How strong a magnetic field can 'tear' you into subatomic particles?
Unlike animals like sea turtles, migratory birds, or even your pet dog, humans don't have a specific sense for sensing magnetic fields. That's why we sometimes forget that we live on the surface of a giant magnet: the Earth.
If you're standing in the middle of an open field, the magnetic field strength you're exposed to on the ground right now is between 30 and 60 microTesla. But if you move gradually from that empty field to near a telephone tower or high voltage power line, the strength of the magnetic field acting on you will increase up to 1,000 times.
The development of electronic and telecommunications technologies that apply the principle of electromagnetic fields is also making people more and more exposed to magnetic fields. The question is, do they have any effect on our body? And when do we have to be careful with magnetic fields?

Sometimes we forget that we are living on the surface of a giant magnet: the Earth.
Humans are exposed to magnetic fields daily and hourly
A magnetic field is a special material medium surrounding moving charged particles. That means whenever a charged particle such as an electron or a proton moves, they generate a magnetic field. Electric currents flowing through blenders, hair dryers, and even wires in your walls are all sources of magnetic fields.
Magnets are one of those special cases in which there are no charged particles moving back and forth, but their electrons rotate in place in the same direction, creating a magnetic field as well.
However, unlike the case of standing under a telephone tower above, the indoor magnetic environment in which you are exposed to all your electronic devices is usually very small. For example, a 220 V current flowing in the wire and power cord to the electronics in your home only creates a magnetic field of a few tens of microTesla.
But because the magnetic strength is attenuated by distance, if you were lying in bed right now, the magnetic field you are exposing yourself to from man-made sources in the room is only about 0.1 microTesla, even small. hundreds of times stronger than the Earth's magnetic field.
Cell phones are probably the most common source of electromagnetic radiation that many people keep close to them. But research shows that even at a distance of as close as 5.5 cm, mobile phones only generate a magnetic field strength of the order of 3-40 microTesla.
In comparison, the magnetic field exposure threshold recommended by the International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation Protection (ICNIRP) is up to 400 milliTesla, which translates to 400,000 microTesla.
It means that in most of our daily activities, our physical body and physical health are not affected by artificial magnetic sources around the house, street or office.
Cases where the magnetic field begins to affect your body
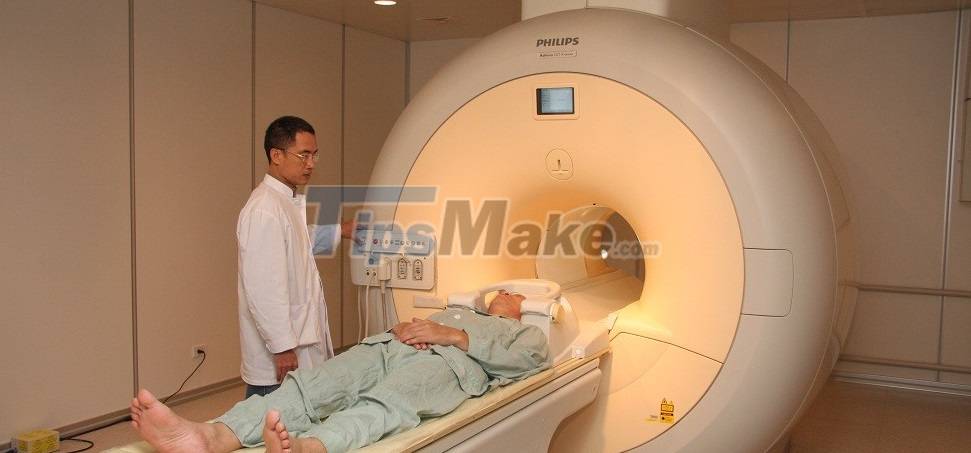
That's when you have to go to the hospital and lie on a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machine. This is a medical imaging device commonly used to detect bone and soft tissue injuries, and evaluate tumors or blood vessels in your body.
Magnetic resonance imaging machines (MRI) are devices that generate the strongest magnetic fields to which the average person can be exposed. Depending on the model, their magnetic strength can range from 0.5-3 Tesla or million microTesla. As you can see, this number has already surpassed the ICNIRP recommended threshold.
That's not to say that you shouldn't have an MRI scan when prescribed by your doctor. Because the machine only generates a static magnetic field, a brief scan of a few minutes to a few tens of minutes will not have much effect on your body.
With one exception, you shouldn't move your head around in a magnetic resonance machine, because that can make you nauseous, lose your balance, or even taste a metallic taste in your mouth (a million dollars). symptoms similar to those exposed to radiation).
The reason is because when you move inside a magnetic field, the variation of the magnetic flux creates electric currents. Your body, or specifically your brain, is working with nerve electrical signals, and so are the ion transport channels between cells.
Interference currents caused when you move through a strong magnetic field can interfere with these signals and cause side effects when you have an MRI without lying still in the machine.

In addition, there is another effect that some people may experience in strong magnetic environments such as those of an MRI machine, which is seeing flashes of light. This phenomenon, known as "magnetophosphenes," occurs when a strong magnetic field can stimulate light-sensing cells in the retina.
According to the scientists, the smallest magnetic field threshold that can cause phenomena like "magnetophosphenes" is about 10,000-20,000 microTesla - much lower than the magnetic field emitted by an MRI machine, but still higher. most of the electromagnetic environment in life.
Therefore, to be able to fall into a situation that makes you feel the magnetic field is not easy. In fact, with special labs, scientists can measure the alpha wave changes in your brain if they reverse the Earth's magnetic field (at the threshold of a few tens of microTesla).
However, these alpha waves did not cause any behavioral changes. In other words, your brain can sense them, but you yourself cannot.
In medicine, there are also some procedures that use weak magnetic fields to heal bones, because magnetic fields can enhance the activity of cells that produce bone and cartilage. However, when you put your injured leg or body part in it, you won't feel this magnetic field either.
When can a magnetic field tear your body apart?
To answer this question, we have to go to Paul Sutter, an astrophysicist at Ohio State University. That's because the sources of super strong magnetic fields that can cause great damage to the human body are actually not found on Earth.
On our planet, the largest man-made magnetic field that man can generate with a machine is only 2,800 Tesla. It will make the universe laugh, as a magnetar star, a type of neutron star that can generate magnetic fields as strong as MegaTesla to GigaTesla (108-1011 Tesla).
As you approach the poles of these magnetar stars, the magnetic field you come into contact with will be trillions of times stronger than the Earth's magnetic field. "A magnetic field this strong would start to cause surprising phenomena," Sutter said.
"At the atomic level, a strong magnetic field will move all the positive charges in your body in one direction and the negative charges in the other." The spherical atoms will be stretched out into ellipses and soon they will start to look like chewing gum being pulled from hand to hand by a child.
The basic chemical processes going on in your body will come to a halt. The normal forces and interactions between atoms and molecules in your body are disrupted. "The first thing you notice is that your entire nervous system, which relies on electrical charges moving throughout the body, goes down," says Sutter. "And then you're basically gone."

Fortunately, Sutter says, however, is that within a radius of several hundred light-years around Earth, our local galaxies don't have a single magnetar star. The nearest magnetar star is also tens of thousands of light years away.
In recent years, astronomers have not detected any strange supermagnetic objects heading towards Earth. Meanwhile, local massive stars cannot turn into magnetar stars when they die.
So, at least for now, we can raise the pillow above our bed without fear of any harmful magnetic field emitted from electronic devices in the room, as well as from outside. window of my house.
You should read it
- ★ 14 interesting facts about the universe amaze you
- ★ If stretched all the way, how big are the human organs?
- ★ What is magnetic water? The 1-0-2 properties of water from
- ★ Warning about air pollution levels: Find magnetic waste in the human brain
- ★ 18 interesting facts about the human body that make you say 'miraculous'