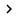Open WiMAX - telecommunications revolution (Part I)
Ensuring open and coordinated access between manufacturers' devices, Open WiMAX (open WiMAX) brings the telecommunications market a centralized environment for service operators. With Open WiMAX - the new telecommunications revolution, the benefit of the telecommunications service provider is always guaranteed.
So what is Open WiMAX? Open WiMAX is a completely open IP architecture for WiMAX access networks and has been validated and tested by the WiMAX Forum in accordance with the specifications given by the WiMAX forum NWG forum. With open technology design, standardization and coordinated technology, Open WiMAX has opened the door to a complete system that impacts network equipment, customer terminals, service delivery and experience. of the end user.
Mobile WiMAX system components and main interfaces
The diagram above shows the main network components and standard interfaces of a mobile WiMAX system. Interfaces among the various elements of the system were named and defined by the WiMAX Forum NWG. The R6 interface is a specially focused interface.
R6 connects the WiMAX radio access network (RAN) to the service provider's IP network through the ASN-GW access service network gateway. ASN-GW is a component of the system that acts as a gateway between the WiMAX network and the IP network and is also responsible for mobile management in the WiMAX network by providing roaming capabilities between radio stations. connect. Open WiMAX needs an open, standard R6 interface and clear separation between RAN function and IP network function. That enhances the coordination between many WiMAX device manufacturers.
Compared to R6, R3 connects the IP-based access service network (ASN) to the service provider connection network. The focus is less than the R3 interface for the following reasons: The majority of the carrier's CAPEX investment costs are focused on components around the R6 interface. Service providers all need the flexibility to choose base stations and ASN-GWs ports from potential manufacturers as well as the manufacturer's high competitiveness in the products they offer. .
R3 currently has the key components of WiMAX network and is fully IP-capable. Here, major manufacturers are in a fully open IP environment, including: many manufacturers, various types of supply and high competition among manufacturers. Therefore, the focus point is the characteristics of the R6 interface, where the major telecommunications equipment manufacturers are keen to create high confidence in the solution they offer.
R6 is the main interface 'Bridging' between the RAN network and the IP network. Controlling this bridge will provide a strategic advantage position to influence other interfaces. The NWG defines three types of implementation profiles for the R6 interface. Profile C defines Open WiMAX. The NWG also defines profiles A and B. Profile B hides the R6 interface in a locked black box. Profile A allows combining radio functions and IP functions in stations and ASN-GW, with different components tightly clamped so that other manufacturers cannot implement integration. In addition, Profile C allows to perform both flat and hierarchical ASN-GW system configurations and profile A only supports hierarchical configuration. In summary, in Profile C, the Radio Resource Management (RRM) function is only available in BTS with a faster roaming mechanism and optimization. In Profile A, the RRM function is included in ASN-GW (slower roaming) and Profile B does not allow the function of the R6 interface to be performed so that the roaming effects depend on the exclusive operation of the station.
Open WiMAX - telecommunications revolution (Part II)
My Dinh