Computers isolated from the internet can still be hacked via the network card LED
Israeli researcher Mordechai Guri has discovered a new method to steal data from air-gapped computers. The method, called ETHERLED, turns the blinking LED lights on network cards into Morse code that can be decoded by hackers .
To capture the signals, a hacker needs a camera with a direct line of sight to the LEDs on the network card of an air-gapped computer. These can be translated into binary data to steal information.
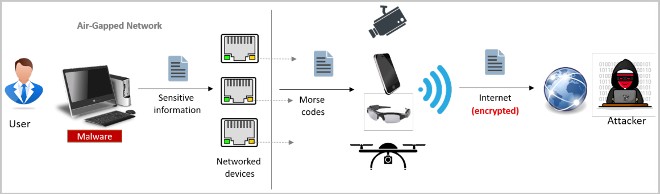
Air-gapped computers are computer systems that are typically installed in highly sensitive environments (e.g. critical infrastructure, weapons control units, etc.). For security reasons, these computers are isolated from the public internet.
However, they still have network cards to connect to the internal network. Mordechai Guri discovered that if hackers can install special malware that replaces the video card driver with software that modifies the LED color and flashing frequency, they can send encrypted data to the outside.
The ETHERLED method can be used on other peripherals and hardware that use LEDs as status indicators such as routers, NAS, printers, scanners, etc.
Compared to previously disclosed data exfiltration methods that monitor keyboard and modem LEDs, ETHERLED is a more covert and less likely to raise suspicions.
Details about ETHERLED
The attack begins by installing malware on the target computer that contains modified firmware for the network card. This allows the hacker to control the frequency, duration, and color of the LED flashes.
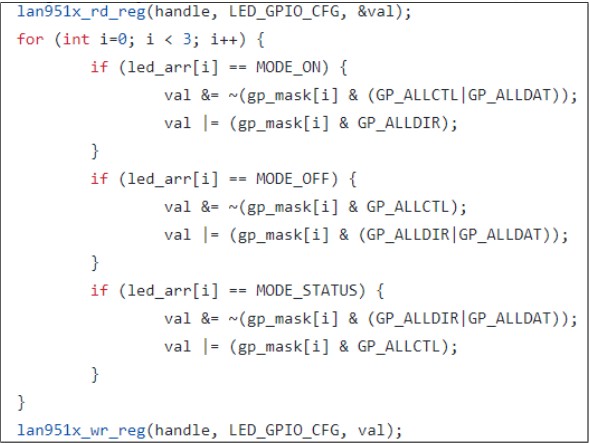
Additionally, malware can directly attack the drive containing the network interface controller (NIC) to change the connection state or adjust the LEDs needed to generate the signal.
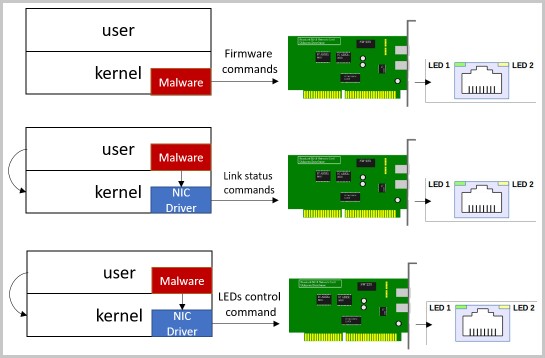
The researcher discovered that the malicious driver can exploit hardware functionality to control network connection speed and enable or disable the Ethernet interface, resulting in flickering and color-changing lights.

Guri's tests showed that each data frame begins with a 1010 sequence, to mark the start of the packet, followed by a 64-bit payload.
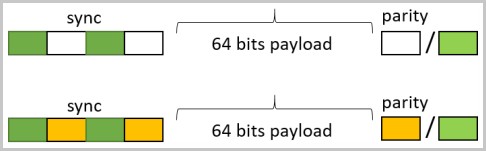
For filtering data through single status LEDs, Morse code dots and dashes lasting from 100ms to 300ms are generated, separated by indicator off intervals ranging from 100ms to 700ms.
Morse code bitrate can be increased up to 10 times (10m dots, 30m dashes and 10-70ms spacing) using driver/firmware attack method.
To capture signals from a distance, hackers can use anything from smartphone cameras (up to 30 meters), drones (up to 50 meters), hacked webcams (10 meters), hacked surveillance cameras (30 meters), and telescopes or cameras with telephoto or super zoom lenses (over 100 meters).
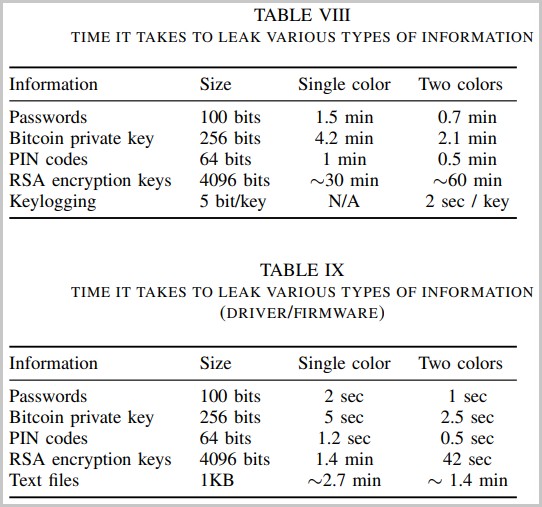
The time it takes to leak secrets like passwords via ETHERLED ranges from 1 second to 1.5 minutes, depending on the attack method used. For complex data like Bitcoin wallet keys, it takes 2.5 seconds to 4.2 minutes, and 42 seconds to 1 hour with a 4096-bit RSA key.
You should read it
- Learn about SQL Injection and how to prevent it
- What is SS7 attack? What can hackers use it for?
- The 13-year-old 'Hacker' enters the school's computer system to create a 'list of the most hated kids'
- It turns out this is how hackers attack your computer through the main screen
- Russian Hacker performs a new attack tactic
- There has been hack Among Us and this is how you find out hacker
 Google: AI can help increase productivity by 122 hours per year
Google: AI can help increase productivity by 122 hours per year Instagram is about to launch Edits to compete with CapCut
Instagram is about to launch Edits to compete with CapCut This Man Successfully Performed Nuclear Fusion at Home with the Help of AI
This Man Successfully Performed Nuclear Fusion at Home with the Help of AI iPhone turns into 'heater' when using Apple Intelligence
iPhone turns into 'heater' when using Apple Intelligence OpenAI Introduces ChatGPT Projects: New Features to Organize Smarter Conversations
OpenAI Introduces ChatGPT Projects: New Features to Organize Smarter Conversations Microsoft: TPM 2.0 in Windows 11 is mandatory and 'non-negotiable'
Microsoft: TPM 2.0 in Windows 11 is mandatory and 'non-negotiable'