Detecting new particulate matter 4 times heavier than proton
The large particle accelerator (LHC) finally discovered a new type of particle four times heavier than the proton. Scientists call it "Xi cc + +" subatomic particles composed of two heavy quarks never seen before.
- Scientists have found a way to create "liquid light" easily
- Gravitational waves can be the key to revealing the existence of another dimension in the universe
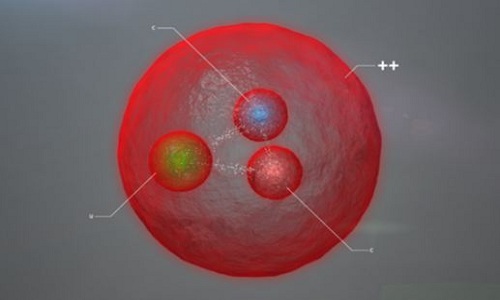
The new subatomic particle is called Xi cc + +.(Photo: CERN.)
For a long time, physicists have hypothesized that such particle combinations exist in nature but they have not found convincing evidence until now.
In 2012, scientists at the European Nuclear Research Organization (CERN) discovered 113 interactions in data collected and 313 interactions of particles in data collected in 2016.
This is the first time researchers have seen Xicc ++ with two such heavy quarks. Quarks form baryon masses such as protons and neutrons, most commonly in the universe. Many baryon particles combine together in atom, forming material constituent molecules.
Xi cc + + is an unstable baryon, it only exists for a very short time in the early universe so today there are no such particles. Scientists can only identify it through particles that are broken down or left behind.
Finding out the Xi cc + + particle is an important step for scientists to better understand how the world works.

The Large Particle Accelerator (LHC) is the world's largest and most accelerated modern particle accelerator built by CERN for the purpose of conducting multiple frontal collisions at high speeds between protons. . The LHC is housed in a circular tunnel circumference 27 km on the border between France and Switzerland.
You should read it
- ★ Large particle accelerator proves ghost does not exist
- ★ Life on Earth may have come from biological particles in cosmic dust
- ★ Finding new materials capable of detecting dark matter
- ★ Science has found evidence of the immortality of pseudo-particles: they replicate themselves after decay
- ★ Ancient particles provide insights into the birth and development of the world's oldest cities