5 gangs that create the world's most dangerous ransomware
Below, Tipsmake lists 5 groups that create the most dangerous ransomware in the world today. According to research, these ransomware groups are not supported or sponsored by any state.
DarkSide
DarkSide is the group behind an attack that rocked the US fuel industry in May, shutting down the fuel distribution network of the Colonial Pipeline plant, raising concerns about gasoline shortages.
August 2020, DarkSide started to gain popularity. The group attacked large companies, causing them to malfunction and disrupt. The group will then demand ransom from the victims. Often such companies will pay cyber insurance, so it's easier for ransomware groups to make money.
DarkSide carries out ransomware attacks, meaning the masterminds often hide their identities to reduce responsibility. After receiving the victim's ransom, they will divide that amount.
REvil
The REvil ransomware group is currently attracting attention because it is attacking Kaseya. Previously, REvil attacked the world's largest meat processing company JBS. REvil is active in 2020-2021.
In April, REvil stole technical data on unreleased Apple products from Quanta Computer, the Taiwanese company that assembles Apple laptops. The attackers demanded a $50 million ransom to not make the stolen data public. It is not yet clear whether this amount has been paid or not.
Clop
Clop was founded in 2019. Clop's signature attack method is 'double blackmail'. Clop demands a ransom in exchange for the decryption key, restoring access to the stolen data to the victim. However, after that, Clop demanded more ransom so that they would not make the stolen data public.
Historical attacks show that victims who pay a ransom once are more likely to pay again. So hackers will tend to target the same organization, demanding more ransom next time than last time.
Syrian Electronic Army
Far from a typical ransomware gang, the Syrian Electronic Army has been conducting online attacks since 2011 for political purposes.
The group's attack method is to distribute fake news through reputable sources. In 2013, a fake tweet created by the Syrian Electronic Army appeared on the AP's Twitter, causing billions of dollars to "fly" from the stock market.
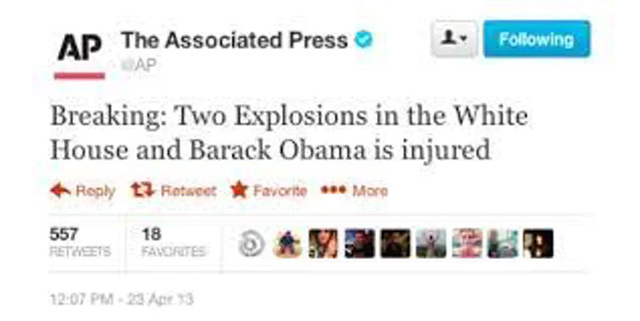
In fact, the Syrian Electronic Army's exploits make most people believe the fake content they create.
FIN7
If this list had a 'supervillain' name, it would be FIN7. Russia-based FIN7, arguably the most successful ransomware group of all time. FIN7 has been operating since 2012.
Many of FIN7's attacks have gone undetected for years. They exploit cross-attack scenarios and stolen data for many purposes. For example, FIN7 demands a ransom, while using the stolen data itself against the victim, such as reselling the stolen data to a third party.
In early 2017, FIN7 was accused of being behind an attack on companies that provided records to the US Securities and Exchange Commission. This confidential information was mined and used for ransom, which was then invested on the stock exchange.
As such, the groups have made huge amounts of money by trading stolen information and data. Cyberattacks over the years are the reason why it's impossible to quantify the exact amount of money that damages the economy. However, it is estimated that the amount of money paid to ransomware gangs is more than 1 billion USD.
You should read it
- ★ Viber website and database are hacked
- ★ REvil ransomware gang sites mysteriously stop working ngừng
- ★ This is the world's fastest ransomware, encrypting 53GB of data in just over 4 minutes
- ★ This ransomware strain is trying to disable Windows Defender and Malwarebytes
- ★ Discover the process of manufacturing terracotta army nearly 8,000 mysterious soldiers of Qin Shihuang