How to Turn on JavaScript
Method 1 of 4:
Google Chrome
-
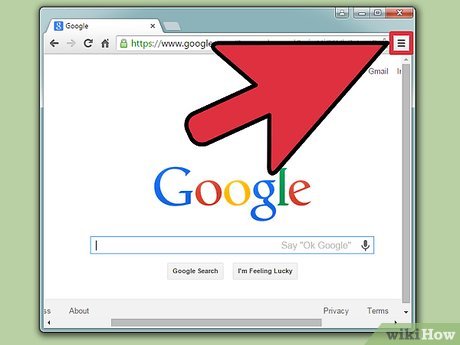
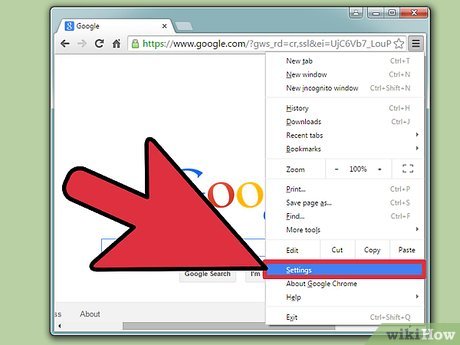
 Click the guide button. Click the icon that looks like three horizontal lines in the upper-right corner of the screen. This will open up a dropdown menu with a list of options.
Click the guide button. Click the icon that looks like three horizontal lines in the upper-right corner of the screen. This will open up a dropdown menu with a list of options. -
 Click Settings. From the dropdown menu, click the Settings option. It should be one of the last options. Clicking should open up a new tab in your Chrome window entitled "Settings."
Click Settings. From the dropdown menu, click the Settings option. It should be one of the last options. Clicking should open up a new tab in your Chrome window entitled "Settings." -
 Click the "Show Advanced Settings" link. Scroll down on the Settings tab to find the "Show Advanced Settings" link at the bottom of the page. Click this link to reveal more settings.
Click the "Show Advanced Settings" link. Scroll down on the Settings tab to find the "Show Advanced Settings" link at the bottom of the page. Click this link to reveal more settings. -
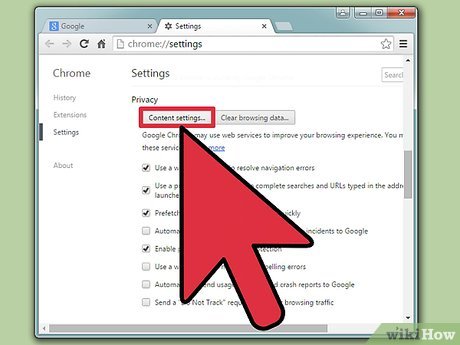
 Click the "Content Settings" button. Scroll down to find the Privacy header. Beneath that header, you should see a button entitled "Content Settings." After clicking the button, a new window should pop up.
Click the "Content Settings" button. Scroll down to find the Privacy header. Beneath that header, you should see a button entitled "Content Settings." After clicking the button, a new window should pop up. -
 Enable JavaScript. You should see a header called "JavaScript." Beneath that, check the option that says "Allow all sites to run JavaScript."
Enable JavaScript. You should see a header called "JavaScript." Beneath that, check the option that says "Allow all sites to run JavaScript." -
 Manage exceptions. Certain sites can use JavaScript in a malicious way to harm your computer. If you have experience with a site doing this, you can block certain sites from running JavaScript by clicking the "Manage Exceptions" button beneath the JavaScript header.
Manage exceptions. Certain sites can use JavaScript in a malicious way to harm your computer. If you have experience with a site doing this, you can block certain sites from running JavaScript by clicking the "Manage Exceptions" button beneath the JavaScript header.- Type in a web address and either choose to Allow or Block the site from running JavaScript. Then, click Done.
-
 Click Done. In the bottom-left corner of the Content Settings window, click the Done button to apply the changes.
Click Done. In the bottom-left corner of the Content Settings window, click the Done button to apply the changes. -
 Refresh your webpage. Refresh your webpage to see the changes that JavaScript makes possible.
Refresh your webpage. Refresh your webpage to see the changes that JavaScript makes possible.
Method 2 of 4:
Internet Explorer 11
-
 Open up Tools. Press the gear icon in the upper-right corner of the screen. Alternatively, press ALT + X. A drop down menu should pop up.
Open up Tools. Press the gear icon in the upper-right corner of the screen. Alternatively, press ALT + X. A drop down menu should pop up. -
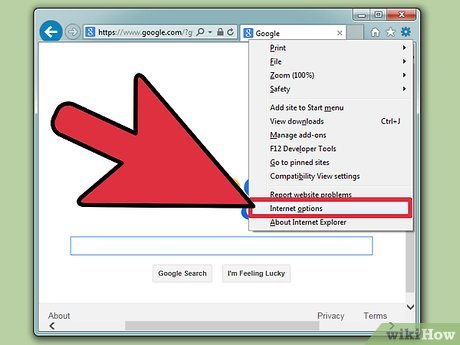
 Choose "Internet Options." From the dropdown menu, click on "Internet Options." It should be one of the last options. After clicking, a new window should appear.
Choose "Internet Options." From the dropdown menu, click on "Internet Options." It should be one of the last options. After clicking, a new window should appear.- Click on the "Security" tab. From the selection of tabs in the header, choose "Security." You should see options such as Internet, Local Intranet, Trusted Sites, and Restricted Sites.
-
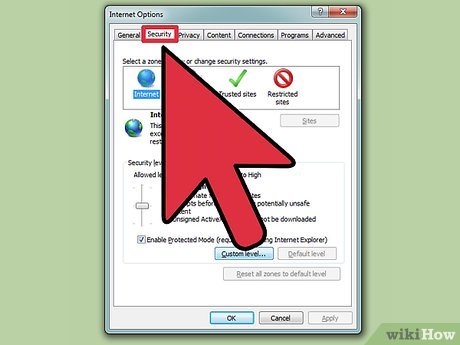
 Click on "Custom Level." Near the bottom of the window, click on the "Custom Level" button. After clicking, another new window should pop up.
Click on "Custom Level." Near the bottom of the window, click on the "Custom Level" button. After clicking, another new window should pop up. -
 Find the "Scripting" section. Scroll down the list of settings until you find the "Scripting" header. It will be close to the bottom of the list.
Find the "Scripting" section. Scroll down the list of settings until you find the "Scripting" header. It will be close to the bottom of the list.- You can also just keep pressing the 's' key to go through the words in the list that start with 's'. This way will be faster.
-
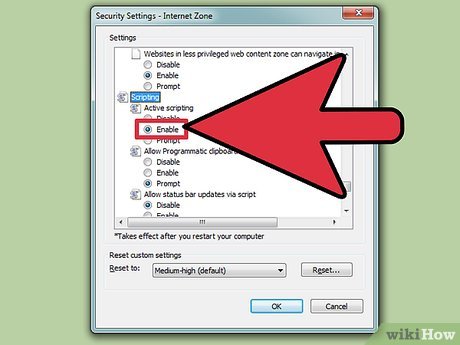
 Enable Active Scripting. Under the Scripting header, you should see an option for Active Scripting with three options beneath -- Disable, Enable, and Prompt. Check the Enable option.
Enable Active Scripting. Under the Scripting header, you should see an option for Active Scripting with three options beneath -- Disable, Enable, and Prompt. Check the Enable option. -
 Press OK. Press the OK button in the bottom right corner of both windows. Refresh the page you were on to see the changes.
Press OK. Press the OK button in the bottom right corner of both windows. Refresh the page you were on to see the changes.
Method 3 of 4:
Mozilla Firefox
-
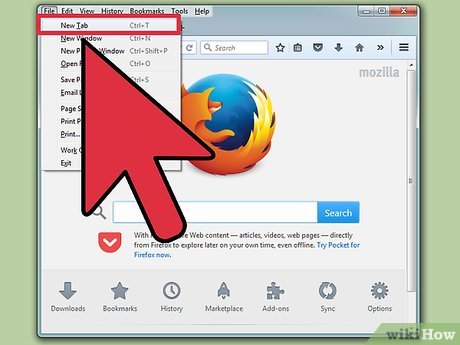
 Open a new FireFox window. The newest version of FireFox does not include a built-in way to disable or enable JavaScript. However, there is a way to work around this.
Open a new FireFox window. The newest version of FireFox does not include a built-in way to disable or enable JavaScript. However, there is a way to work around this. -
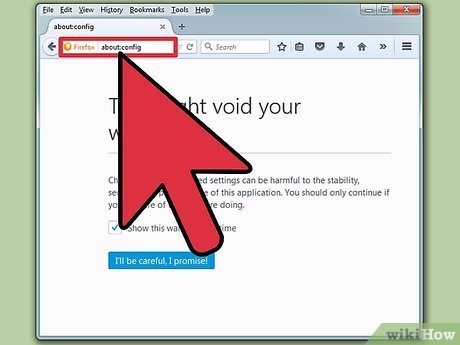
 Type about:config into the address bar. In your new FireFox window, type about:config into the address bar and press ↵ Enter.
Type about:config into the address bar. In your new FireFox window, type about:config into the address bar and press ↵ Enter. -
 Click "I'll be careful, I promise." Like the prompt says, disabling certain options in this page could disable your warranty or open up your browser and computer to malicious attacks. Try to stick to the task of enabling JavaScript.
Click "I'll be careful, I promise." Like the prompt says, disabling certain options in this page could disable your warranty or open up your browser and computer to malicious attacks. Try to stick to the task of enabling JavaScript. -
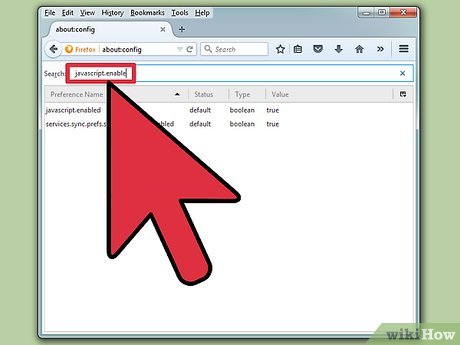
 Search for javascript.enabled. In the search bar in the upper portion of the window, search for javascript.enabled. You will see two results appear.
Search for javascript.enabled. In the search bar in the upper portion of the window, search for javascript.enabled. You will see two results appear.- Be sure you are searching in the right search bar. Type the query into the larger search bar, rather than the smaller one. The correct search bar will be the second one from the top of the window.
-
 Enable JavaScript. Right click on the javascript.enabled result and click Toggle. The value on the right should change from "false" to "true."
Enable JavaScript. Right click on the javascript.enabled result and click Toggle. The value on the right should change from "false" to "true."- Alternatively, you can just double click javascript.enabled to disable/enable JavaScript.
-
 Exit the window. Click the red X in the upper-right corner of the screen to exit the window and apply your changes. JavaScript should now be enabled and sites will function properly.
Exit the window. Click the red X in the upper-right corner of the screen to exit the window and apply your changes. JavaScript should now be enabled and sites will function properly. -
 Restrict certain sites. If you are security-conscious and would like to enable or disable JavaScript from running on certain sites, you will have to download Firefox Addons. One recommendation is: No-Script[1].
Restrict certain sites. If you are security-conscious and would like to enable or disable JavaScript from running on certain sites, you will have to download Firefox Addons. One recommendation is: No-Script[1].
Method 4 of 4:
Safari
-
 Open Preferences. While in a Safari window, click on "Safari" in the upper-right corner and then "Preferences" from the dropdown menu.
Open Preferences. While in a Safari window, click on "Safari" in the upper-right corner and then "Preferences" from the dropdown menu.- Alternatively, press ⌘ + , to open Preferences directly.
-
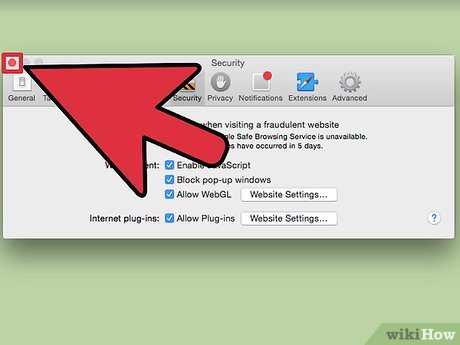
 Click on Security. From the taps on the top of the new window, click "Security"
Click on Security. From the taps on the top of the new window, click "Security" -
 Enable JavaScript. From the options next to the "Web Content" header, check the "Enable JavaScript" option.
Enable JavaScript. From the options next to the "Web Content" header, check the "Enable JavaScript" option. -
 Close the window. Press the red button in the upper left corner of the window to close the window and apply your changes.
Close the window. Press the red button in the upper left corner of the window to close the window and apply your changes. -
 Restart Safari. In order for the changes to take effect, you will have to restart Safari. You may, additionally, have to restart your Mac computer.
Restart Safari. In order for the changes to take effect, you will have to restart Safari. You may, additionally, have to restart your Mac computer.
Share by
Samuel Daniel
Update 05 March 2020