Property (Property) in C #
Properties - Property is the member named for the Layer, Structure, and Interface. Member variables or methods in a class or structure are called Fields. Attribute is an inheritance of Fields and is accessed using the same syntax. They use accessor through the values of Private Fields that can be read, written, and manipulated.
The Property does not name storage locations. Instead, they have accessors that read, write or calculate their values.
For example, we have a class called Student, with Private Fields for age, name, and code. We cannot directly access these Fields from outside that class, but we can have properties to access these Private Fields.
Accessor in C #
In C #, accessor is an attribute that contains executable commands, which help in retrieving (reading or calculating) or setting (writing) properties. Accessor declarations can be obtained by getting accessor, a set accessor, or both. For example:
// khai báo một thuộc tính Code có kiểu dữ liệu string: public string Code { get { return code ; } set { code = value ; } } // khai báo một thuộc tính Name có kiểu dữ liệu String: public string Name { get { return name ; } set { name = value ; } } // khai báo một thuộc tính Age có kiểu dữ liệu int: public int Age { get { return age ; } set { age = value ; } } For example
The following example illustrates the usage of properties in C #: create two classes named Student, TestCsharp as follows:
Student Class:
using System ; namespace QTMCsharp { class Student { private string code = "N/A" ; private string name = "unknown" ; private int age = 0 ; // khai bao thuoc tinh Code co kieu string: public string Code { get { return code ; } set { code = value ; } } // khai bao thuoc tinh Name co kieu string: public string Name { get { return name ; } set { name = value ; } } // khai bao thuoc tinh Age co kieu int: public int Age { get { return age ; } set { age = value ; } } public override string ToString () { return "MSSV = " + Code + ", Ho Ten = " + Name + ", Tuoi = " + Age ; } } } TestCsharp class:
dùng System;
using System.Reflection;
QTMCsharp namespace
{
class TestCsharp
{
static void Main (string [] args)
{
Console.WriteLine ("Property" in C # ");
Console.WriteLine ("------------------------------------");
// create a student doi tuong
Student s = new Student ();
// Learn the code, name and age for Student
s.Code = "001";
s.Name = "Minh Chinh";
s.Age = 21;
Console.WriteLine ("Student Information: {0}", s);
// fly an extra age 1
s.Age + = 1;
Console.WriteLine ("Student Information: {0}", s);
Console.ReadLine ();
Console.ReadKey ();
}
}
}
If you do not use the Console.ReadKey () command; then the program will run and finish (so fast that you can not see the results). This command allows us to see the results more clearly.
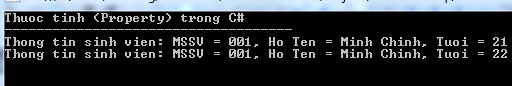
Compiling and running the above C # program will produce the following results:
Abstract attribute in C #
An Abstract class can have an abstract attribute, which should be implemented in the inheritance class. The following program illustrates this:
Create 3 classes named respectively Person, Student, TestCsharp as follows:
Abstract class Person :
sing System ; namespace QTMCsharp { public abstract class Person { public abstract string Name { get ; set ; } public abstract int Age { get ; set ; } } } Student Class:
dùng System;
QTMCsharp namespace
{
class Student: Person
{
private string code = "N / A";
private string name = "N / A";
private int age = 0;
// declare the code Code has string:
public string Code
{
get
{
return code;
}
set
{
code = value;
}
}
// declare the name of the string name:
public override string Name
{
get
{
return name;
}
set
{
name = value;
}
}
// Declare Age code has int int:
public override int Age
{
get
{
return age;
}
set
{
age = value;
}
}
public override string ToString ()
{
return "MSSV =" + Code + ", Ho ten =" + Name + ", Tuoi =" + Age;
}
}
}
Class TestCsharp
dùng System;
using System.Reflection;
QTMCsharp namespace
{
class TestCsharp
{
static void Main (string [] args)
{
Console.WriteLine ("Property" in C # ");
Console.WriteLine ("------------------------------------");
// create a student doi tuong
Student s = new Student ();
// Learn the code, name and age for Student
s.Code = "001";
s.Name = "Minh Chinh";
s.Age = 21;
Console.WriteLine ("Student Information: {0}", s);
// fly an extra age 1
s.Age + = 1;
Console.WriteLine ("Student Information: {0}", s);
Console.ReadLine ();
Console.ReadKey ();
}
}
}
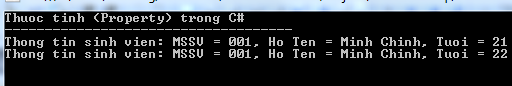
Compiling and running the above C # program will produce the following results:
According to Tutorialspoint
Previous lesson: Print pages in JavaScript
Next article: Objects in JavaScript