Li explained the law of conserving energy with just one coin
Energy is a wonderful thing, exists around our lives, from energy that sustains life for people to energy to generate electricity . But to answer what energy is, not everyone give the correct answer.
Associate Professor of Physics Rhett Allain at Southeastern University of Louisiana has explained the law of conservation of energy through the story of three boys named Alby, Bobby and Cami to help anyone understand, what energy is.
And this is the story of these 3 guys:
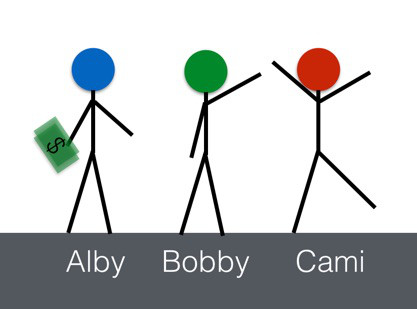
Alby has $ 10 and decides to give all the money to the other two. Bobby received $ 5 and Cami received $ 4.99.

One missing coin has disappeared. Could Alby have dropped?
In fact, that coin still exists even if Alby drops it and the sum added is still 10 USD.
This can also be considered a money-conserving law, whether it is a toy or a drop, the total amount remains unchanged before and after the event of losing money takes place. Money is just a tool people use to compare and exchange goods more conveniently, but no money can not .
In fact, energy is like money. The example below will show you that. When pressing a ball into a spring tube inside, there will be 3 states:
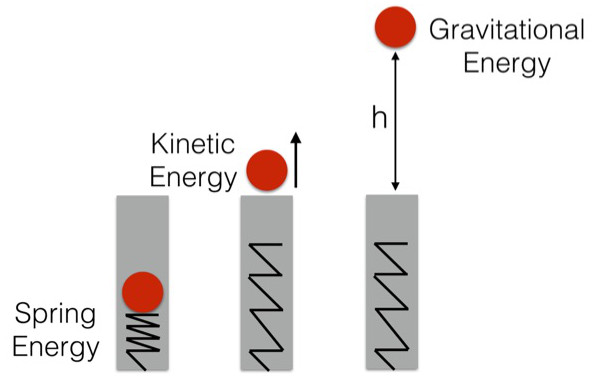
The energy stored in the spring causes the ball to be shot up. At this time, the ball has energy, called kinetic energy. When it reaches the highest height it can reach, the speed of the ball returns to 0 and at that point, it is pulled down by gravity.
Now, if you calculate the possible energy before the spring shoots the ball, suppose that is equal to 10 Joule (J). When released, it may have only 9J kinetic energy and 1J of gravitational force because the ball is now high. When the ball is climbing to the highest height, it has less momentum than the energy from gravity. When it has climbed to its highest level, it has enough 10J of potential gravity.
The total measurement of force is always a constant and is preserved despite constantly changing different forces.

And this is another, smaller example. The nucleus of an atom consists of protons and neutrons. The carbon 14 element consists of 6 protons and 8 neutrons, but it is not completely stable but will be radioactive decay, through a process called beta decay. The result is a nitro atom called nitro 14 and a single electron. They all have momentum and are calculated by the famous E = mc2 .
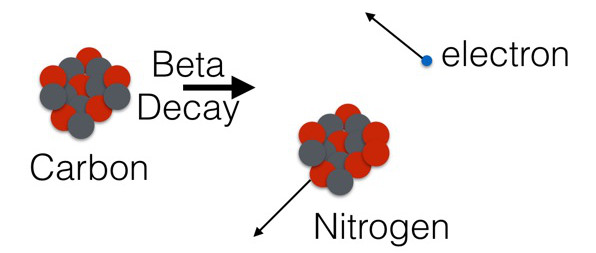
One can rely on the difference in carbon mass, nitro mass in decay to find the total amount of energy as well as the speed and kinetic energy from the other electrons. Suppose it is 10J and we get a value of 3.99J from carbon, then we can get 6J from nitro, so 0.1J energy does not go anywhere.
In 1930, Wolfgang Pauli, an Austrian-Swedish American physicist, conducted an experiment and showed that there was another particle during beta decay that kept this lost energy of 0.1J, which carried neutrino name.
In short, the total energy before and after the event must be equal, if there is a difference, there will be a mysterious element that we do not know.