Plastic surface self-cleaning, even antibiotic-resistant bacteria can not cling to
Scientists Leyla Soleymani and Tohid Didar from McMaster University, Canada have successfully developed a plastic surface with chemically treated nano wrinkles capable of blocking all foreign molecules, not allowing they stick to it. That means, if a drop of water, a drop of blood or even a bacterium falls into it, it slips off and cannot stick.
As announced by the scientists, nanomaterials can self-clean up to 84-87% compared to conventional materials. Scientists dripped droplets of water containing MRSA (methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus), Pseudomonas (among the top 3 most dangerous bacteria) and E. coli on surfaces of common and nano materials. new self-cleaning. The results showed that nearly all Pseudomonas and E. coli bacteria were cleaned, only a small amount of MRSA bacteria remained on the new self-cleaning nanomaterials.
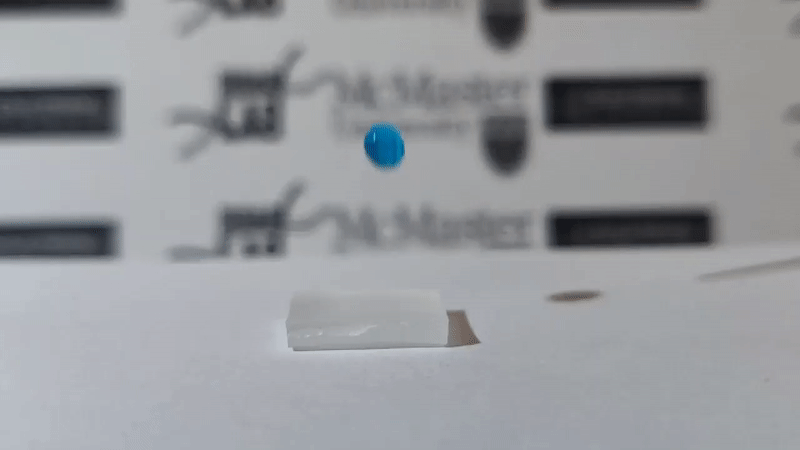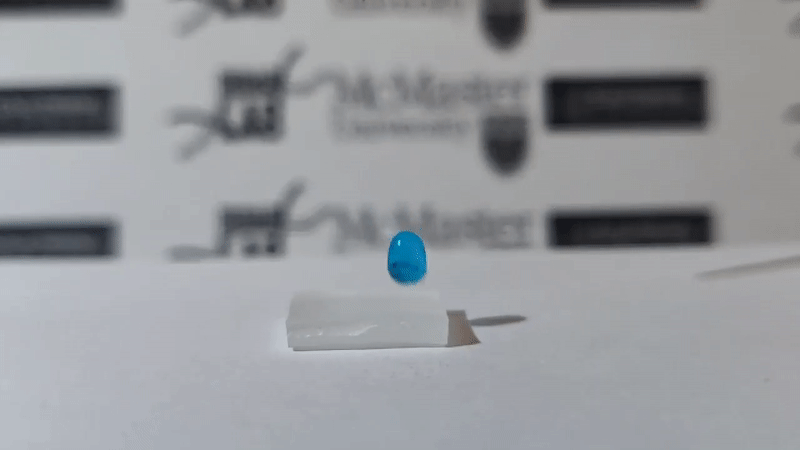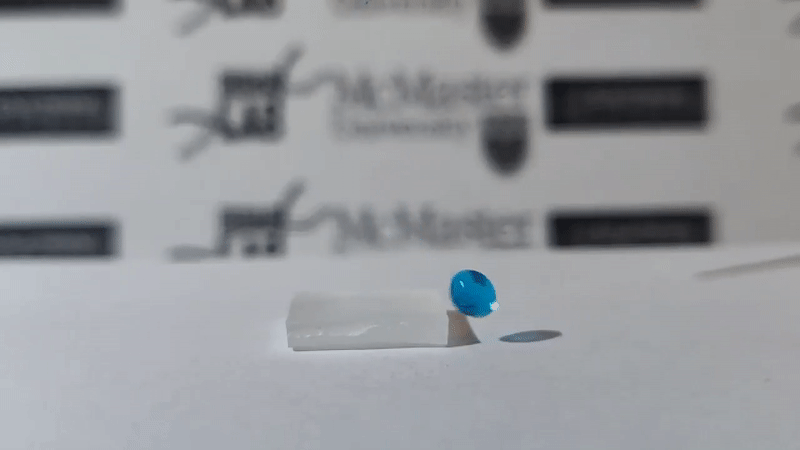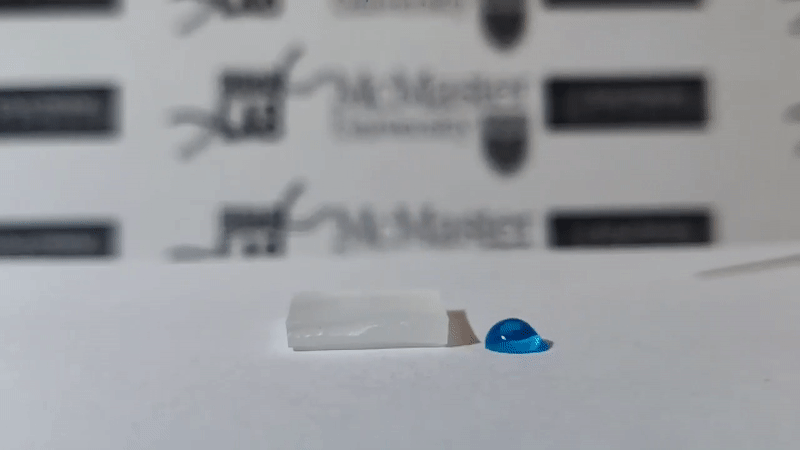
Soleymani said that the great thing is that this self-cleaning plastic surface is flexible, durable, simple and low-cost, and can be applied in all areas.
The scientists hope the new self-cleaning plastic surface can be coated on every surface in the hospital, from balustrades, hospital beds, infusion bags, and door handles, to prevent viruses. Antibiotic-resistant bacteria spread in medical environments. New self-cleaning materials can also be used as food packaging to help prevent the spread of pathogens between foods.
- Successfully fabricated flexible glass, which can only be bent, not broken
- Successfully manufactured meat from the air