The first 'wandering black hole' was discovered, 7 times as massive as the sun, and it took scientists 6 years to observe it
Black holes are a special form of celestial body in the universe, do not emit light, do not reflect light but absorb light, however we rely on electromagnetic waves like light to observe celestial objects in the universe. pillar. So seeing the black hole is very important. Usually only when the black hole's gravity acts on other objects, or when the black hole absorbs the matter of other objects to form an accretion disk.
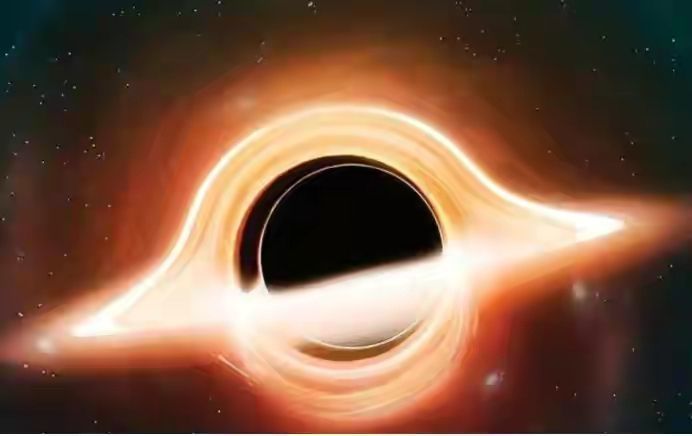
Black holes have accretion disks, commonly known as quasars.
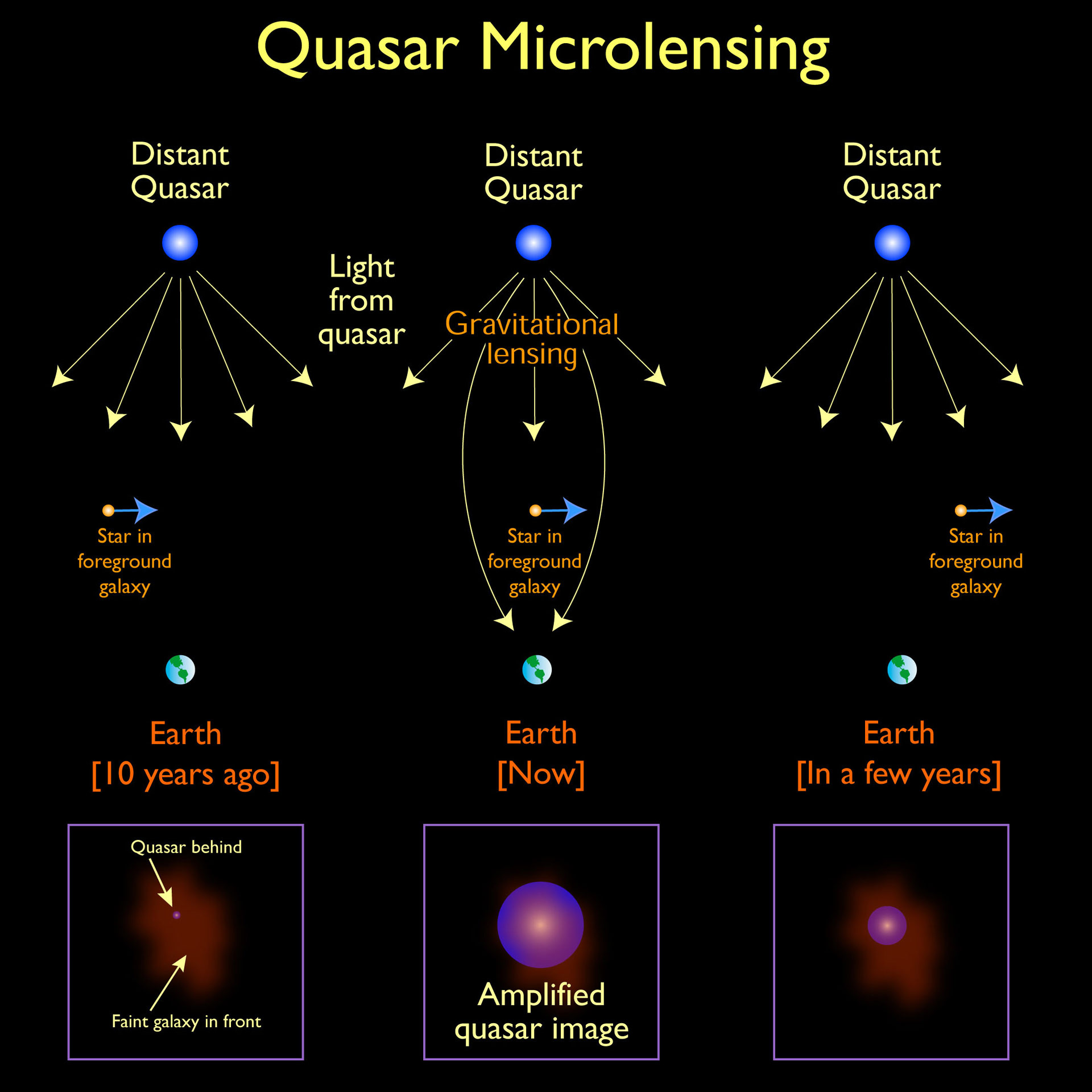
However, on February 5, an announcement from the "Organizational Network of Physicists" said that an international astronomical research team had discovered a "roaming black hole" through the phenomenon of "microlensing". " - an astronomical phenomenon due to the gravitational lensing effect. It can be used to detect objects that range from the mass of a planet to the mass of a star, regardless of the light they emit - This is a way to explore guinea pigs ladder.

The team of astronomers analyzed the data they collected and came to the conclusion that the object could be a black hole, not a star. They even calculated its approximate mass to be 7.1 times that of the sun. The black hole is named MOA-2011-BLG-191/OGLE-2011-BLG-0462.
Although this news has only recently been reported, the discovery was made in 2011, when the team discovered a lonely black hole moving between stars. This 'wanderer' has formed a 'microlensing' with gravity so strong that it can bend and twist the light of the stars and galaxies behind it. And this is also considered to be the first wandering black hole observed.

The "microlensing" effect refers to the phenomenon where a celestial body has a strong gravitational field that causes the background light of the object behind it to be distorted. And the distribution of gravity in the universe is very uneven, when the gravitational field is strong, electromagnetic waves such as light rays will be distorted by the gravitational field, which forms a kind of gravitational lens. The light of the celestial background is refracted through this lens, the shape will be bent, the position will be shifted, and the brightness will also decrease. So even if the object causing the gravitational lensing cannot be seen, its existence can still be sensed, even if the object is a black hole, that's why "black hole languishes". ladder" is detected.
This black hole is 5,153 light-years away, in the Milky Way, and has a mass 7 times that of the sun. It is passing nearby stars at about 45 km/s, or about 162,000 km/h. Scientists also believe that there are many similar stellar wandering black holes, but because the black holes themselves do not emit light, and the micro-lensing effect is not easy to detect, so the wandering black holes not easily observed. In fact, it's much harder to observe than roaming stars or even roaming planets.
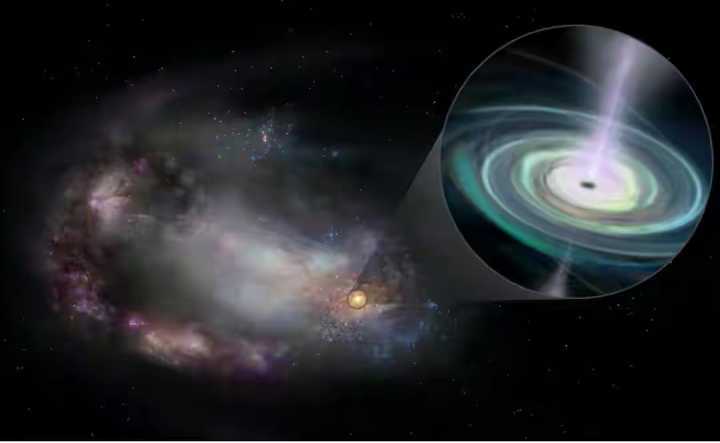

The team started observing this wandering black hole in 2011, when scientists only discovered that a star's brightness increased for no reason, when they assumed it was due to activity. motion of the star itself.
Through continuous observation, they found that this did not happen after continuous monitoring. Over the course of 6 years, through the strange changes in the brightness and position of the star and its surroundings, they determined that this was definitely caused by the microlensing effect. They therefore believed that the light emitted by the star was blocked in front of it (closer to the direction of the observer) by an invisible object that was bent, and because the object was invisible, so it is considered a black hole. It was then evaluated by various factors and concluded that this was definitely a wandering black hole.
Black holes of this mass are usually formed by supernova explosions of massive stars, but they can also be formed by the direct collapse of massive stars, so they commonly known as stellar black holes. Astronomers hypothesize that there are at least 1 million to 100 million such black holes in the Milky Way.

In fact, wandering black holes are very dangerous for planets that have life in the universe or have developed civilizations, because they are difficult to observe and their gravity is so strong. If there were such a black hole near the solar system, at our current human level, we would not be able to perceive its existence, and of course, we would be wiped out.
You should read it
- ★ Explaining the mysterious gravity loss phenomenon in some places in Canada?
- ★ How fast can a rocket fly to win gravity and escape the Earth?
- ★ Isaac Newton discovered that the gravitational force of a falling apple was anecdote
- ★ Decode the ball mystery itself 'climb the slope' at the 'non-gravity' hill
- ★ If you want to be a data scientist, learn these 3 languages right away!