6 most vulnerable Wi-Fi security errors
TipsMake.com - In this article we will list the 6 biggest Wi-Fi security errors that users often get with the aim of helping you avoid and protect your wireless network better .
Wireless network offers a lot of convenience in use. However, in contrast to convenience in use, there are complexities in security issues. Here are six of the most common security mistakes that we often make when setting up and using a wireless network. Avoiding this problem, your network and data will be safer.
6 typical Wi-Fi security errors
1. Do not encrypt or use only insecure WEP security
Wireless network encryption is necessary for two reasons: it does not allow non-authenticated users to connect to the network and prevent eavesdropping of Internet traffic. If random users can connect to the network, they can access your shared folders or other network resources. If they can eavesdrop, they can capture the password or hijack the website or the logged-in service accounts do not use SSL encryption.
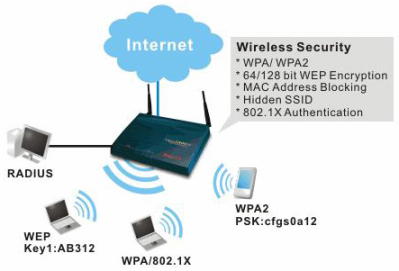
Remember that WEP encryption is not safe and it can be cracked easily. At the very least, you should use WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK. These two security modes will encrypt traffic and prevent unauthorized access. However, they are still vulnerable to brute force attacks, so create and use strong encryption passwords (passphrases). Use long passwords (up to 63 characters) and mix characters, numbers, special characters, .
2. Do not use WAP2-Enterprise securely with 802.1X authentication
All wireless networks used by organizations and businesses with multiple employees should use WPA-Enterprise security mode. This security mode requires a separate server (this server is called a RADIUS server) to perform 802.1X authentication, but in some cases access points can be used to support the RADIUS server function. go with. There are also many services (such as AuthenticateMyWiFi) that support the whole process.
This Enterprise mode increases security and allows you to manage better access to Wi-Fi networks. Instead of having to use the same password on all computers and wireless access devices, you can assign each user a separate account or a digital certificate that they must use to connect. So when an employee leaves a company or a device is lost, you only have to change one account. If you use WPA-Personal mode, you must change the password on all your access points, computers, and devices.
WPA-Enterprise mode also prevents users on the wireless network from eavesdropping on traffic of other users. Unlike the case of using Personal mode, users cannot use hacker software applications to capture passwords and take control of other users' accounts.
3. Do not secure the 802.1X client settings
If you are using WPA-Enterprise mode, you should configure all user accounts with a complete security level to prevent 'man-in-the-middle' attacks. In the client's EAP settings (such as Windows), make sure it is set to validate the server certificate, the server address to be pre-set and choose the root CA certificate.
4. Trust in MAC address filtering
MAC address filtering is always provided in wireless routers and access points. It allows you to define a list of authorized computers and devices that are not allowed to connect, based on the MAC address of the devices.
However, the MAC address can still be faked easily. Someone may know a certain MAC address is authenticated and then change the MAC address on their computer like the authentic MAC address, it is perfectly possible to connect. Never use MAC address filtering on unencrypted wireless networks. You can imagine, if you don't allow others to access the network but your network is not encrypted, it can still be eavesdropped.
If using encryption, you can use MAC address filtering to manage which computer or device the user authenticates to connect to the wireless network.
5. Trust in hidden SSIDs
Wireless routers and access points allow you to hide network names (SSIDs). This is a way for strangers to detect your network, but SSID still appears in some packets. They can completely use special tools (free and easy to find) to quickly discover your hidden SSID. This method only blinds ordinary users and not prevents hackers.
It can be assumed that hiding an SSID is like adding another layer of security - making it difficult for attackers - but it should be noted that this approach makes network usage even more difficult as well. reduce network performance. This is because you have to manually create a profile on your computers and devices, because you cannot see them and click to connect. This problem also generates a lot of data that is not worth the network, accidentally reducing network bandwidth.
6. There is no restriction on the SSID that an employee can connect to
One of the most often overlooked security issues is that users can easily connect to other wireless signals. These signals can be transmitted from an unsecured Wi-Fi router, belonging to another organization or set up by a hacker to steal user credentials. Users can intentionally connect, for example, to avoid web filtering, or not intentionally. However, in any case, it can expose your computer or device to malicious scams.
In Windows Vista and later versions, you can set a limit for the SSID to view and connect to the network through the netsh wlan command from the Command Prompt. This method cannot be performed in Windows XP. And make sure that the configured settings allow you to automatically connect to available networks and delete other networks from the list of favorite networks.
You should read it
- ★ Microsoft patches new security for Internet Explorer
- ★ How to fix BlueKeep security error for Windows 2003, Windows XP, Windows 7, Windows Server 2008
- ★ IBM developed a new technology to patch security holes
- ★ Cisco bit 4 dangerous product WLAN Controller error
- ★ Security bugs on iOS 13 still exist on iOS 13.1, users note