Warning: Quantum Ransomware is being rapidly deployed in lightning attacks
This is a completely new strain of ransomware, first discovered in August 2021. Quantum Ransomware is dangerous in that it can perform attacks with strong intensity and escalate quickly. , leaving system administrators as well as defense systems with very little time to react. In typical attacks, the threat actor often uses the IcedID malware as one of the initial access vectors to the target system. This is a bridge to deploy Cobalt Strike to remotely access the system, leading to data theft and encryption using Quantum Locker.
The security team at The DFIR Report analyzed the technical details of a typical Quantum ransomware attack. The results showed that the attack lasted only 3 hours and 44 minutes, from the time of initial infection until the malware completely encrypts the entire device. This is clearly a 'shocking' number for any defense system.
Use IcedID as the initial access bridge
The Quantum ransomware attack observed by DFIR used the IcedID malware as initial access to the target system, most likely through a phishing email containing an ISO attachment.
IcedID is a banking trojan module used for the past 5 years, mainly to deploy second stage payloads, loader and ransomware. The combination of IcedID and ISO archive has tended to be used in recent Quantum ransomware attacks, with its remarkable ability to bypass email security control barriers.
Two hours after the initial infection, threat actors inject Cobalt Strike into the C:/Windows/SysWOW64/cmd.exe system process to avoid detection.

At this stage, intruders will steal Windows domain credentials by destroying LSASS's memory, allowing them to propagate horizontally across the network.
"For the next hour, the threat agent makes RDP connections with other servers in the infection environment. After handling the domain layout, the threat agent prepares to deploy the ransomware by copy malicious code (named ttsel.exe) to each server via the C$ share' folder, the DFIR team detailed in the report.
Finally, the threat actors used WMI and PsExec to deploy the Quantum ransomware payload and encryption devices.
As mentioned, the entire attack took place in less than four hours. More importantly, they often happen late at night or on the weekend, leaving network administrators and operators in a passive state and making it difficult to respond to an attack in a timely manner.
What is Quantum Locker?
Quantum Locker Ransomware is a rebrand of the MountLocker ransomware operation, which appeared in September 2020.
Since then, this ransomware gang has rebranded to various names, including AstroLocker, XingLocker and now Quantum Locker.
The rebranding to Quantum is credited to August 2021, when the ransomware encoder started adding the .quantum extension to encrypted filenames and removed a ransom note called README_TO_DECRYPT.html.
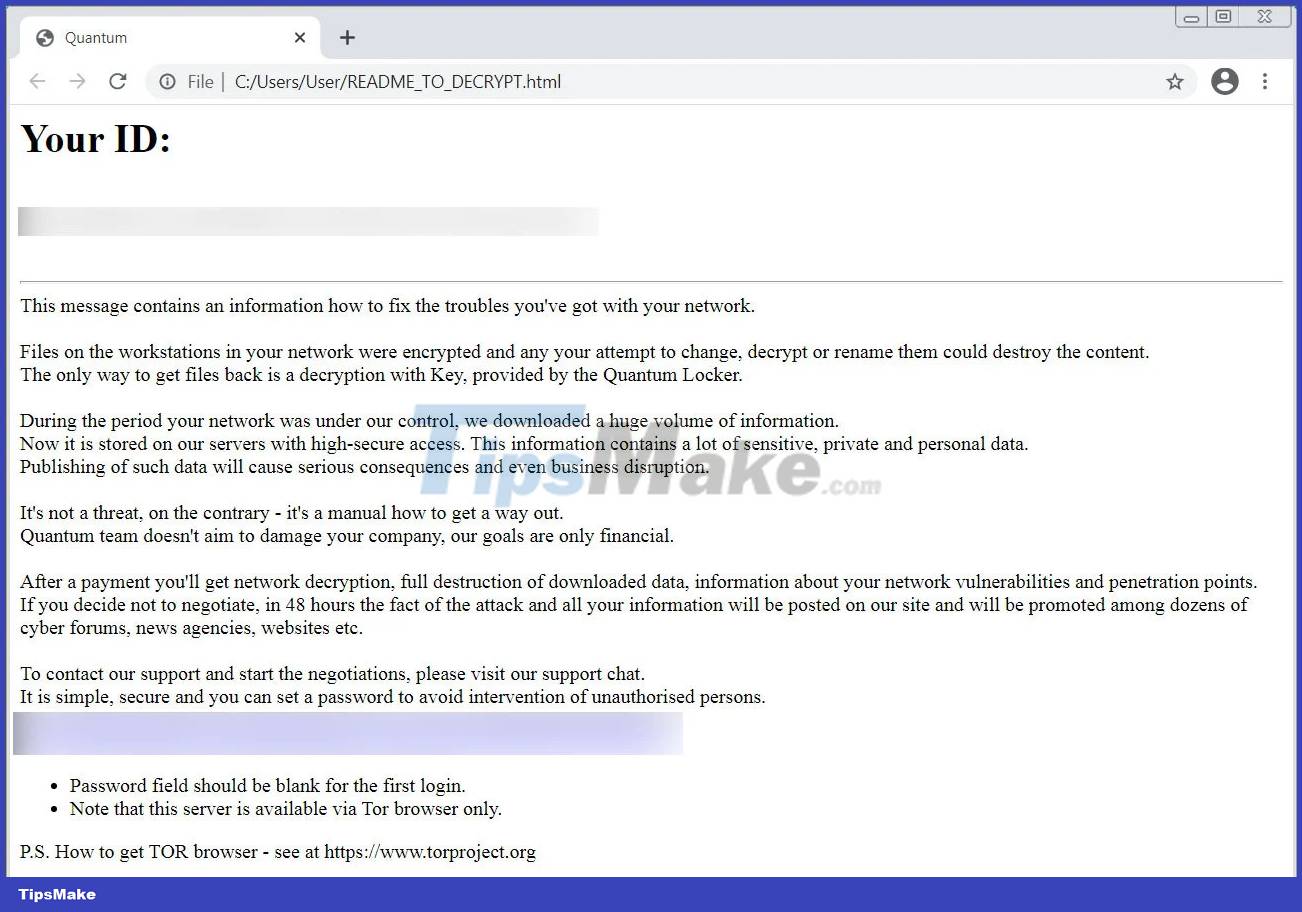
The contents of the note include a link to a Tor ransom negotiation website, and a unique ID associated with the victim. The ransom notes also indicate that data has been stolen and will be released if the ransom is not paid. The ransom ranges from 150,000 to millions of dollars.
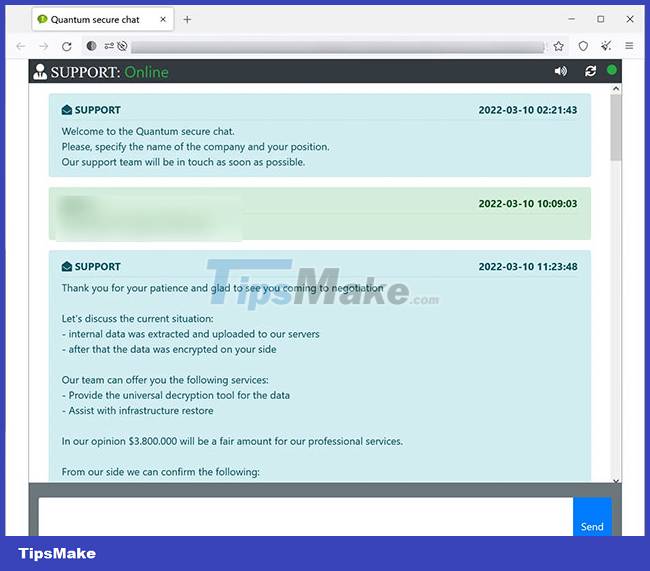
The danger of the Quantum Locker is undisputed. Fortunately, the activity of this ransomware strain is not very active with only a handful of attacks recorded each month.
You should read it
- What is quantum computing and how did people develop this technology?
- New chip technology can enhance quantum computing
- For the first time successfully implementing underwater quantum teleportation, China took the lead in the quantum communication race
- China successfully developed 'handheld' quantum satellite communications equipment
- List of the 3 most dangerous and scary Ransomware viruses
- Quantum computing - the future of humanity
 HP publishes a series of critical vulnerabilities in the Teradici PCoIP protocol
HP publishes a series of critical vulnerabilities in the Teradici PCoIP protocol Notorious hacker group Hafnium deployed malicious code to target Windows, Microsoft stood still
Notorious hacker group Hafnium deployed malicious code to target Windows, Microsoft stood still New banking malware discovered that can remotely control Android devices
New banking malware discovered that can remotely control Android devices Malware spreads through crack software specializing in stealing Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter accounts
Malware spreads through crack software specializing in stealing Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter accounts VMware patches RCE Spring4Shell vulnerability on a wide range of products
VMware patches RCE Spring4Shell vulnerability on a wide range of products GitLab patches critical vulnerability that allows hackers to take control of accounts
GitLab patches critical vulnerability that allows hackers to take control of accounts