 1,000 km from the ground and is where the International Space Station (ISS) is on duty, along with thousands of other satellites. Most of our artificial objects in space are located in this orbit.
- Up to a height of 36,000 km above the ground, the forces acting on satellites make them in the same position in their orbit. This is called Geostationary Earth Orbit (GEO). The satellites here stand still on a single point compared to the Earth, so the antennas can reach them in a fixed way and still remain connected to satellites, which makes them particularly suitable. and useful for weather forecast and contact activities. GEO is the preferred trajectory for companies that exploit the operation of artificial satellites (including telecom and television satellites). Satellite position can only vary by longitude.
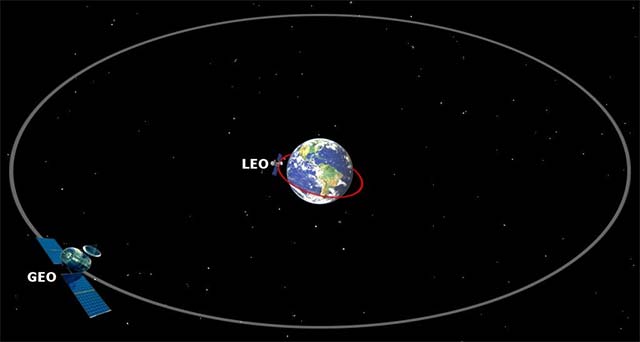 Simulate low-altitude Earth Orbit and Geostationary Orbit
Simulate low-altitude Earth Orbit and Geostationary Orbit
As mentioned, LEO is currently crowded with thousands of active satellites (after Elon Musk's billionaire Starlink project is complete, there will be an additional 12,000 satellites in this Orbit). Every collision situation here can create a rain of debris so wide that these fragments can continue to collide with other satellites as a domino effect, thereby creating more and more fragments such as A dangerous and extremely difficult chain reaction.
In the end, the entire Earth Orbit could become a mess of debris that cannot be used or decomposed. These fragments have, are, and will make LEO a huge landfill. Now is the time to be more suitable to develop and test technologies to eliminate this kind of unpleasant waste before it's too late.
- NASA 'Mars' helicopter model is almost ready for the journey to conquer Red Planet
 International Space Station (ISS) is on duty at the Low Earth Orbital
International Space Station (ISS) is on duty at the Low Earth Orbital
But up to GEO, things become even more difficult. In this atmosphere, when a satellite arrives at the end of its life cycle, the owner will try to bring it into the 'Cemetery orbit' at a higher level. Here, these expired satellites can drift about 300km to 400km away from the protected area according to the international agreement. However, only about 80% of satellites operating in GEO may actually have gone to the graveyard orbit after cessation. Thus, 20% will become dangerous space waste, directly threatening the safety of other satellites. They need to be treated as an urgent matter - and that is when a recycling facility for space waste will work.
- Admire the design of the most award winning NASA space design competition: Harmony, full of comfort, and safety
Recycling waste in space
The graveyard orbit can be considered an unattended abandoned landfill. Glare is often seen in this 'dead land', and scientists believe it is because the satellite is colliding or exploding by unused fuel or by a broken battery. However, it is worth mentioning that these fragments are fully capable of falling back to GEO and threatening satellites operating at this orbit.
International laws on the use and exploitation of aerospace are not (yet) directed towards a neutral solution to the problem of spatial waste and high consensus among nations, leading to solutions Synchronization and transparency are hard to come up with. Even if an out-of-control satellite is directly threatening another modern, active satellite worth billions of dollars, existing international agreements can still become barriers to succession. plan to eliminate that dangerous satellite without the owner's permission, even if a space plane can intervene and bring it to the graveyard orbit. In other words, the overlap in the current regulations on aerospace exploitation makes dangerous situations despite being warned but still cannot be prevented.
- Admire 10 priceless photos taken by NASA's Spitzer telescope
 This material can help build a spacecraft or build more 'exploratory outposts' in the future
This material can help build a spacecraft or build more 'exploratory outposts' in the future
By repairing, reusing or recycling satellites and garbage space directly at an Earth Orbital facility, this material can help build a spacecraft or build more 'money. Rumor explorer 'in the future, like a base on the moon. Not only does it help reduce space junk, keep devices safe, and this plan also saves billions of dollars in investment in new material production each year, just like you break. the old house and make use of healthy bricks to build a new house - a great savings.
Recycling of satellites and floating debris in the universe can create not only raw materials to build more research facilities in space, but also a source of income to sustain the chapter. This universe cleaning process. A recent study has shown that when operating at a high level, Gateway Earth will be able to access most GEO objects, including active satellites as well as death. Since then, all satellites can be "towed" by space planes into recycling centers for processing if needed.
It is estimated that the recycling and repair of space-flying objects can generate revenue of more than $ 8 billion per year. However, as said, in order for this project to be operational, existing space laws will need to be modified, and this is not simple at all because it is related to the interests of each country. Certainly, there will be long and stressful negotiations. Fortunately, this is what the United Nations is trying to do, and the members of Gateway Earth are also working hard with the aerospace agencies of each country to gradually remove all. barriers.
- Written rocket launch on the universe to broadcast ads in the sky, advertising trends in the future?
For satellites that can no longer be maintained and reused, scientists will remove their components and shells for use for other purposes. Some recyclable materials from cosmic trash can be crushed and used to shield radiation for Gateway Earth stations. The research team has shown that the efficiency of recycled solar panels from unused satellites is reduced to only about 24% after 15 years, so they can be collected and reused as sources. Energy efficient for the station.
You may not know, but the world's most 'top' cameras are floating in space after a long time of duty, this is a huge waste. They can be repaired and reused on the Gateway Earth as well as new satellites to continue to participate in more complex new space missions. Besides, when the deployment and use of satellites is set to develop at an 'extraordinary' speed, owning an 'outpost' within Earth Orbit to be able to manage all This satellite will become extremely urgent.
The researchers behind the Gateway Earth project also plan to create more revenue in the future by acting as a space hotel, a satellite / spacecraft building facility, and a supply center. Fuel for spacecraft on duty as well as while moving between planets. Similar to the utility combinations that we often see on the current highways.
- Chinese scientists revealed plans for the Laser Station to clean up the garbage
 Damaged objects and satellites can completely be towed to the graveyard or Gateway Earth for recycling
Damaged objects and satellites can completely be towed to the graveyard or Gateway Earth for recycling
After all, humanity needs an effective and urgent space cleaning plan before things get out of control. Unlike plastic waste that is flooding the Earth, in the universe, we still have time. But that does not mean that it is allowed to be 'foot-like vessel', Earth Orbital cleanup plans need to be done now, with the efforts and efforts of all humanity.
What do you think about the Gateway Earth universe cleaning project? Please leave a comment below!
You should read it
- ★ Chinese scientists revealed plans for the Laser Station to clean up the garbage
- ★ The next robot can cure satellites, destroying the space fleet
- ★ How fast can a rocket fly to win gravity and escape the Earth?
- ★ SpaceX's Crew Dragon spacecraft successfully assembled with the ISS station, completely automated
- ★ 4 websites to help see where the ISS station is in the sky