Fog Computing - What is fog computing?
Fog computing extends the concept of cloud computing to a new level, making it an ideal for Internet of Things (IoT) and other applications that require real-time interaction.
What is fog computing?
Fog computing is the concept of a type of network construction that extends from outside boundaries where the data is created to where it will eventually be stored, whether it is in the cloud or in a visitor's data center. line.
Fog is another layer of distributed network environment and is closely linked to cloud computing and Internet of Things (IoT). Public infrastructure as a cloud service provider (IaaS) can be considered a high end and global endpoint for data. Network boundaries are where data from IoT devices are created.
Fog computing is the idea of a distribution network connecting these two environments. Mung Chiang, Principal of Purdue Technical University and one of the nation's leading researchers in fog computing, said: 'Fog computing provides the missing link for data to be pushed. to the cloud and what can be locally analyzed at the boundary. "
According to the OpenFog Consortium, a group of suppliers and research organizations supports the advancement of standards in this technology, fog computing is' structure equivalent to the system level, resource allocation and translation. computer, store, control and connect anywhere from Cloud to Everything. '
Benefits of fog computing
Basically, the development of the fog computing framework gives organizations more options for data processing wherever it is best to do this. For some applications, data may need to be processed as quickly as possible - for example, when used for production purposes, connected machines need to be able to respond to incidents as soon as possible. good.
Fog computing can create low-latency network connections between analytical devices and endpoints. This structure in turn reduces the amount of bandwidth needed compared to all data being sent back to a data center or cloud for processing. It can also be used in situations where there is no bandwidth connection to send data, so it must be processed near where it was created. As an added benefit, users can place security features in a foggy network, from segmented network traffic to virtual firewalls to protect it.
Application of fog computing
Fog computing has just been officially deployed, but there are many different use cases that have been identified as ideal and potential scenarios for fog computing.
The cars are connected

The birth of semi-autonomous and self-driving cars will merely increase in quantity. Independent cars require the ability to locally analyze certain data in real time, such as surroundings, driving conditions and directions. Other data may need to be returned to the manufacturer to help improve vehicle maintenance or monitor vehicle use. A foggy computing environment will allow transmission of all these data sources at both the boundary (in the vehicle) and to its endpoint (manufacturer).
Smart city and smart grid
Like connected cars, these utility systems are increasingly using real-time data to increase efficiency for systems. Sometimes this data is in remote areas, so processing near it is essential. Other times, data needs to be aggregated from a large number of sensors. The fog computing structure can be given to solve both of these problems.
Real-time analysis
A variety of use cases require real-time analysis. From production systems it is necessary to be able to react to incidents when they occur, to financial institutions using real-time data to inform trading decisions or fraud monitoring. The implementation of fog computing can help facilitate data transfer between the place of creation and the many places where data needs to come.
5G fog computing and mobile computing

Some experts believe that deploying 5G mobile connections in 2018 and beyond can create more opportunities for fog computing. "5G technology in some cases requires very strong deployment of antenna networks," explains Andrew Duggan, senior vice president of network planning and network architecture at CenturyLink. In some cases, the antennas need to be separated within a distance of less than 20 km. In such a use case, the fog computing structure that can be created between these stations includes a centralized controller that manages applications running on this 5G network and handles the connect to data centers or cloud.
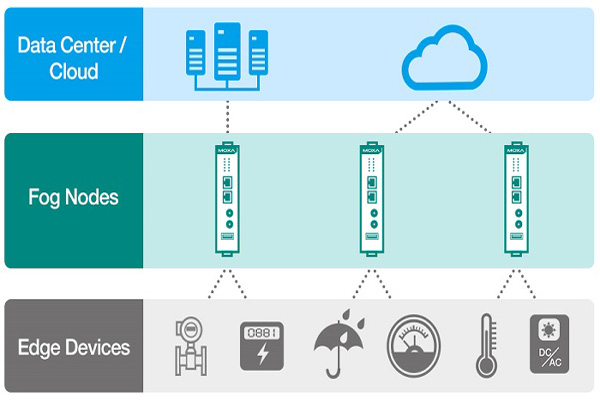
How does foggy computing work?
A fog computing structure can have many different components and functions. It may include foggy gateways that accept data from collected IoT devices. It may include a variety of wired and wireless detailed data collection endpoints, including routers and switches. Other aspects may include customer premise equipment (CPE) and ports for accessing limited nodes. The foggy computing structures with higher stacks will also reach central networks and routers and eventually global cloud servers and services.
The OpenFog Consortium Association, the reference architecture development team, has outlined three goals to develop a foggy computing framework. Fog environments should be able to expand horizontally, meaning that it will support multiple use cases along the industry; can work in the cloud with everything constantly; and is a system-level technology, extending from everything, through network limitations, through the cloud and across various network protocols.
Is fog computing and boundary computing the same?
Helder Antunes, senior director of strategic innovation at a Cisco company and a member of the OpenFog Association, says boundary computing is a component, or a subset of fog computing. Imagine the fog computing as the way data is processed from where it was created to where it will be stored. Boundary computing only refers to the data being processed near where it was created. Fog computing includes not only boundary computing but also network connections needed to carry that data from the boundary to its endpoint.
See more:
- Build your own computing cloud system with Ubuntu
- This is why 10 years from now, every company will use blockchain
- Review important milestones in the history of more than 60 years of artificial intelligence development