Things you need to know about 'Germanium' - Germanium
Germanium ( or Germanium ) is a silvery-white, shiny, but brittle metal that is very brittle and fragile. Germanium is an important component in semiconductors and fiber optic cables. Some people believe that germanium is beneficial for health, but no research has proven that these claims are true.
 Germanium is a silver-white needle. This is a germanium polycrystalline piece about 2-3 cm long, weighing about 12 grams.Photo source: Jurii / Creative Commons
Germanium is a silver-white needle. This is a germanium polycrystalline piece about 2-3 cm long, weighing about 12 grams.Photo source: Jurii / Creative Commons
General properties of Germanium
- Number of atoms (number of protons in the nucleus): 32
- Chemical symbols ( in the periodic table of elements ): Ge
- Atomic mass: 72,63
- Density: 5,323 grams / cm 3 ( 3,077 ounces / inch 3 )
- Material state: solid
- Melting temperature: 938.3 degrees C ( 1720.9 degrees Fahrenheit )
- Boiling temperature: 2833 degrees C ( 5131 degrees F )
- The number of natural isotopes ( atoms of the same element have different numbers of neutrons ): 5. In addition, there are 19 artificial isotopes created in the laboratory.
- The most common isotope: Ge-74 ( 36.28% natural quantity ), Ge-72 ( 27.54% natural quantity ), Ge-79 ( 20.84% natural quantity ), Ge- 73 ( 7.73% of natural quantity ), Ge-76 ( 7.61% of natural quantity )
History of germanium
On the Chemistry Explained website, the existence of germanium was predicted by a Russian chemist , Dmitri Mendeleev, in 1869, after adding to the periodic table of elements. Arrange elements by atomic weight leaving some empty cells in the periodic table. According to theory, Mendeleev said: " There are a number of elements that have not been discovered, including element number 32 ". In 1885, a German chemist, Clemens Winkler , discovered the same missing element of the silicon group and called it " eka-silicon ", the element in the ore called acgirodik . In ore atoms contain silver, sulfur, iron oxide and zinc with about 7% of unknown metals.
According to Chemistry Explained, Mendeleev predicted that element 32 would have a density of 5.5 grams / cm 3 ( 5.5 times the density of water ) and atomic mass of 70 ( nearly 4 times the atomic weight). of water ). In fact, germanium atom has a density of about 5,323 grams / cm 3 and atomic mass is 72,630. Mendeleev 's precise prediction increased the chemistry order in the periodic table.
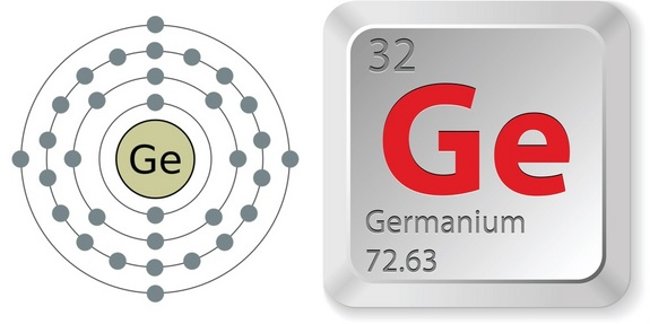 Electronic configuration and elemental properties of Germanium.(Photo source: Greg Robson / Creative Commons, Andrei Marincas Shutterstock)
Electronic configuration and elemental properties of Germanium.(Photo source: Greg Robson / Creative Commons, Andrei Marincas Shutterstock)
Things to know about Germanium
- According to Los Alamos National Laboratory, Germanium is a non-metal, which means it has both metallic and non-metallic properties. The other needles in the periodic table are boron ( Bo ), silicon ( Sliclic ), arsenic ( Arsenic ), antimony ( Antimony ), tellurium ( Telua ) and polonium ( Poloni) .
- According to Chemicool, Germanium is one of the few elements that grows when frozen like water. Other elements include gallium ( gallium ), silicon ( silicon ), bismuth ( Bitmut ) and antimony ( Antimony ).
- According to Jefferson Laboratory, the name " germanium " is derived from the German " germania " Latin - the name of Winkler 's countryside.
- According to Chemicool, the abundance of germanium in the Earth's crust is about 1.5 parts per million by weight and in the solar system is about 200 parts per billion by weight.
- According to Emily Darby , a chemistry student at Harvey Mudd University, the value of Germanium was recognized during World War II, when she used a high-resolution radar receiver. Soon after, the first transistor radio was invented.
- According to the US Geological Survey, the approximate percentage of Germanium applications is: 30% due to infrared ( IR ) optics including measuring devices; 20% fiber optics used in communications; 20% of polyester resin is used to produce a wide range of products such as fabrics, food containers and plastic; 15% used in electronics and solar cells; 5% is used in phosphorus, metallurgy and organic substances including medicines.
- According to Los Alamos National Laboratory, Germanium is primarily mined with zinc ore as well as acgirodik, germanite and coal. According to Chemistry Explained, Germanium is mined in Alaska, Tennessee, China, England, Ukraine, Russia and Belgium.
For health
There are many claims that Germanium is beneficial to health including strengthening the immune system, providing oxygen to the body and removing toxins from the body. According to the Healthline website, Germanium also helps in the treatment of allergies, asthma, arthritis, HIV / AIDS and other cancers.
However, science has yet to prove these statements. According to the Healthline website, the use of Germanium supplements or drugs containing Germanium can lead to many side effects such as kidney failure, anemia, weakness and lack of coordination in the body and increased liver enzymes.
According to Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center: " In studies, derivatives of Germanium called" spirogermanium "have been shown to prevent cancer cells from spreading, but some studies have been conducted. Onions of the human body show side effects and are not suitable for treating against cancer . "
Recent studies

According to a study published in 2016's Applied Physics Letters, Germanium is often used in detectors in different fields. The study discusses the high efficiency of Germanium photodetectors when used in visible light and near infrared rays. Germanium detectors are compared to conventional silicon photodetectors, and according to the authors, there is a better signal of the signal-to-noise ratio and the purpose of the spectrum on the lamp is can be observed by detector.
According to LaserFocusWorld, Germanium has been tested for use in semiconductors due to semiconductors or easily capable of sending electrons to a higher energy state, common in semiconductor metals. These photoconductors are used in many technologies in our daily lives such as remote control, automatic rolling doors in large stores and fiber optic communication systems as well as in Many scientific applications in astronomy, laboratory research and environmental control. The increase in efficiency is due to higher absorption of Germanium in optical detectors than traditional materials such as silicon, in order to receive more and more information in the target wavelength length.
You should read it
- ★ Successfully fabricated new conductive 2D materials at the speed of light
- ★ 6 'most powerful' women in Silicon Valley
- ★ Antiferromagnetism: A miracle material that can replace silicon in the field of memory chips
- ★ Linux 6.2 officially supports Apple Silicon
- ★ Silicon Valley engineers rushed to send their children to the 'old night school' for fear of the harmful effects of technology