What is IP spoofing? And what is a denial of service (DoS) attack?
To access your network, the external computer must 'win' a trusted IP address on the network. So an attacker must use an IP address within your network. Alternatively, an attacker can use an external but reliable IP address on your network.
1. What is IP spoofing?
When a computer outside your network is 'pretending' to be a trusted computer in the system, this attacker's action is called IP Spoofing.
To access your network, the external computer must 'win' a trusted IP address on the network. So an attacker must use an IP address within your network. Alternatively, an attacker can use an external but reliable IP address on your network.
IP addresses may be trusted by the system because these addresses have special privileges on critical resources on the network.
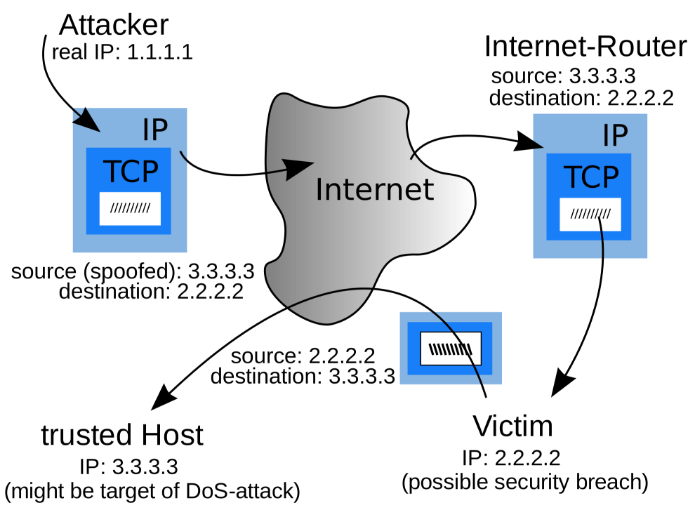
What are some different ways to attack IP Spoofing?
- Attack data or set commands that exist on the data stream being converted between a client and Server application (server).
- Attack data or commands in peer-to-peer network connection.
However, an attacker must also change routing tables on the network. Changing routing tables on the network allows an attacker to get two-way communication. For this purpose, an attacker "targets" all routing tables into a fake IP address.
Once the routing table has changed, the attackers start receiving all the data transferred from the network to the fake IP address. Even these impostors can respond to data packets like a trusted user.
2. Denial of Service (DOS) (denial of service attack)
You may think that a denial of service (DoS) attack is the version of the IP address Spoofing. Unlike IP Spoofing, in a denial of service (DoS) attack, an attacker doesn't need to worry about getting any response from the server they target.
The attacker will attack the Flood-style system with a lot of requests, making the system 'busy' responding to requests.
If attacked in this form, the targeted server will receive a TCP SYN and respond to a SYN-ACK. After sending a SYN-ACK, the attacker waits for a response to complete the TCP handshake - the process never happens.
Therefore in the process of waiting for a response, the attacker will use system resources and even the server has no right to answer other legitimate requests.
Refer to some of the following articles:
- 6 ways to view IP addresses on computers, smartphones or Tablet
- 6 simple ways to find the fastest computer IP address
- Steps to change IP addresses on computers and Macs
Wish you have moments of fun!