How to create a Gigabit Ethernet cable with simple tools
A wired Ethernet connection has a higher bandwidth than a wireless connection. They are also very reliable, with no bandwidth loss due to wireless interference. Wired connections always have less latency, which is essential when playing online games.
You may prefer to use a wireless connection for convenience. Even so, you should still connect the backbone network (between routers) with a cable. Wired network routers and switches have a remarkably long lifespan. Making your own LAN cable is easy and requires only inexpensive tools. Once you get the hang of it, your wired network will be not only fast, but also very neat.
Necessary tools to create LAN cable/Ethernet jumper
These are the tools needed to make LAN cables:
- CAT . wire
- RJ45 . Connector
- Crimping pliers
- Ethernet cable tester

What kind of cable to use?
Having evolved over the decades, Ethernet cables provide a faster network connection than WiFi. Each cable has 8 wires twisted into 4 pairs.
The wires carry the signal and each cable supports a certain frequency. The higher the frequency, the larger the bandwidth. Choosing the right Ethernet cable is the first and most important step to achieving the desired network speed.
The speeds of Ethernet CAT cables (types) vary on their maximum length as follows:
| Model CAT | Frequency | Network speed |
| Cat5 | 100 MHz | 100 Mbps |
| Cat5e | 100 MHz | 1 Gbps |
| Cat6 | 250 MHz | 1 Gbps |
| Cat6A | 500 MHz | 10 Gbps |
| Cat7 | 600 MHz | 10 Gbps |
| Cat8 | 2000 MHz | 40 Gbps |
The price difference between the cables is not much, and the reasons for choosing gigabit Ethernet are clear. Cat6A balances both performance and price well. It is best to choose a cable that supports at least 10 Gbps.
You may not be using the full bandwidth right away if your router and switch are 1 Gbps. But in doing so, you don't have to tear down walls to change cabling. The good news is that all cables are backwards compatible.

Straight cable press
Straight cables, as the name suggests, have the same pin configuration on both ends of the cable. In this example, both ends of your straight cable will have a T568B pin configuration.
1. The Ethernet cord comes with a thick sleeve for protection. You need to remove this cover to reveal the wire inside.

2. Remove about 4cm of cover. Place the cable in the cutter section, twist a few times, and pull outward to remove the sheath.

3. Ethernet cable has 4 pairs of wires inside. Disconnect these pairs of wires.
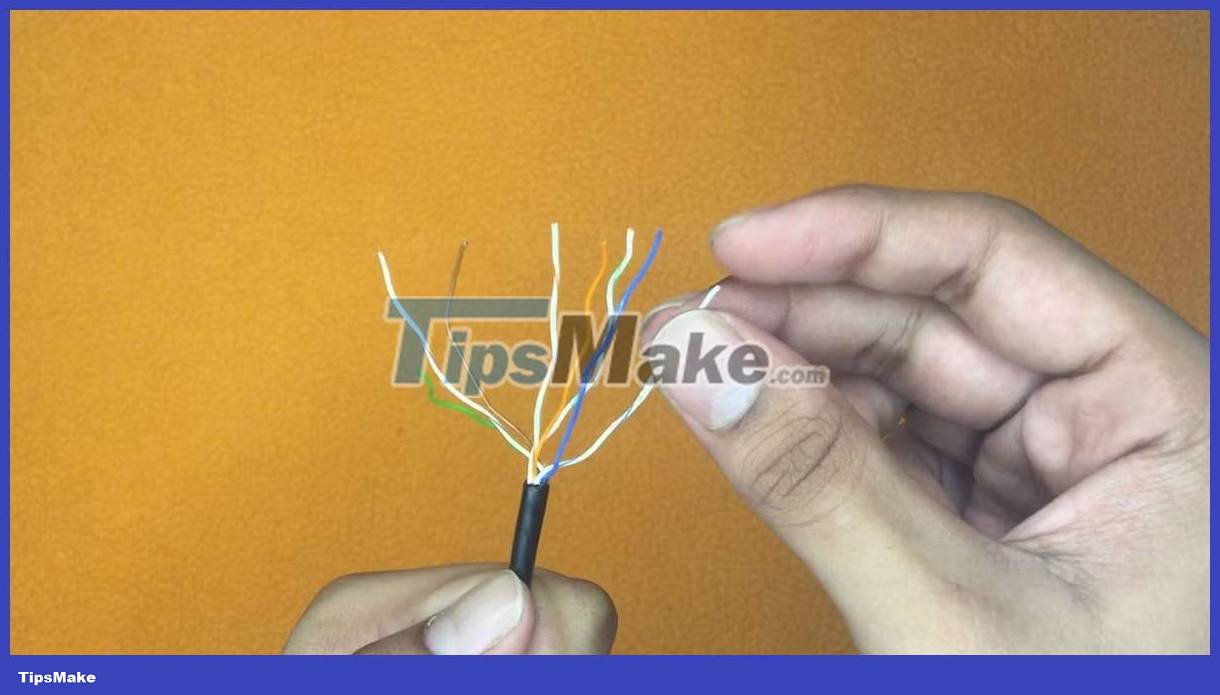

4. Straighten the wires and place them in the correct order, according to color code T568B.

5. Carefully push the wires into the RJ45 connector. You can easily tell if the arrangement of the wires is correct through the connector.
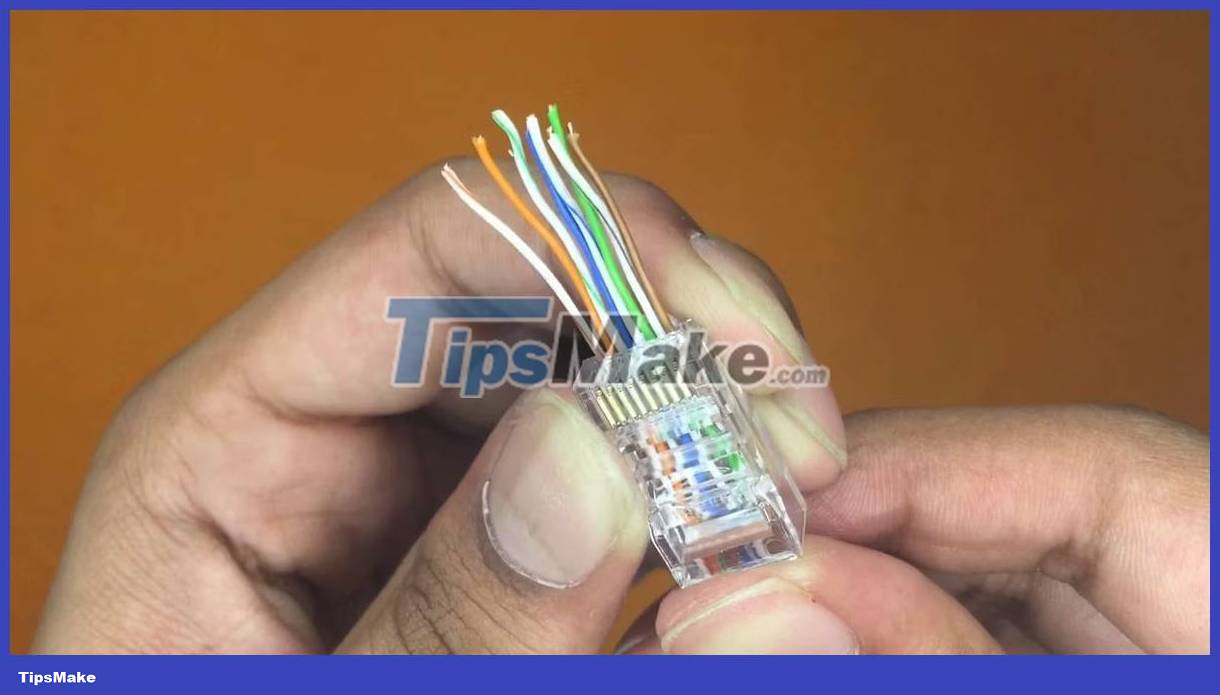

6. Place the RJ45 connector into the network clamp, and then press it with full force for a few seconds.

7. Cut off the excess wire with the cutter part of the pliers.

8. You need to use a cable tester to check the quality of the cable. Insert the ends of the newly created Ethernet cable into the test device.

9. Turn on the tester and it will indicate whether the connections are complete or not. The LEDs will light up in sequence while the machine checks each pin.
Crossover cable
Straight cables are useful when connecting a computer's Ethernet port to a router. But what if you want to connect two computers without using any network devices in between?
To do this, you need to use a special type of wire, called a crossover cable. One end of the cable still follows the T568B standard. The wiring of the other end will be different: The transmit (TX) pins terminate at the receive (RX) pins on the other end. This eliminates the need for network equipment in between.
Many newer Ethernet cards have auto-sensing. Therefore, they will automatically detect the pinout. This facilitates the use of straight cables for use as crossover cables. However, if you have older equipment, you will need a true crossover cable.
The figure below is the pinout of the gigabit crossover cable. It is also backward compatible with 100 Mbps Ethernet cards. The left jack is T568B; the one on the right is another wired jack.

The cabling process is the same. Once done, use a cable tester to test the connections. As you can see, the LEDs glow in a cross-pin arrangement.
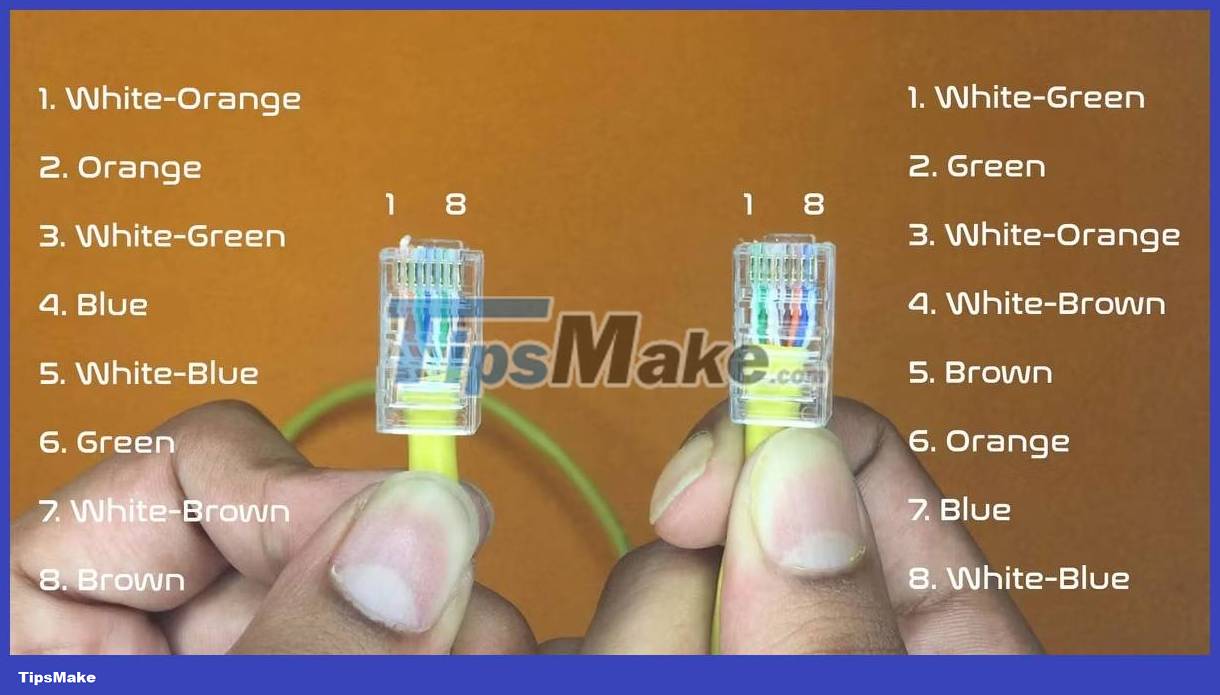
Crossover cable is very fast, even faster than straight cable transmitting data through router or switch. The reason is that switches have buffer memory that stores and forwards data. The crossover mechanism does not need to store packets, so it can operate at the theoretical maximum speed. Crossover cables are also used to connect a hub to another hub or a switch to another switch - essentially the same device.