black hole, white hole, deep hole
A black hole is a concept that is no longer new to most astronomers and physicists. In this article I will try to write in a short and understandable way possible about the concepts: black holes, white holes and deep holes.
Black hole
The first prediction of black holes (or some Vietnamese documents translated as black holes) started very soon right after Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity was born in 1916. Black holes were proposed by Karl Schwarzschild as a predict solutions for space described by Einstein's school equations. This is in theory until the discovery of neutron stars, the first evidence of gravitational collapse after stars burn off their energy.
Formation and some basic concepts
Conventional black holes form the following mechanism:
When stars burn off their energy, exactly the whole hydrogen is combined (thermonuclear reaction) to produce helium, they no longer have the energy released to balance their gravity. towards the mind, the star shrinks.
During this contraction Helium nuclei are tightly packed and combine to produce heavier nuclei (C, O or more), this process releases an amount of energy to make the outer shell bulge ( red giant stage) while the inner core is still shrinking very fast.
With Sun-sized stars, the outer shell is broken when it swells to a certain limit. For heavy stars, the inner core is the last to burst due to the energy released from the star core heavy nucleus, this is a supernova (often translated as supernova in Vietnamese), the shell This is broken into a large cloud of dust called the planetary nebula.
Humans cannot observe black holes.
The inner core after this explosion continues to shrink and become after white dwarfs with stars like the Sun, which means they become a very low radiation object, then gradually turn off, no longer emitting light. For stars larger than 1.5 times the mass of the Sun (Chandrasekhar limit), they continue to contract, to the point where they push electrons (electrons) into the proton to become neutrons, then the whole star is one neutron masses with extremely large density and extremely high rotational speeds, which are neutron stars. The more massive stars, about 3-4 times the mass of the Sun or more (the Tolman – Oppenheimer – Volkoff limit), have not ended the shrinkage process even after becoming neutron stars. Material is compressed to the point of creating a collapse .
The gravitational field described in Einstein's general theory of relativity is that space is influenced by gravity due to the presence of mass (like the electric field around an electric carrier), when this mass of matter collapses (but mass itself does not disappear) it entails distortion of the gravitational field, or the distortion of the surrounding space. A region of space around the dead star is now bent into a closed area (can be conceived as a sphere) .
The star described above has become a black hole and the closed space above is called the event horizon of the black hole. The whole material of the core of the star collapses into a central point of the event horizon called singularity. Call it bizarre, simply because it does not follow the laws of physics that we have, similar to the Big Bang that formed the universe, because simply the laws of physics today only describe the general space-time of the universe today.
The mechanism of black holes is simple to understand:
Because the space containing the gravitational field has been bent as shown above, no object that touches the black hole's event horizon can escape even light.
This is the same as if you meet a curve, whether you like it or not, you will have to follow it because you simply can't go straight, not because you see some interesting restaurants or a girl. beautiful waiting at the end of that road.
So that the light is also bent when it approaches the black hole and will not be able to escape if it misses the event horizon without proving a bit for the assumption that the photon particle has a dynamic mass like some ordinary people. mistaken.
It is with light, but with ordinary matter there is a note that because inside the black hole's event horizon, gravity is so large that it is infinite, so it will tear everything of the size can get into it (there are only basic particles available). Although it is not excluded that there are lines or gaps to allow exceptions, it has so far only existed on fictional works. The fact is that we have no chance of surviving if we get caught in a black hole, and so are the objects we carry, no probe will tell us what happens inside one. black hole.
A common question is: can humans observe black holes?
The answer is no , because simply our eyes see things because of the light from them, with the black hole it does not emit and does not reflect light (because the light has been swallowed by it when approaching) so seeing a black hole is impossible. However the existence of black holes is still predicted based on the interaction they create around them, such as the gravitational attraction of a companion star (if the black hole was previously a star in a system of two or more or the effect of observing the bending of light (gravitational lens).
According to the current model of galaxies, most galaxies at the center have a massive mass black hole (super massive black hole). This black hole has a mass of millions or even billions of times our Sun. These black holes do not form from the end of a star, but from large-scale material collapse in the early part of the galaxy, during which time they continue to swallow small stars and black holes. around to grow up like today.
Another familiar question about black holes is: Where does matter and the information they carry after being sucked into the black hole go?
In 1997, Stephen Hawking made a bet with John Preskill about black holes evaporating, dissipating in space-time carrying all the information they stole. Preskill is the one who believes that the information does not go away after the black hole evaporation. By 2004, Hawking had conceded to lose this bet (of course only by the results of equations on theoretical models because we were not qualified and had no chance to observe the evaporation of any Every black hole).
What about permanent black holes that don't evaporate? Let us refer to another theoretical argument.
White hole
Unlike the black hole that has been tested for at least the direct effects it causes as outlined above, the white hole is a pure theoretical object that has never been tested by any real observation. experience
WHITE HOLE is a theoretical concept, opposite to the black hole. The white hole also has an event horizon and a singular spot in its center. But while the black hole shows matter through the event horizon without letting go, the white hole only releases the radiation outside the event horizon without allowing them to go inside.
A good question to appear here is that the white hole just pushes out and doesn't suck in, is it an anti-gravity case?
The answer is no . The white hole also has gravity and it draws everything towards it , but everything will be blocked and reflected back when it hits its event horizon.
The white hole is another prediction based on Schwarzschild's model to balance Einstein's field equations, whereby information disappearing in the black hole can be "smashed" out of the white hole. Such a white hole may be in the future or the past of a black hole, the reverse process of a black hole or in a completely different space-time, another universe.

In contrast to the black hole, the white hole indicates the matter that goes out rather than entering.
The problems encountered in the first white hole model are that if described, it could be the reverse process of the black hole, ie it goes in the opposite direction of the physical processes, exactly that. violating the second law of thermodynamics, this is too absurd, and secondly, if it really exists in our universe, its rate of material liberation will make it disappear only In a very short period of time, we have no chance to observe a white hole as predicted by the theory.
One solution to this situation is that white holes are not in our current universe, but in a different space-time or a completely different universe. The material it provides and then exits outside may come to another space-time black hole through a tunnel that runs through space-time or even across universes called deep holes.
Deep hole
Schwarzschild geometry suggests that the standard model for black holes and white holes corresponding to Einstein's field equation must consist of two universes (or two different spacetime systems) that one contains a black hole and one containing a white hole, connected by a tunnel called DEEP (wormhole).
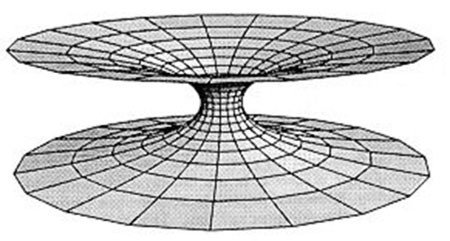
Deep holes cannot exist in our visible universe.
The birth of this concept is a solution to Einstein's equations, as well as an alternative to the Einstein-Rosen bridge theory (Einstein-Rosen Bridge).
We should note the last time that the wormhole as well as the white hole violates the second law of thermodynamics, so in fact they cannot exist in our visible universe. However, in Einstein's general theory of relativity time is symmetrical (no concept of forward or backward time), so this model is accepted. That means white holes and deep holes connecting them to black holes can exist in other space-time areas that we cannot observe, or even in another universe.
With a capability that is not quite as stable as mentioned above, the deep hole is still highly expected by enthusiasts. It is believed that a deep hole can help people cross space faster than light by a technology called warp drive or travel to the past or to the future (time travel). .

Dreadnought space ship in tactical game Astro Empires uses warp drive technology to move between galaxies.
In recent years, people have repeatedly tried to explain mysterious phenomena such as the sudden disappearance of people or ships, flights . that they have lost in a deep hole opened immediately. on the earth.
However, it is worth mentioning that all the existence of white holes and deep holes still exist only in Schwarzschild geometry, and the theoretical model itself shows that it is very difficult to exist. of these things in our visible universe.
Dang Vu Tuan Son
- 10 interesting facts about black holes in the universe (Part 1)
- 10 interesting facts about black holes in the universe (Part 2)
- What happens when the Earth falls into a black hole?
You should read it
- ★ This is a photograph of the first black hole of mankind, located in a galaxy 55 million light-years from Earth
- ★ Discover a monster black hole 100,000 times bigger than the Sun, the second largest in the Milky Way
- ★ What happens when the Earth falls into a black hole?
- ★ Black force - a new force in the universe, becomes even more strange
- ★ The streams of plasma sprayed from black holes can kill anything