Database security (common usage guidelines)
Recently, the database security issue has spread widely on the mass media and Internet news network. The first is the Slammer worm and most recently the illegal access to more than 8 million credit card numbers.
Many people ask the question: ' Do system administrators administer the wheel after they work? . Like the Internet was bombed. People often use cheaper facilities of web-based information systems, so they become lazy to apply basic security measures.
The problem here is to apply safety measures to a wise system administrator. The first question for executives is usually ' How fast is it ', not ' How many dangers ' as before. To solve the current problem, we must first adjust the consciousness and thoughts in each person.
We now provide some of the following basic security methods. Hope they will help you more or less protect important databases.
Base security structure
Businesses now seem too focused on each security component but forget the overall picture: ' If there is no basic security organization system, any security policy will fail. .
The system administrator often manages security according to his or her own preferences, with no or only a few supervisors from a higher manager. This raises questions:
- Who guarantees that the system administrator follows the security guidelines?
- How does an organization ensure all system administrators update the latest patches?
- What does an organization take to ensure the latest patch has been tested to make sure it does not become a cause of system failure?
- Who verifies security for the entire corporation or corporation?

An example of an effective and clear network security organization
Despite having a proper structure, you still encounter clutter in important issues like security. These messy problems cause many major fluctuations, such as:
Jim at the East Coast office updated all patches but he had an unsafe connection with Bill on the west coast. This brother failed to set up a suitable configuration for the firewall. And just that is enough for a total attack.
Before such cases, you need a full review when setting up the basic security structure.
Now, after we have the basic security organization for the system, we will begin to consider the technical issues of database security.
Database vulnerability (want to war on security!)
Database security can basically be attacked in the following areas:
- Security services (Server Security)
- Database connections (Database Connection)
- Table access control (Table Access Control)
- Restrict database access (Restricting Database Access)
Security services (Server Security)
Server Security is a program that limits real access to database services. This is the most important aspect of security, so you should carefully plan it.
Its basic idea is: ' You can't access what you can't see '. This is not a web server and should not be an anonymous connection. When you need to provide information to dynamic web, your database should not be placed on the same machine as the web server. That is not only for security purposes but also for the implementation process. If the database is in response to the web server, the configuration only allows connection to that web server.
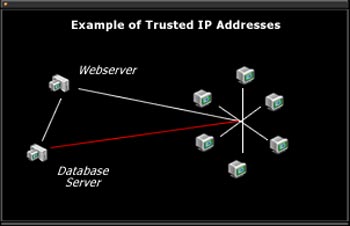
Access trusted IP addresses, limit database services only in response requests from known IP web servers
Trusted IP address
Each server should only configure permissions for trusted IP addresses. Similar to your home, you don't allow your child to talk to strangers, so here you should know exactly who is entitled to 'talk' to the database server.
If the endpoint is a web server, it should only allow that web server address to access the database server. If the database server provides information for the main application running on the local network, then the address limit should be limited to the local network only.
Do not leave weak status of web databases on the same server with internal database information.
Database connections (Database Connection)
Dynamic applications are now becoming the reason why many people update databases directly without evaluation. If you allow users to update the database via the website, make sure that the update is safe. For example, with SQL source code, a regular user should never enter data if that data has never been considered.
If you need to use an ODBC connection, make sure that only some users have access to shared files. Have every employee in your company had the right to have all the keys of every room in the company? Therefore, never allow user accounts to use all connections and data sources on the server.
Table access control (Table Access Control)
Controlling table access is one of the most overlooked forms of database security. Because it is very difficult to inherit and apply it. Proper use of table access control requires the cooperation of both system administrators and database developers. And we all know that 'cooperation' is a strange word in the IT industry.
Many users will charge for having access to the system by the system administrator for the database to be public. Or if the table is only used for the system level, why does it have other access rights besides admin rights.
Unfortunately, the proper table structure, relational database, and development issues are not in the scope of this article. Maybe we will discuss more carefully in the next article.
Restrict database access (Restricting Database Access)
This is the final milestone in the database security review we are reviewing. The main problem in this section is the network access system, which focuses on internet databases. Most of the targeted attacks are network-based databases, all web-based applications have ports for attackers to 'listen'.
Cybercriminals are now mostly using simple 'port scan' methods to find open ports that are defaulted to the common database system. Saying is the default because you can change the ports to the listener service, which is a good way to avoid attacks.
They will first try to detect whether a machine has a specific address. They use ping commands, simply by opening a command prompt window and typing the keyword 'ping', for example:
C: ping 127.0.0.1
good
root @ localhost: ~ $: ping 127.0.0.1
Answers can be in the form of:
Pinging 127.0.0.1 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 127.0.0.1: bytes = 32 timeReply from 127.0.0.1: bytes = 32 timeReply from 127.0.0.1: bytes = 32 timeReply from 127.0.0.1: bytes = 32 timePing statistics for 127.0.0.1:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms
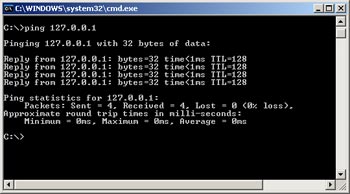
Example of ping command
Today's cybercriminals know very well the system's answers to these addresses. The first preventive measure is to disable ICMP packets. It can also prevent replies from ping requests.
There are many ways to prevent Internet access. Each database system has a unique set of components as well as the operating system. Here are just a few methods:
- Trusted IP addresses : UNIX services are configured to answer only ping commands in a trusted host list. In UNIX, complete this by configuring the rhosts file, restricting server access to a specific user list.
- Disabling the server account : If you are suspending an ID server after three wrong passwords, you have postponed the attack. Otherwise, an attacker can run a program that generates millions of passwords until it guesses the correct user ID and password.
- Special functions : you can use some products like RealSecure by ISS. It sends an alert when an external service is trying to violate your system security.
Oracle database has many testing methods:
- Kerberos Security : This is a popular 'ticket', helping to avoid having to use a basic authentication system.
- Virtual private database ( VPD ): VPD technology can limit access by selecting some rows of columns.
- Grant-execute security : The privilege to execute a subroutine can be tightly combined with the user. When a user executes a subroutine, they are granted database access, but only within the scope of the subroutine.
- Authentication services : Security authentication services provide predefined identities to external users.
- Port access security : All Oracle applications are listened to directly at a specific port on the server. Like any other standard HTTP service, Oracle Web Listener can be configured to restrict access.
Hopefully with the above basic knowledge, you can eliminate or at least minimize the risk of attack for the database. Database security is very important and pay close attention.