How to Make 3D Plots Using MATLAB
Part 1 of 3:
Constructing the Domain
-
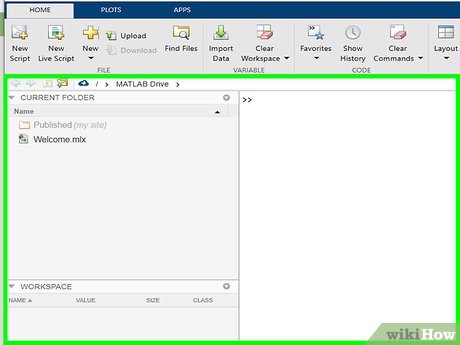
 Open the command window. In the default layout this should appear automatically as the biggest window displayed.
Open the command window. In the default layout this should appear automatically as the biggest window displayed. -
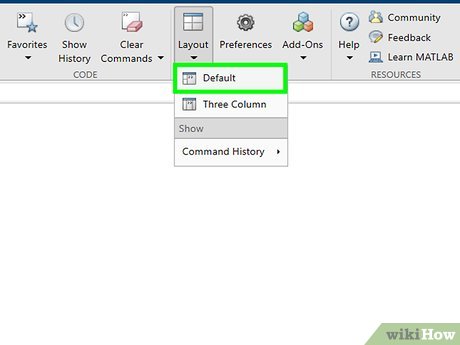
 If the command window isn't present, select home in the upper left corner. Afterwards, select layout and then "Default".
If the command window isn't present, select home in the upper left corner. Afterwards, select layout and then "Default". -
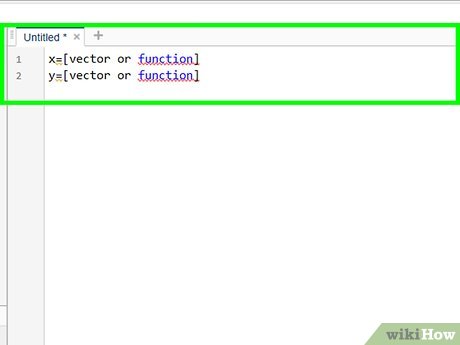
 In the command window, define both of your x and y vectors.
In the command window, define both of your x and y vectors.- This is typically done in the form of x=[vector or function] and y=[vector or function]
- Remember to use the dot operator when multiplying or dividing vectors and matrices. Otherwise errors will occur.
Part 2 of 3:
Producing the Grid in the xy-Plane
-
 Define a relationship between x and y. In order to accomplish this, two commands must be used.
Define a relationship between x and y. In order to accomplish this, two commands must be used.- The first is the mesh function. By using this, the result will be a wireframe mesh graph.
- The other is the surf function. When using surf, the result will be a 3-D surface plot.
-
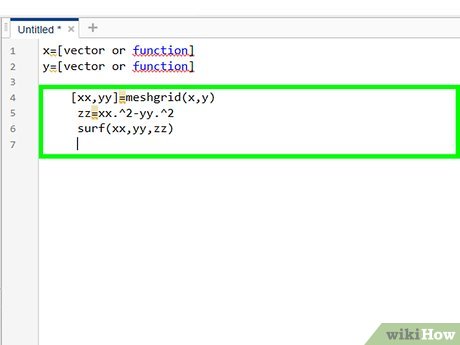
 When using mesh, input meshgrid to the command window.
When using mesh, input meshgrid to the command window.- The command will be formatted as follows: [xx,yy]=meshgrid(x,y).
- In the workspace window you will see that the variables xx and yy have been defined.
Part 3 of 3:
Defining "zz" and Plotting the Surface
-
 Define zz in terms of xx and yy because of its reliance on those sets of data.
Define zz in terms of xx and yy because of its reliance on those sets of data.- Use the relationship you know exists between x and y. This is likely to be a function or formula.
- e.g., zz=xx.^2-yy.^2
-
 Plot the surface using the surf command.
Plot the surface using the surf command.- From the z components in the matrix "zz", the surf command will create a 3-D shaded surface.
- This is the point in which you will relate xx, yy, and zz together.
- The actual command line will be in the format of surf(xx,yy,zz) .
-
 Watch for your new window to appear showing your 3-D plot.
Watch for your new window to appear showing your 3-D plot. -
 Customize as you'd like. There is a toolbar at the top of the window where the new plot has appeared. This toolbar contains many options and features that can be used to manipulate your 3-D plot.
Customize as you'd like. There is a toolbar at the top of the window where the new plot has appeared. This toolbar contains many options and features that can be used to manipulate your 3-D plot.- Some of these options include:
- Inserting a label for the x, y, or z axis
- Inserting a legend to help readers
- Rotating the plot in it's 3-D space
- Inserting a light source to show the effects of shadows
- A list of complex surface properties can be found at http://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/examples/changing-surface-properties.html
- Some of these options include:
-
 Smooth the color map across the entire surface of the graph, if you'd like. This is done by using the command line shading interp.
Smooth the color map across the entire surface of the graph, if you'd like. This is done by using the command line shading interp.
Share by
Kareem Winters
Update 05 March 2020
You should read it
- ★ Color command in Windows
- ★ Surface Pro 3 receives new updates, improves drivers for the Surface Pen
- ★ How to add 'Open command window here as administrator' to the right-click menu on Windows 10
- ★ How to use the command history function in Command Prompt
- ★ Surface Book 3 officially launched, becoming the most powerful Surface